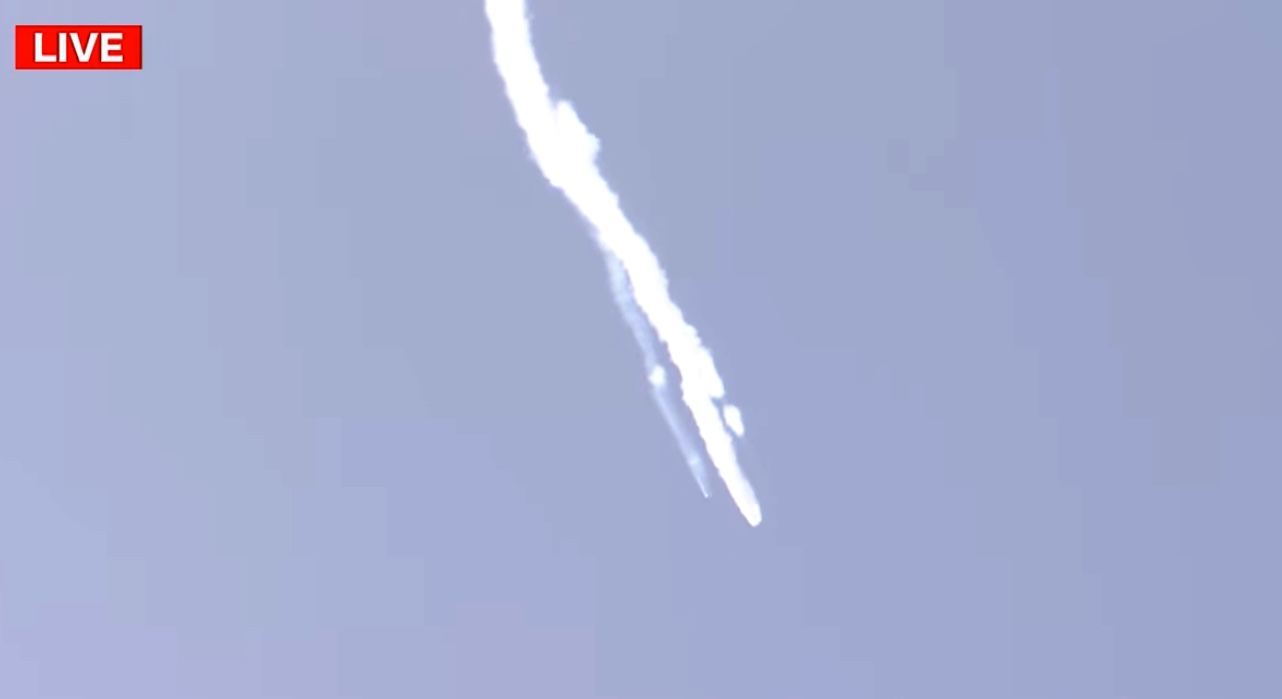
WASHINGTON — The third launch of a small launch vehicle developed by a Japanese company failed shortly after liftoff March 4, raising questions about the rocket’s future. A Kairos rocket
Rapiddominance Unisex Adult Basic Military T’s NASA 2: A True Tribute to Comfort and Pride Greetings, fellow Earthlings! Imagine a garment that beautifully combines the spirit of adventure and the
PLD Space’s manufacturing facilities show the flow of production for its Miura 5 rockets. Image: PLD Space Spanish startup launch company, PLD Space, raised €180 million ($209 million) in its
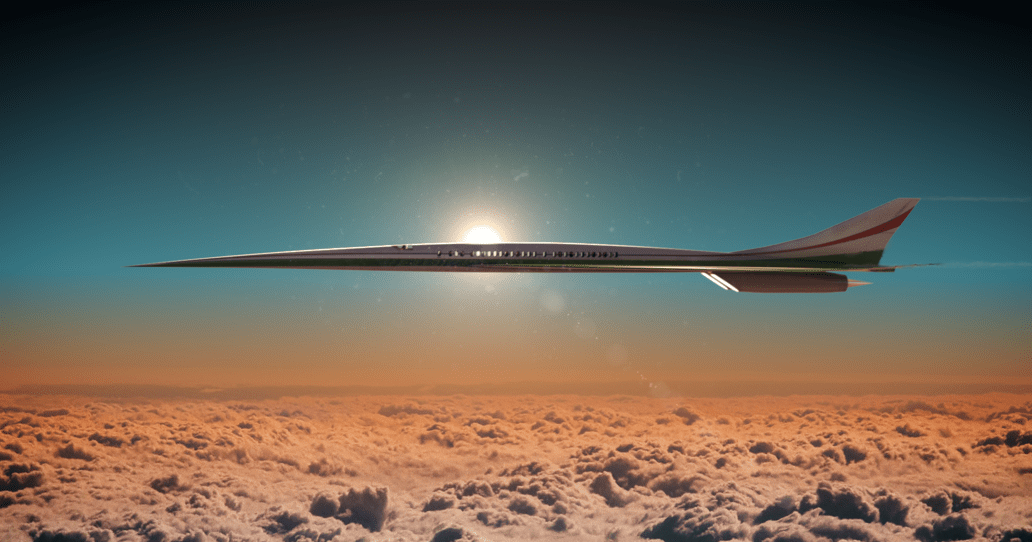
1 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) Artist concept of a high-speed point-to-point vehicle. NASA Langley What We do The High-Speed Flight (HSF) project develops technologies
WASHINGTON — The Senate Commerce Committee advanced a revised NASA authorization bill that implements some of the changes to the Artemis lunar exploration effort sought by the agency while also
TAMPA, Fla. — Canadian telco Telus has agreed to take a stake in AST SpaceMobile and invest in ground infrastructure needed to connect subscribers to the operator’s planned direct-to-smartphone constellation.
WASHINGTON — The U.S. Space Force is intensifying its push for more personnel and training resources as military leaders warn that the Pentagon’s reliance on space capabilities is expanding faster
When people think of supernova explosions, they’re most-often thinking of Type II core-collapse supernovae, where a massive star becomes a red supergiant before collapsing on itself and exploding. New research
Just a few days in simulated microgravity can subtly change the way women’s blood clots, sparking bigger questions about health monitoring protocols for astronauts who can spend six months or
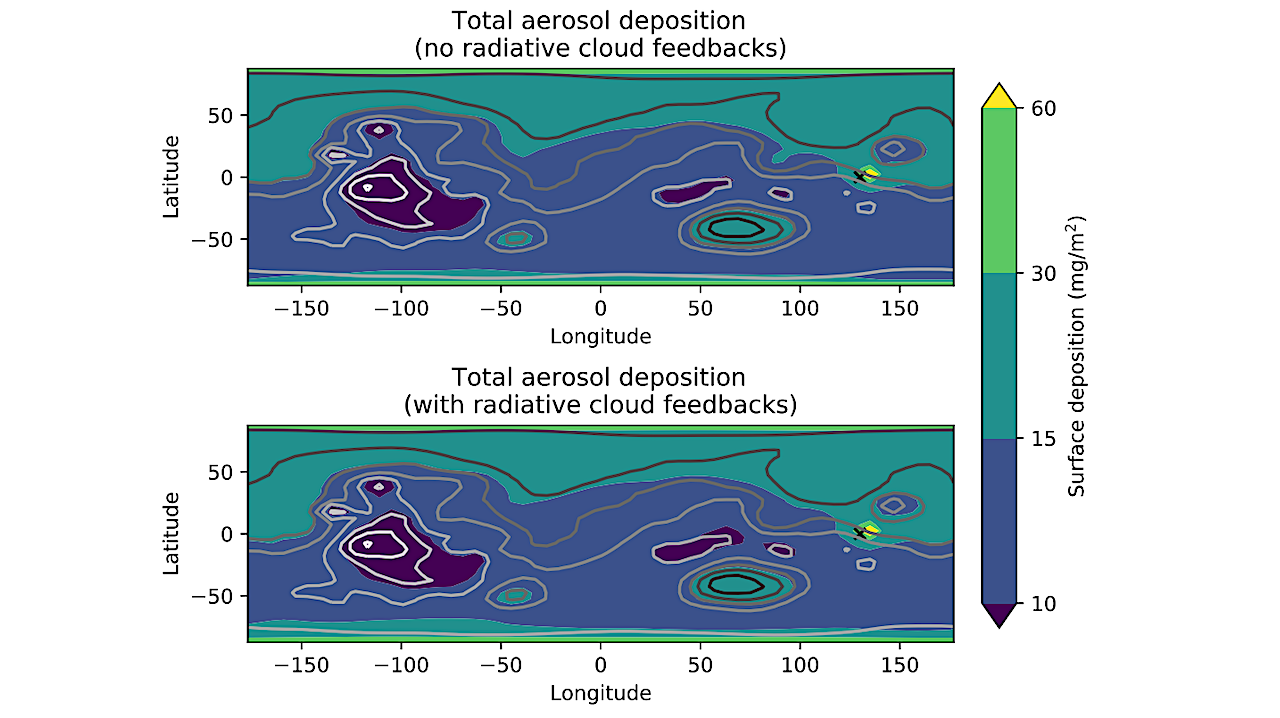
Aerosol deposition on the surface following 5 Mars years of 2.5 l/s release and 15 Mars years of shutoff. The distribution is comparatively uniform, with more deposition at low elevations,
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
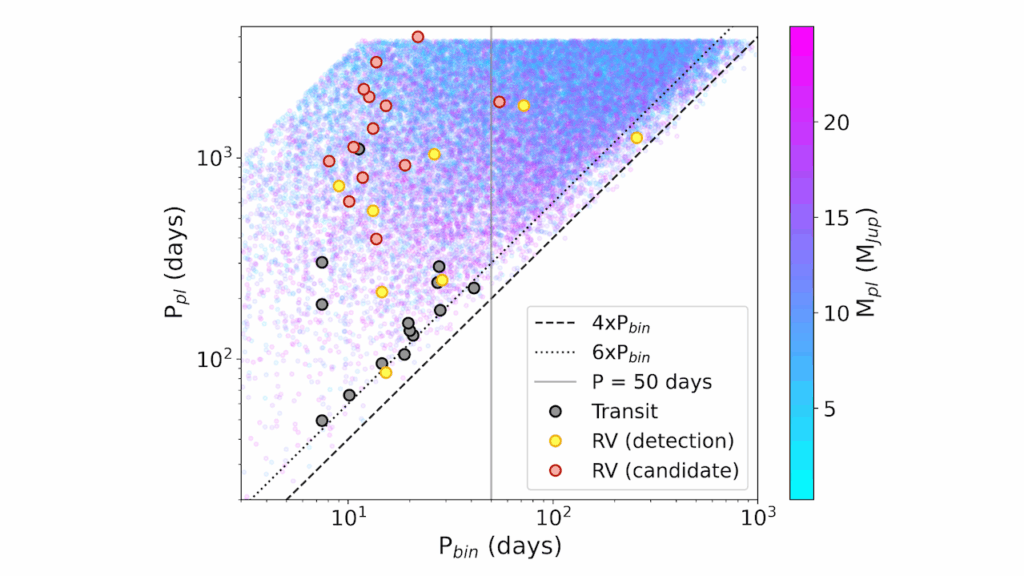
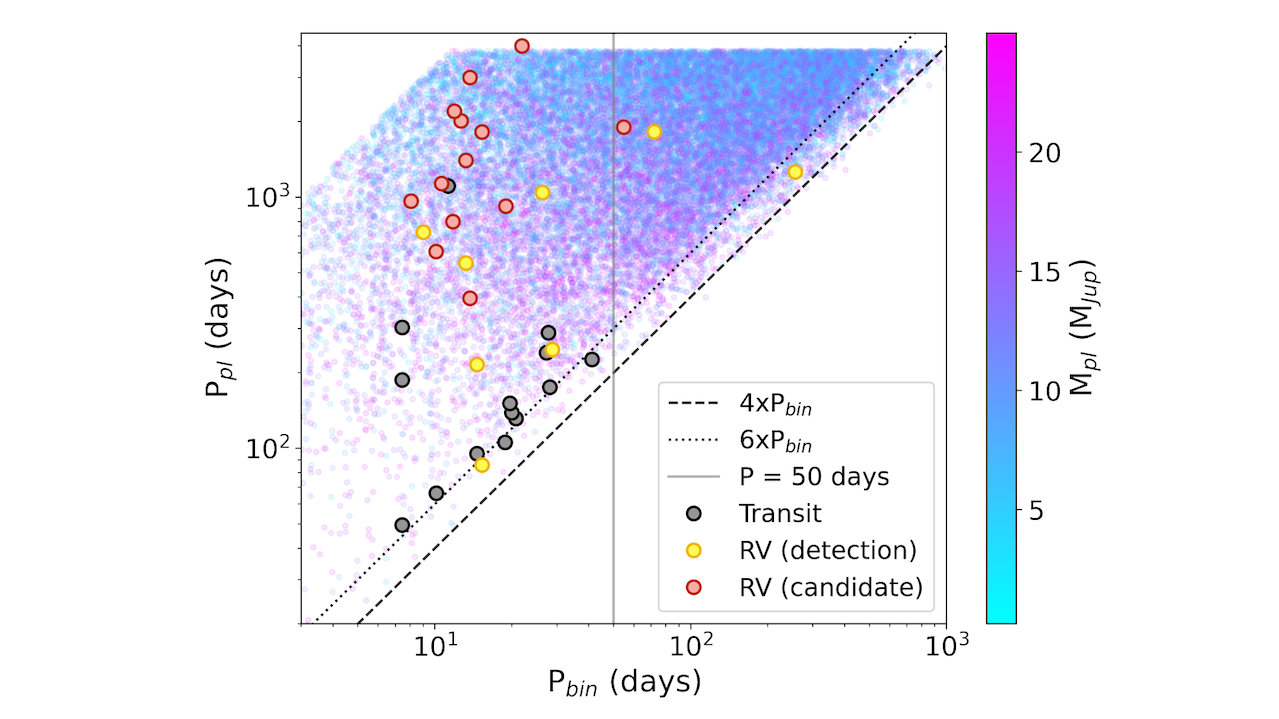
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly