Now Reading: 3 powerful solar flares erupt in less than 24 hours, ending weeks of calm on the sun (video)
-
01
3 powerful solar flares erupt in less than 24 hours, ending weeks of calm on the sun (video)
3 powerful solar flares erupt in less than 24 hours, ending weeks of calm on the sun (video)
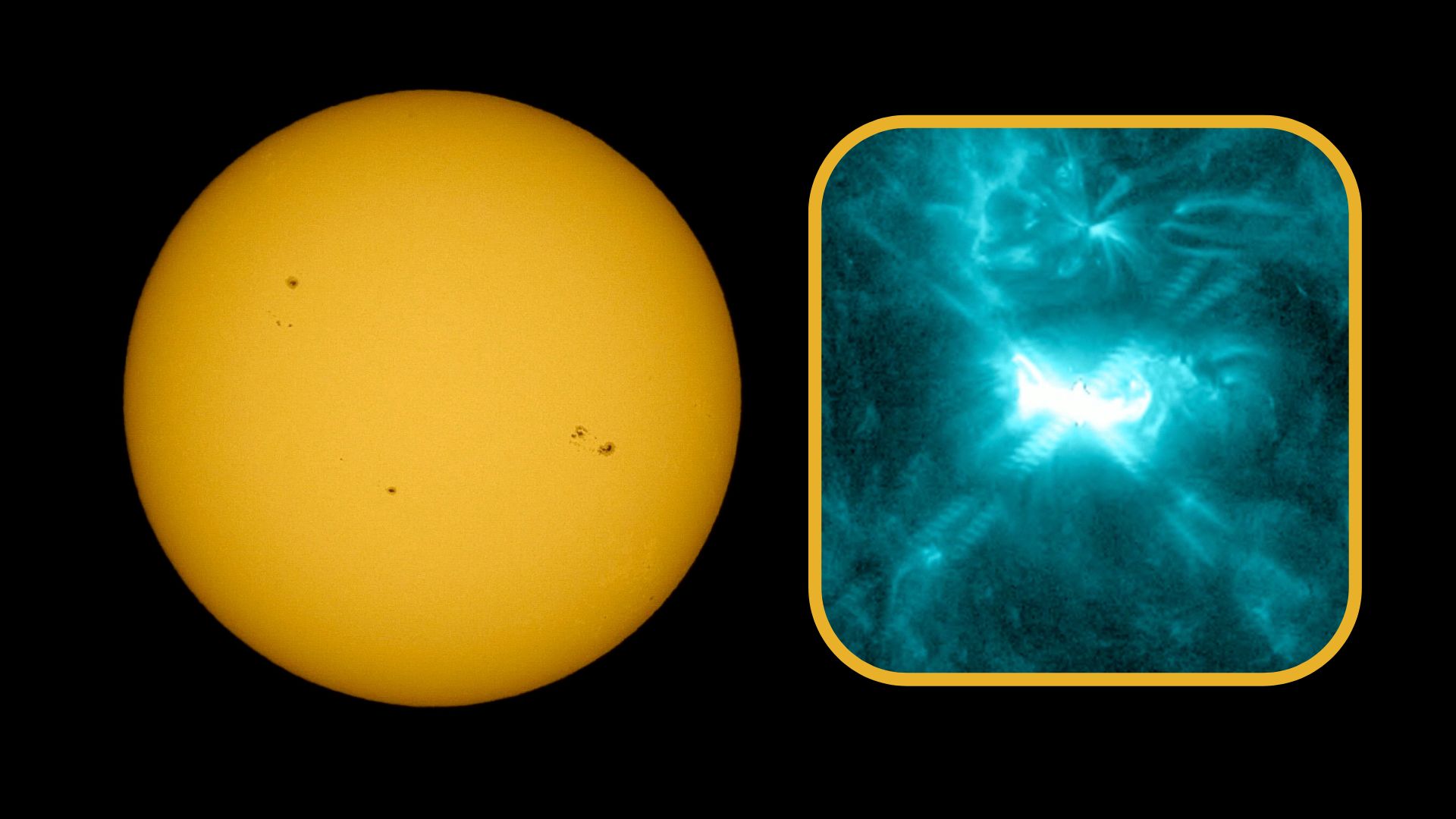

After more than three weeks without a powerful solar flare, the sun has suddenly ramped up its activity, firing off three M-class solar flares in less than 24 hours.
While the sun has been popping off plenty of smaller C-class flares lately, Sunday’s M2.9 eruption at 10:01 a.m. EDT (1401 GMT) on Aug. 3 was the first M-class flare since July 12, according to space weather website SolarHam.com’s post on X. The flare marked the end of a 22-day lull in moderate solar flare activity.
Two more followed in rapid succession: an M2 flare at 1:05 a.m. EDT (0505) on Aug. 4 and an M1.4 peaked just 16 minutes later at 1:21 a.m. EDT (0521 GMT). All three eruptions came from sunspot region AR 4168, which rapidly developed a more complex magnetic structure over the weekend.
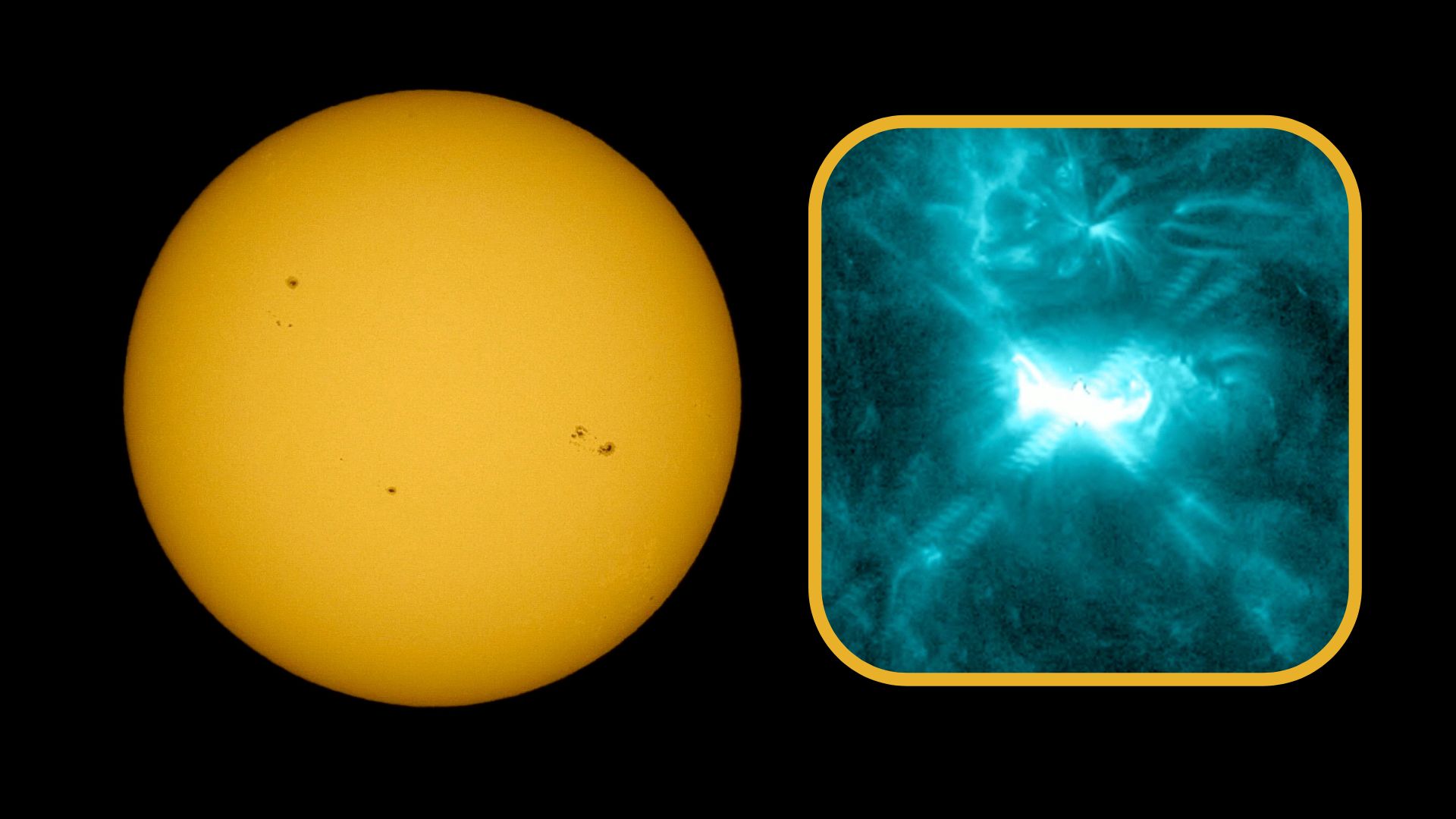

Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation from the sun’s atmosphere, caused by sudden releases of magnetic energy near sunspots. They’re classified by strength into five categories: A, B, C, M, and X. Each level represents a tenfold increase in energy output. While C-class flares are generally minor, M-class flares are moderate and can sometimes disrupt radio communications. The most intense, X-class flares, have the potential to trigger widespread radio blackouts and even impact satellites and power grids on Earth.

According to Spaceweather.com, both active regions 4168 and 4167 now harbor unstable “delta-class” magnetic fields, an arrangement known to power strong solar eruptions, including potential X-class flares and Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
So far, no major space weather impacts have been confirmed, but the M2.9 flare may have launched a weak CME toward Earth. Vincent Ledvina, an aurora chaser and space physics student, noted on X that modeling suggests the CME could arrive around midnight UTC on Aug. 7, with only a 12% chance of impact.
Looks like our M2.9 CME has been modeled by HUXt. Earth impact around August 7 midnight UTC with a 12% hit chance, so nothing worth getting hyped up about. Still, it’s good to know what’s coming, especially as we gear up for a high-speed stream later this week. pic.twitter.com/ux3U2aBnJjAugust 4, 2025
Ledvina added that Monday morning’s M2 flare may have triggered a second weak CME, possibly a stealth CME, a slow and faint solar ejection that’s notoriously hard to spot. “This now marks the second Earth-directed CME from this region with potentially more to follow,” he wrote.
Developing: AR 4168 has just generated a potentially Earth-directed (weak) stealth CME as it fired off an M2.0 solar flare. More info to come later, but this now marks the second Earth-directed CME from this region with potentially more to follow. pic.twitter.com/atfutUH42UAugust 4, 2025
Space weather forecaster Sara Housseal declared “Flare drought is over!” in a post after Sunday’s flare. While the eruptions are “likely nothing significant,” she added later in another post that they “could result in a bump in activity in a few days,” highlighting the challenges space weather forecasters face when working with “little to no data.” A limitation that stems from the lack of dedicated satellites and limited real-time imagery available to monitor faint, slow-moving CMEs.
Space weather forecasters are keeping a close eye on sunspot region 4168. Its growing complexity and flaring activity suggest the region may still have more surprises in store.
Keep up with northern lights forecasts and geomagnetic activity warnings with our aurora forecast live blog.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly