Now Reading: The Nature Of LUCA – The Last Universal Common Ancestor – and its Impact on the Early Earth System
-
01
The Nature Of LUCA – The Last Universal Common Ancestor – and its Impact on the Early Earth System
The Nature Of LUCA – The Last Universal Common Ancestor – and its Impact on the Early Earth System
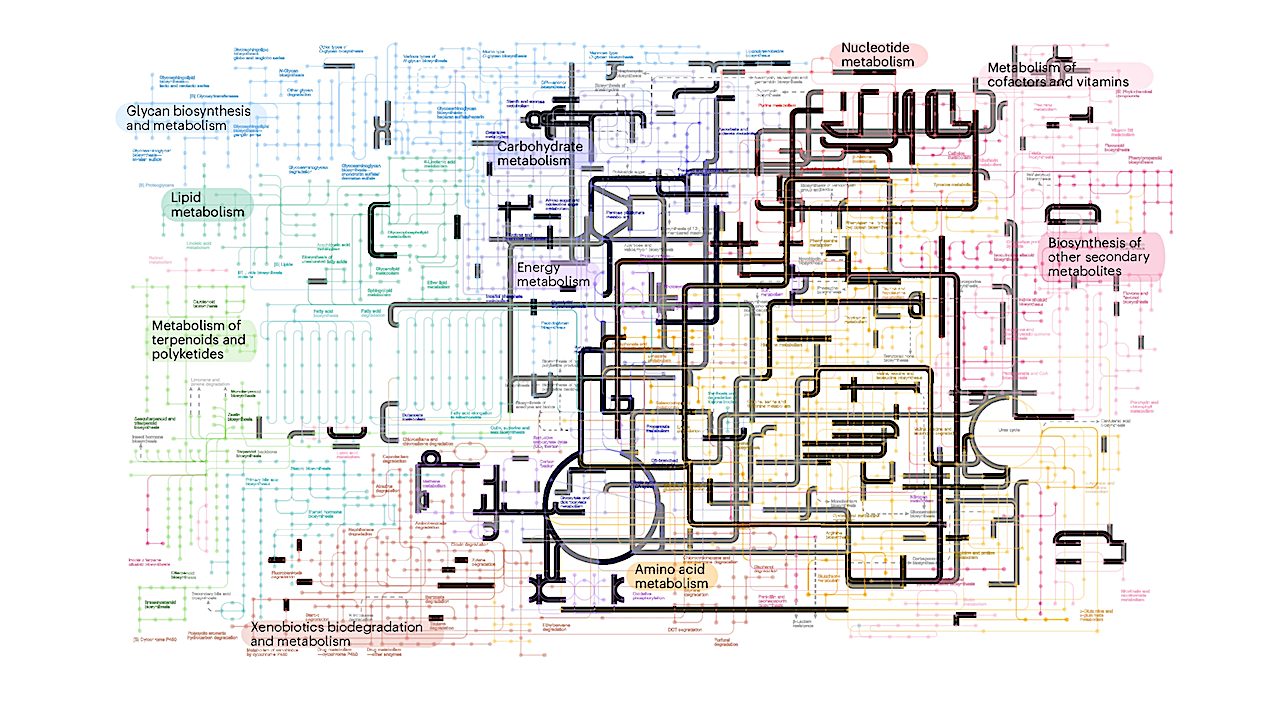

In black: enzymes and metabolic pathways inferred to be present in LUCA with at least PP = 0.75, with sampling in both prokaryotic domains. In grey: those inferred in our least-stringent threshold of PP = 0.50. The analysis supports the presence of a complete WLP and an almost complete TCA cycle across multiple confidence thresholds. Metabolic maps derived from KEGG47 database through iPath109. GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol; DDT, 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane. — Nature
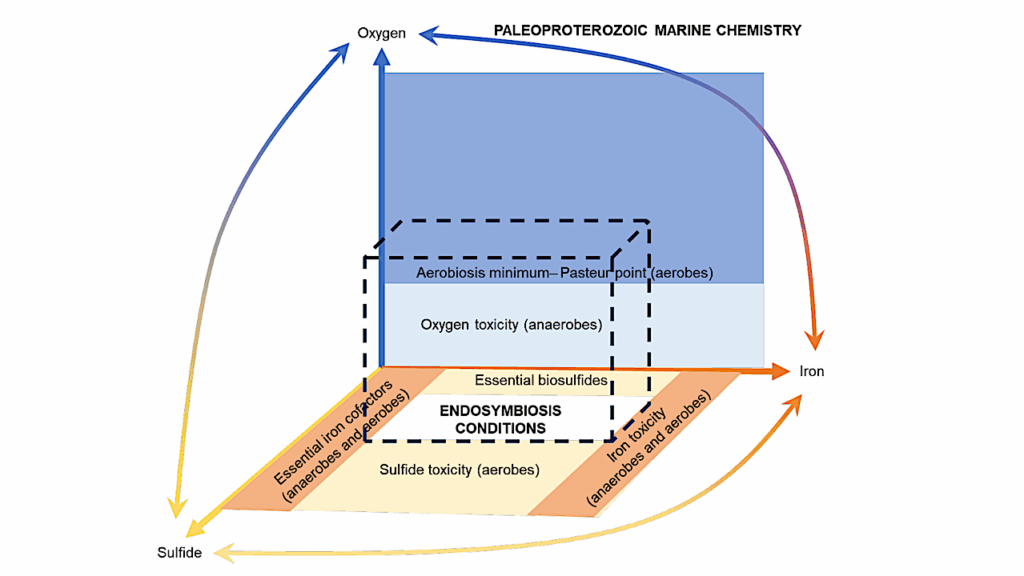
The nature of the last universal common ancestor (LUCA), its age and its impact on the Earth system have been the subject of vigorous debate across diverse disciplines, often based on disparate data and methods.
Age estimates for LUCA are usually based on the fossil record, varying with every reinterpretation. The nature of LUCA’s metabolism has proven equally contentious, with some attributing all core metabolisms to LUCA, whereas others reconstruct a simpler life form dependent on geochemistry.
Here we infer that LUCA lived ~4.2 Ga (4.09-4.33 Ga) through divergence time analysis of pre-LUCA gene duplicates, calibrated using microbial fossils and isotope records under a new cross-bracing implementation. Phylogenetic reconciliation suggests that LUCA had a genome of at least 2.5 Mb (2.49-2.99 Mb), encoding around 2,600 proteins, comparable to modern prokaryotes.
Our results suggest LUCA was a prokaryote-grade anaerobic acetogen that possessed an early immune system. Although LUCA is sometimes perceived as living in isolation, we infer LUCA to have been part of an established ecological system.
The metabolism of LUCA would have provided a niche for other microbial community members and hydrogen recycling by atmospheric photochemistry could have supported a modestly productive early ecosystem.

Our results suggest that LUCA lived around 4.2 Ga, with a 95% confidence interval spanning 4.09–4.33 Ga under the ILN relaxed-clock model (orange) and 4.18–4.33 Ga under the GBM relaxed-clock model (teal). Under a cross-bracing approach, nodes corresponding to the same species divergences (that is, mirrored nodes) have the same posterior time densities. This figure shows the corresponding posterior time densities of the mirrored nodes for the last universal, archaeal, bacterial and eukaryotic common ancestors (LUCA, LACA, LBCA and LECA, respectively); the last common ancestor of the mitochondrial lineage (Mito-LECA); and the last plastid-bearing common ancestor (LPCA). Purple stars indicate nodes calibrated with fossils. Arc, Archaea; Bac, Bacteria; Euk, Eukarya. — Nature
Astrobiology, genomics,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly -
 07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits