Now Reading: China’s Shijian spacecraft separate after pioneering geosynchronous orbit refueling tests
-
01
China’s Shijian spacecraft separate after pioneering geosynchronous orbit refueling tests
China’s Shijian spacecraft separate after pioneering geosynchronous orbit refueling tests
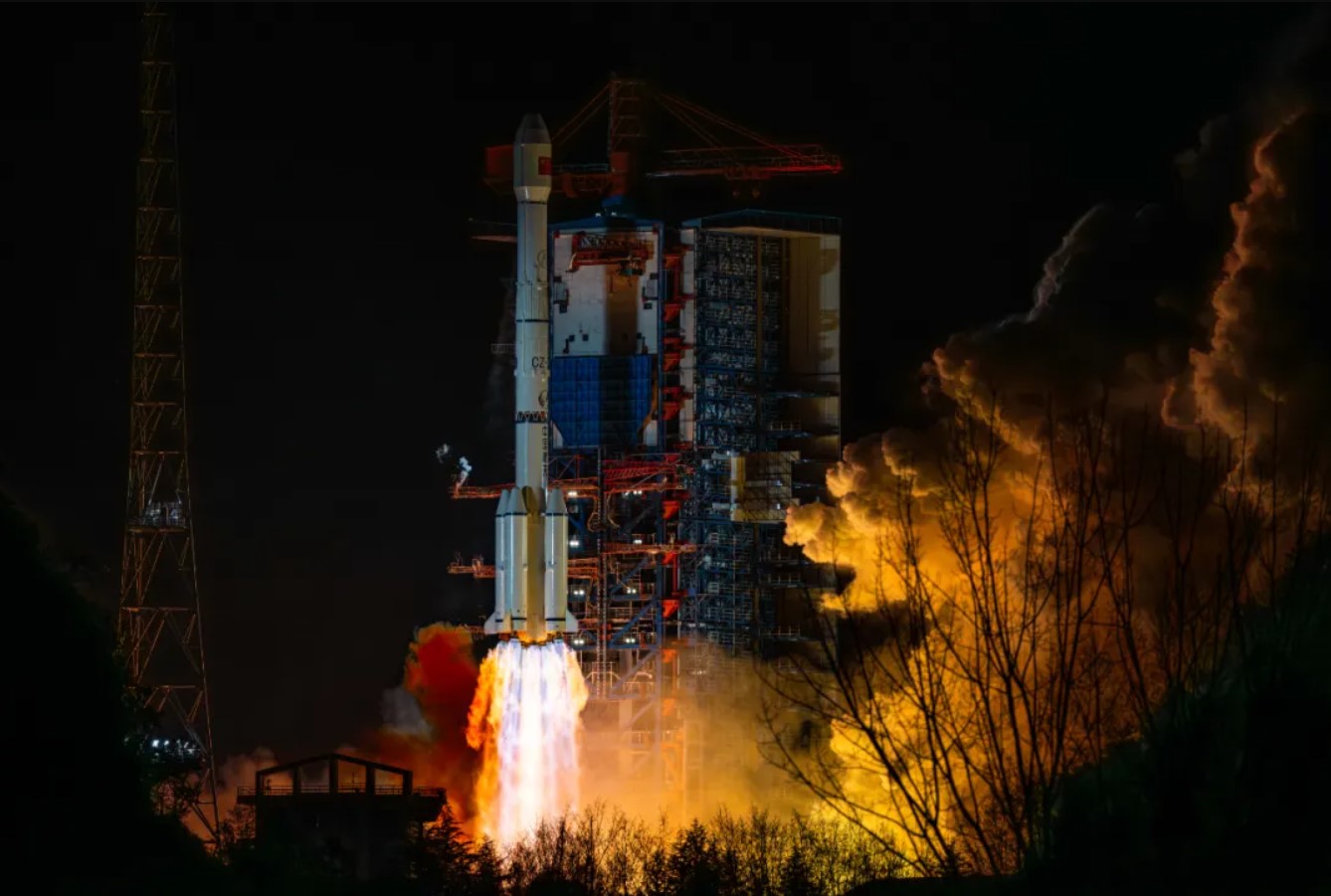


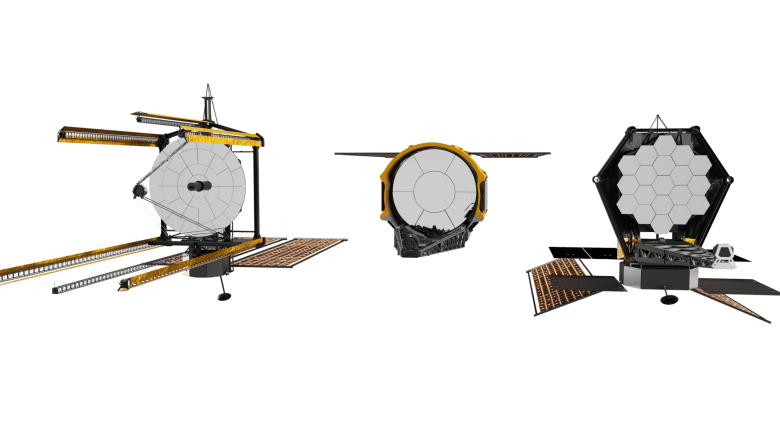
HELSINKI — China’s experimental Shijian-21 and Shijian-25 satellites have separated in geosynchronous orbit after being docked for months conducting apparent low-profile on-orbit refueling tests.
Shijian-21 and Shijian-25 performed rendezvous and proximity operations during the first half of the year before apparently docking in late June or early July, when the pair became virtually indistinguishable when viewed from the ground, likely marking the start of planned refueling tests, according to independent satellite-tracking analyses. The docked pair then later performed fuel-intensive orbital plane change maneuvers, reducing their orbital inclination.
Optical ground observations Nov. 29 made by S2a systems, a Swiss company which develops and operates customized systems for optical space surveillance worldwide, reveal that the two satellites have now separated in geosynchronous orbit, close to the geostationary belt (GEO) at 35,786 km above Earth’s equator. The orbits of the pair are inclined by 4.6 degrees with respect to GEO.
The separation could mark a successful conclusion to a world-first refueling operation in GEO. However, neither China’s space authorities nor the satellites’ manufacturer have commented on the mission since the launch of Shijian-25 in January.
The lack of transparency means little information about the mission is available. The opacity will also raise concerns, as while on-orbit servicing can be for civilian purposes, the inherent ability to rendezvous, dock, and manipulate objects in GEO has military implications. GEO hosts satellites for uses including communications, weather monitoring and remote sensing and missile early warning.
Further tracking of the satellites’ activities and changes in orbit, especially those of the older Shijian-21, could provide insight into whether or not the apparent refueling test operations were successful.
A successful test would be a boost for China’s space capabilities. On-orbit servicing, including refueling, orbit adjustment, or repositioning, offers a way to keep expensive or strategic spacecraft, such as communications satellites, active longer or to repurpose older satellites.
According to assessments by Integrity ISR in August, the plane change maneuvers put the SJ-21 and SJ-25 satellites into a similar inclination as a number of Chinese GEO satellites, including TJS-11 and TJS-19, technology demonstration satellites which were developed by the , the Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology (SAST), which also developed SJ-21 and SJ-25. Yaogan-41, a military optical remote sensing satellite, and Shijian-23, another experimental satellite developed by SAST, are also in similar orbits. These could provide potential targets for followup RPO and refueling tests.
Other observers have noted that the inclination of Shijian-21 and Shijian-25 closely matches those of some U.S. satellites, meaning future approaches could be possible, with cat and mouse activities in GEO involving Chinese, American and Russian satellites becoming more common in recent years.
Shijian-25 was launched in January to test on-orbit refueling and mission extension technologies in GEO, according to SAST. Shijian-21 was launched in October 2021. SJ-21 towed a defunct Beidou-2 G2 navigation satellite into a graveyard orbit above GEO as its primary mission.
On-orbit servicing and refueling capabilities can potentially reduce costs and improve sustainability of space operations, while also reducing debris. Additionally, the People’s Liberation Army is known to be working on the technology and training tools for on-orbit satellite refueling for both peacetime and wartime scenarios.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly -
 07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits