Now Reading: China launches 4 times in 4 days, boosting megaconstellation and surveillance assets
-
01
China launches 4 times in 4 days, boosting megaconstellation and surveillance assets
China launches 4 times in 4 days, boosting megaconstellation and surveillance assets
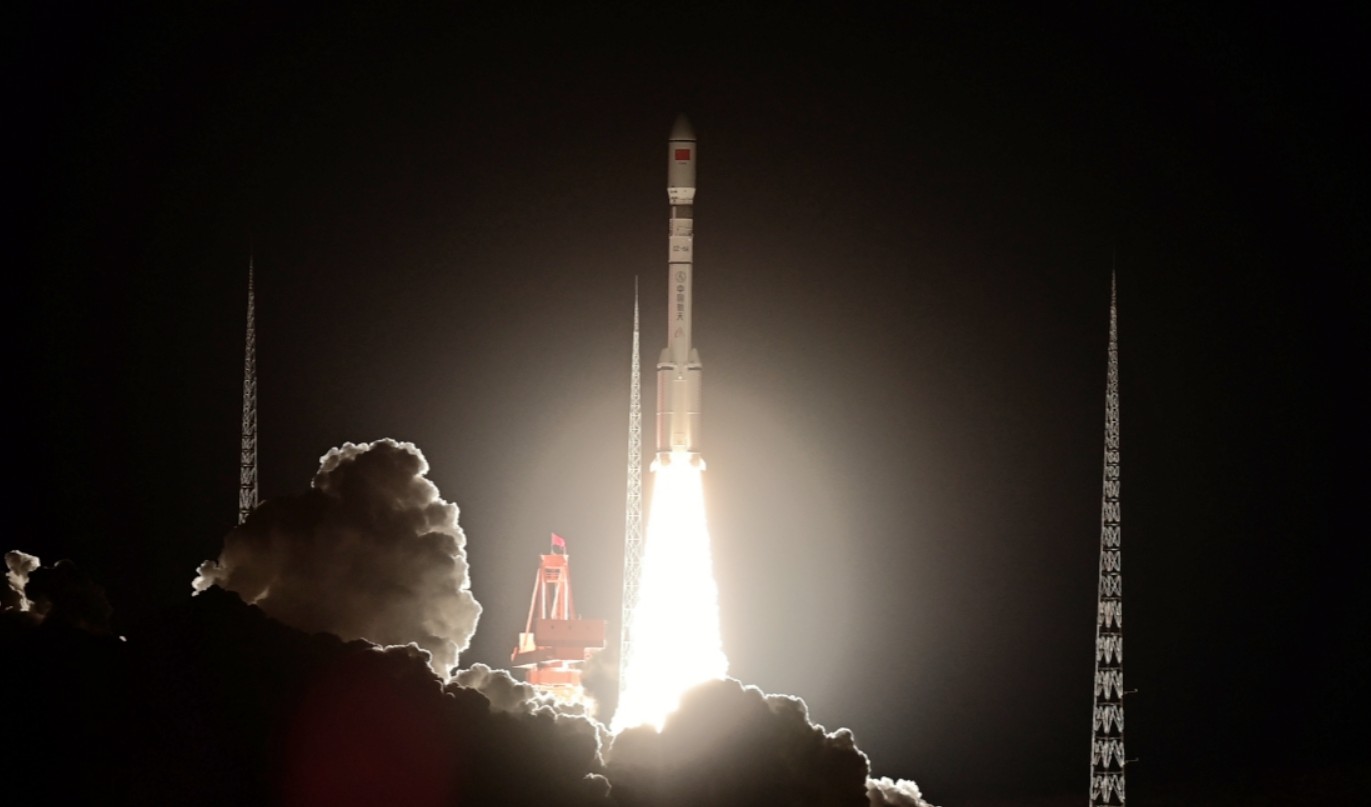


HELSINKI — China launched four missions in four days, accelerating its record-setting launch cadence while expanding its Guowang LEO megaconstellation and deploying new Yaogan reconnaissance assets.
An intensive period of launches kicked off with a Kuaizhou-1A solid rocket lifting off at 4:00 a.m. Eastern (0900 UTC) Dec. 5 from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert. The launch carried the VDES (VHF Data Exchange System) A and B satellites into orbit. The pair were later catalogued by U.S. Space Force space domain awareness in roughly circular, 510-kilometer-altitude orbits inclined by 80 degrees.
The Kuaizhou-1A, operated by Expace, a commercial arm of the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC), a giant state-owned defense and space contractor, previously launched the PRSC‑01 satellite for Pakistan’s Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO) in late July. The rocket that time launched from Xichang in southwest China.
Guowang group 14
This was followed by a Long March 8A kerosene-liquid oxygen rocket launch from the coastal Hainan commercial spaceport Dec. 6, lifting off at 2:53 a.m. Eastern (0753 UTC). The launch carried the 14th group of satellites for the national Guowang low Earth orbit (LEO) communications megaconstellation, according to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
Nine satellites were cataloged in roughly 900-km orbits inclined by 50 degrees. CASC stated that the satellites were developed under the leadership of its China Academy of Space Technology (CAST). CASC also stated that the Long March 8A is being prepared for high-intensity launches and its launch campaign has been cut in half to around two weeks.
The previous Guowang batch launched on a Long March 12 from the same spaceport Nov. 10. Both pad 1 and 2 at Hainan commercial spaceport will now primarily use coal-based aerospace-grade kerosene as fuel for launches, according to Chinese media reports.
Guowang group 15
The next mission saw another launch of Guowang satellites, this time with five satellites aboard a kerolox Long March 6A rocket with solid side boosters lifting off from a dedicated pad at 5:21 p.m. Eastern (2221 UTC) Dec. 8 from Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center, north China.
It was the 15th group of Guowang satellites, and the fifth time a Long March 6A carried Guowang satellites. The earlier 6A missions carried five satellites each, with CASC stating that CAST produced the satellites. China now has 118 operational Guowang satellites in orbit, along with a number of experimental satellites.
Guowang is led by state-owned China SatNet with plans for nearly 13,000 LEO satellites. The near-term target for Guowang is to have 400 satellites in orbit by 2027. It is part of China’s response to Starlink, both commercially and strategically.
Yaogan-47
The Guowang mission was followed shortly after by a further launch from Jiuquan spaceport, this time with a hypergolic Long March 4B lifting off at 10:41 p.m. Eastern, Dec. 8 (0341 UTC, Dec. 9). CASC declared launch success, revealing the previously undisclosed payload to be the Yaogan-47 satellite, part of a largely classified series of remote sensing satellites.
The satellite will mainly be used for land surveys, urban planning, road network design, crop yield estimation, environmental management, and comprehensive disaster prevention and mitigation, according to CASC.
A pair of recent Yaogan satellites—Yaogan-45 and 46—headed, for the first time, into medium Earth orbit, suggesting the construction of a constant mid-latitude surveying capability, with inclinations of 20 degrees and at altitudes of 7,500 km. Those satellites launched on the much more powerful Long March 7A. Overall, China has proportionally relied less on its older, hypergolic rockets in 2025 as the country’s launch cadence increases.
The launches were orbital attempts 78-81 for China in 2025, having already surpassed its previous record of launches in a calendar year of 68, set in 2024. Launch 82 is currently scheduled for just after 10:00 a.m. Eastern (1500 UTC), Dec. 9, with a Long March 3B rocket due to launch from Xichang.
The period of intense launches is set to continue, with a Kinetica-1 solid rocket from CAS Space expected to launch late Dec. 9 Eastern, while a Long March 12 is scheduled for launch Dec. 11. The debut launch and landing attempt of the reusable Long March 12A could also take place within the next week or so. It follows the successful launch and failed landing of the Zhuque-3 rocket from Landspace Dec. 3.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly -
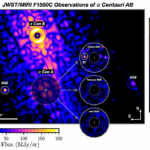 07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits