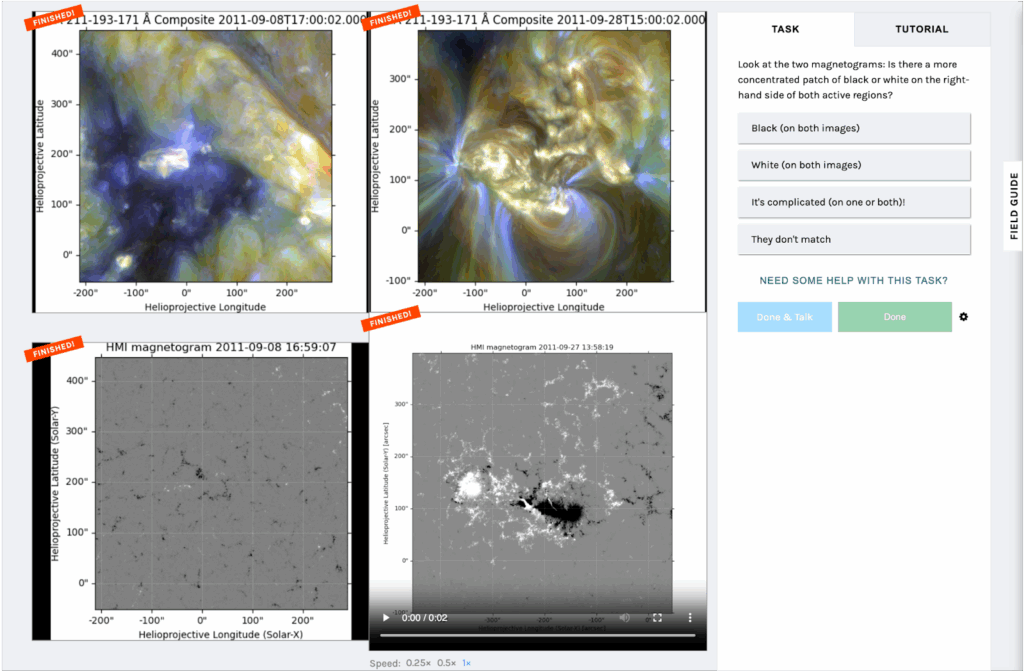
Life’s capacity to survive in simulated lunar and Martian soils has been explored in two papers published in Scientific Reports. Treating simulated lunar soil with both symbiotic fungi and worm-produced
If you’ve ever gazed up at the night sky and felt a sense of wonder, the “Collins Stars and Planets Guide: The Definitive Fifth Edition” is your perfect companion on
Ever since physicist Freeman Dyson first proposed the concept in 1960, the “Dyson sphere” has been the holy grail of techno-signature hunters. A highly advanced civilization could build a “sphere”
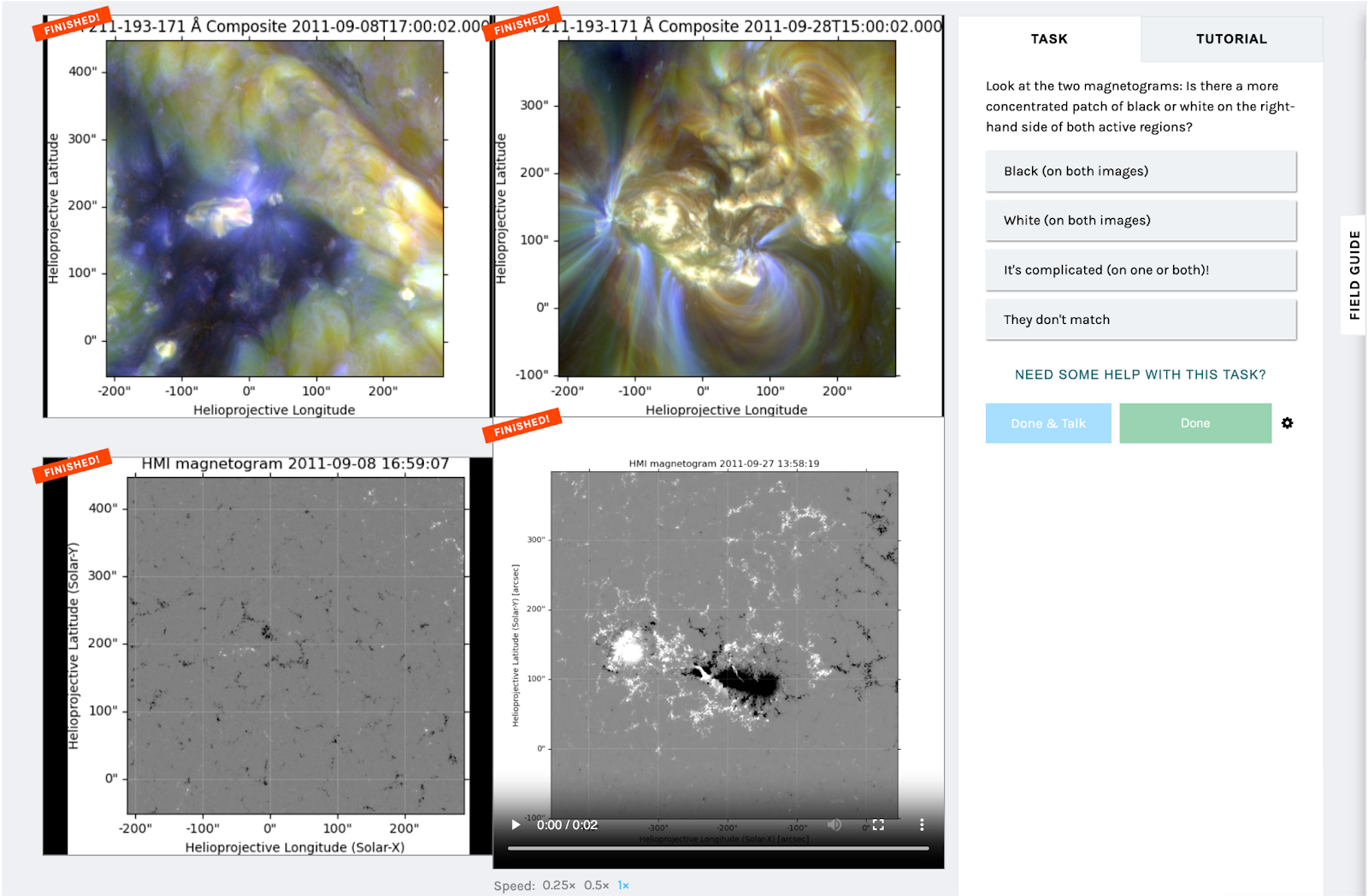
Mechanistic interpretability of Evo 2 reveals DNA, RNA, protein and organism-level features — Nature The DNA foundation model Evo 2, first released in February 2025 as a preprint, is now
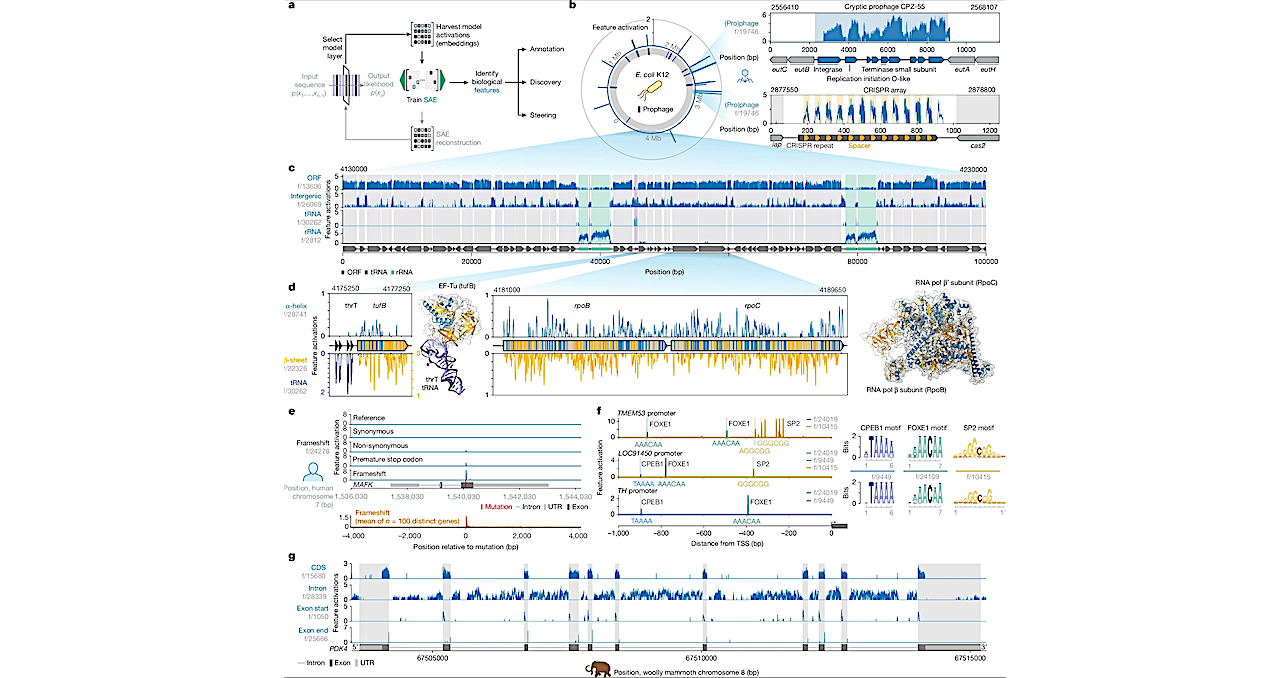
Liquid CWP distributions for different rotation periods (columns). The top row shows zonal mean values for MG (blue) and CARMA (red). The middle and bottom rows show annual mean maps
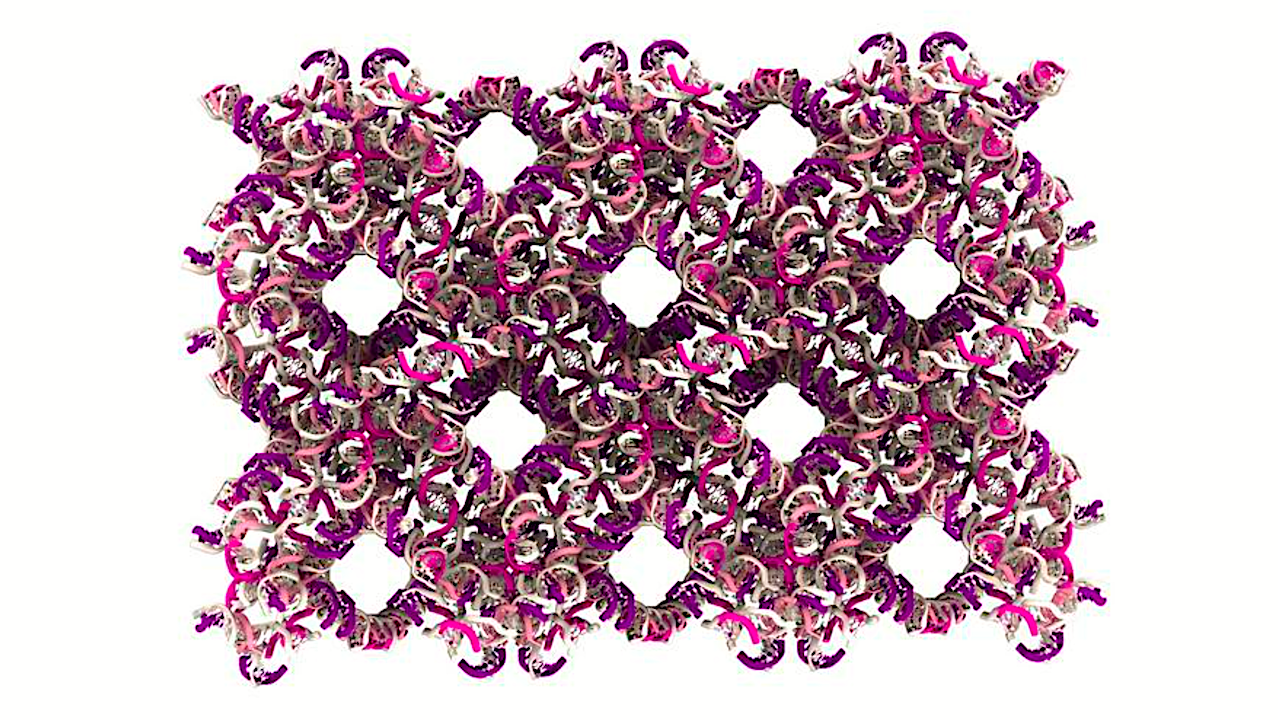
Complex DNA architectures are obtained by stacking triangular units, much like well-placed bricks without mortar. Credit Simon Vecchioni No “sticky ends”? No problem. A new study by NYU chemists finds
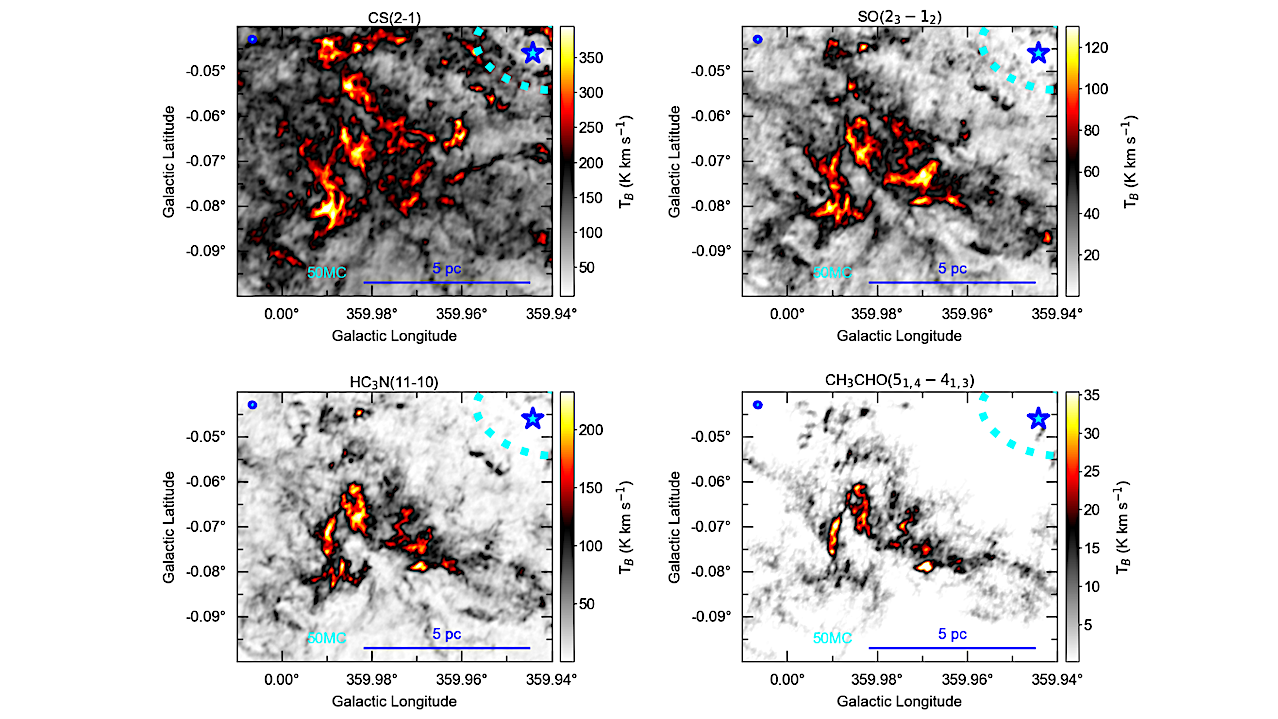
The mom 0 images of the 50 km s−1 cloud. The Sgr A* is labeled with the blue star. The CND is outlined with a cyan dotted line. The CS(2
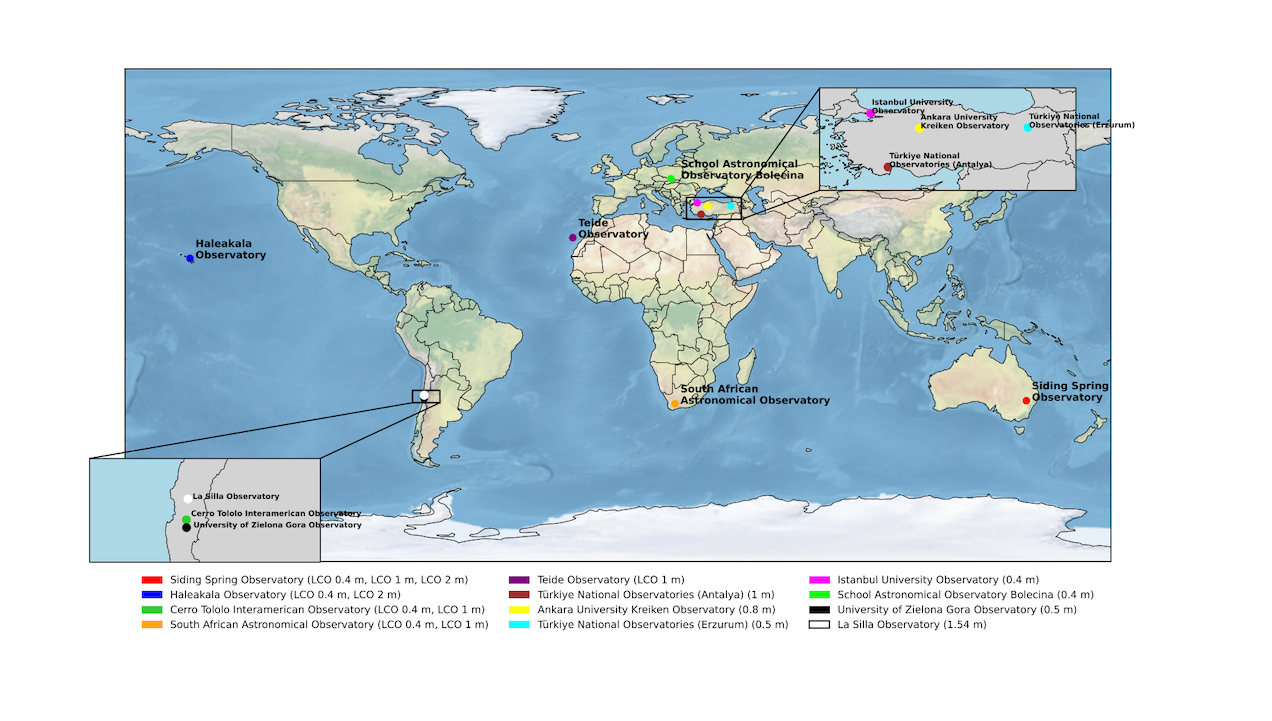
Geographic locations of the observatories from which photometric data were obtained. Colors correspond to observatory names and telescope apertures given in the legend. Insets indicate regions with clustered sites. —
Italian astronomers have performed extensive spectroscopic monitoring of a recently discovered nova known as Vulpeculae 2024, also known as V615 Vul. Results of the new observations, presented in a paper
WASHINGTON — The Air Force Research Laboratory has awarded BlackSky a contract worth up to $99 million to develop a large optical imaging payload intended for future space-based intelligence systems.
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly