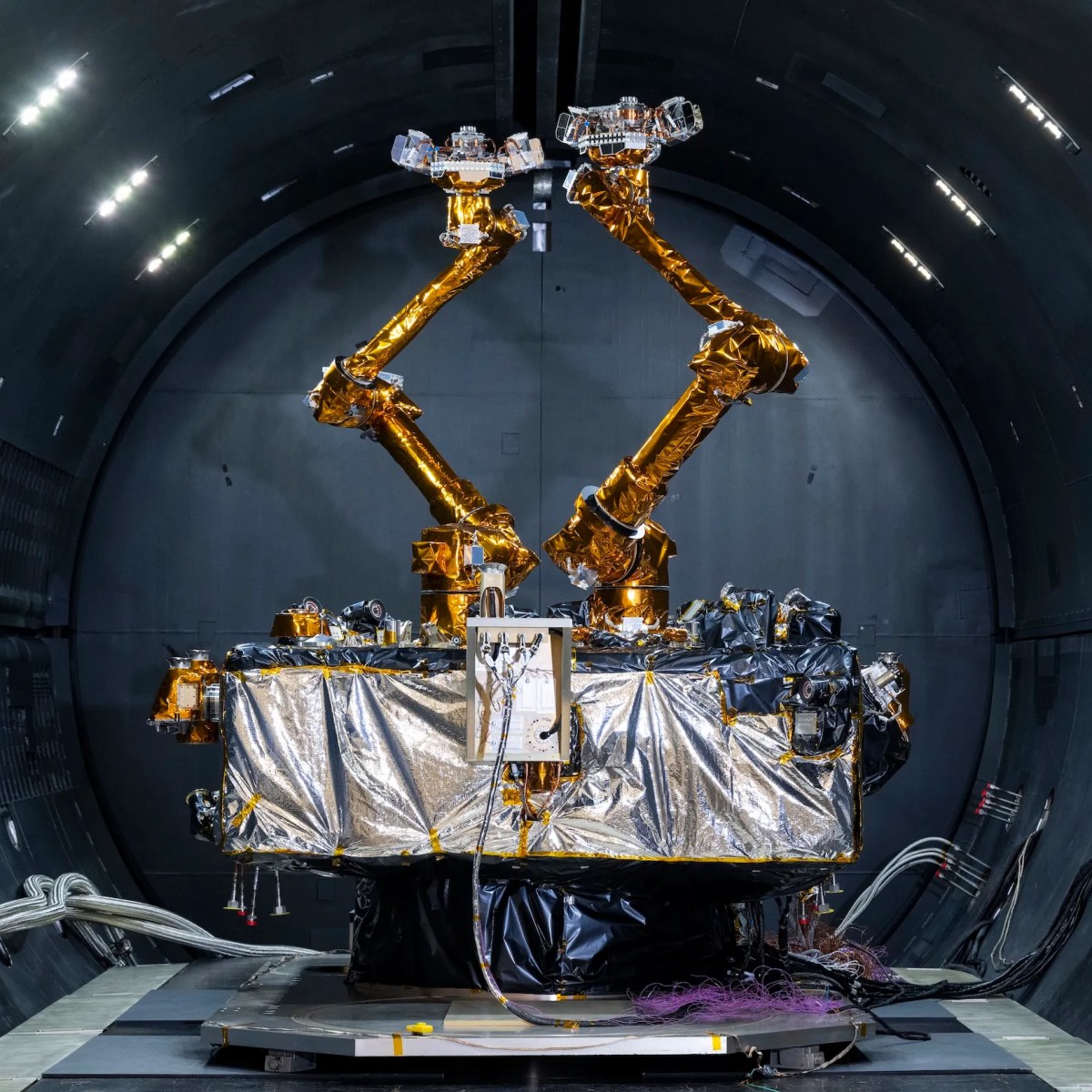
WASHINGTON — Northrop Grumman’s SpaceLogistics subsidiary is eyeing a 2026 launch for its next-generation satellite servicing vehicle, the Mission Robotic Vehicle (MRV). Equipped with robotic arms developed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), the MRV aims to extend the lifespan of satellites in geostationary orbit more than 22,500 miles above Earth.
NRL announced Nov. 14 that the pair of robotic arms completed crucial thermal vacuum testing and are now at Northrop’s satellite integration facility in Dulles, Virginia. The arms were developed under a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) contract.
“This robotic payload promises to transform satellite operations in geostationary orbit, reduce costs for satellite operators, and enable capabilities well beyond what we have today,” said NRL’s director of research Bruce Danly.
Broader range of services
SpaceLogistics is using the robotic arms for the MRV under a partnership with DARPA. The company has already secured three customers for its MRV services — two satellites from Intelsat and one from Optus. These clients will receive Mission Extension Pods (MEPs), propulsion jet packs that can add approximately six years of operational life to aging satellites.
“There’s about 500 satellites in GEO today and about 10 or more of those each year reach their end of life because they’ve run out of fuel,” SpaceLogistics President Rob Hauge told SpaceNews. The company expects to attract additional commercial and government customers for MRV missions before and after the 2026 launch.
SpaceLogistics is positioning the MRV as a versatile solution in the space-servicing market, which includes satellite repair, repositioning, and debris removal. The MRV’s robotic arms will enable more sophisticated tasks, such as detailed inspections and repairs and satellite relocations, said Hauge.
“Our primary focus is delivering on commitments to our existing customers, but we’re engaged in ongoing discussions with other commercial and government operators who are interested in MRV’s advanced capabilities,” he said. The MRV will stay in orbit for several years.
Hauge said the MRV builds upon Northrop Grumman’s experience with its Mission Extension Vehicles (MEV), which have successfully serviced two Intelsat communications satellites.
The 350-kilogram MEPs represent a more affordable option compared to the much larger MEVs. The mission extension pods, unlike the MEVs, do not have their own rendezvous and docking systems, which helps reduce costs, Hauge explained. The pods will be launched to a transfer orbit and use electric propulsion to reach geosynchronous orbit, where they will dock with the MRV.
The MRV will then transport each pod to its client satellite, using one of the robotic arms to attach it to the client’s engine nozzle. Once installed, the MEP assumes propulsion responsibilities, maintaining the satellite’s orbital position and enabling necessary maneuvers without depleting its original fuel supply.