Now Reading: The Hidden Lives of the Universe’s Ultramassive Galaxies
1
-
01
The Hidden Lives of the Universe’s Ultramassive Galaxies
The Hidden Lives of the Universe’s Ultramassive Galaxies
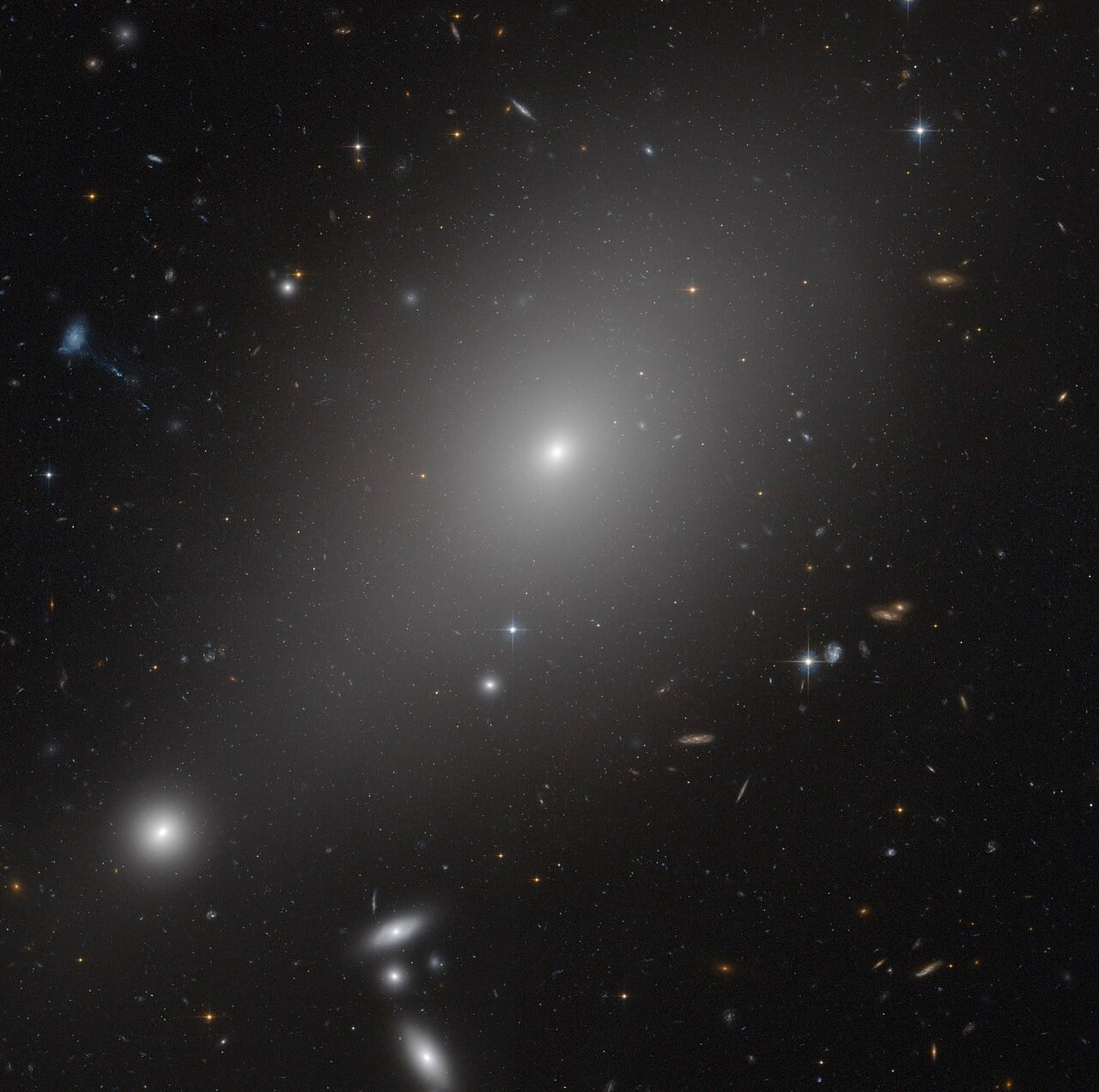
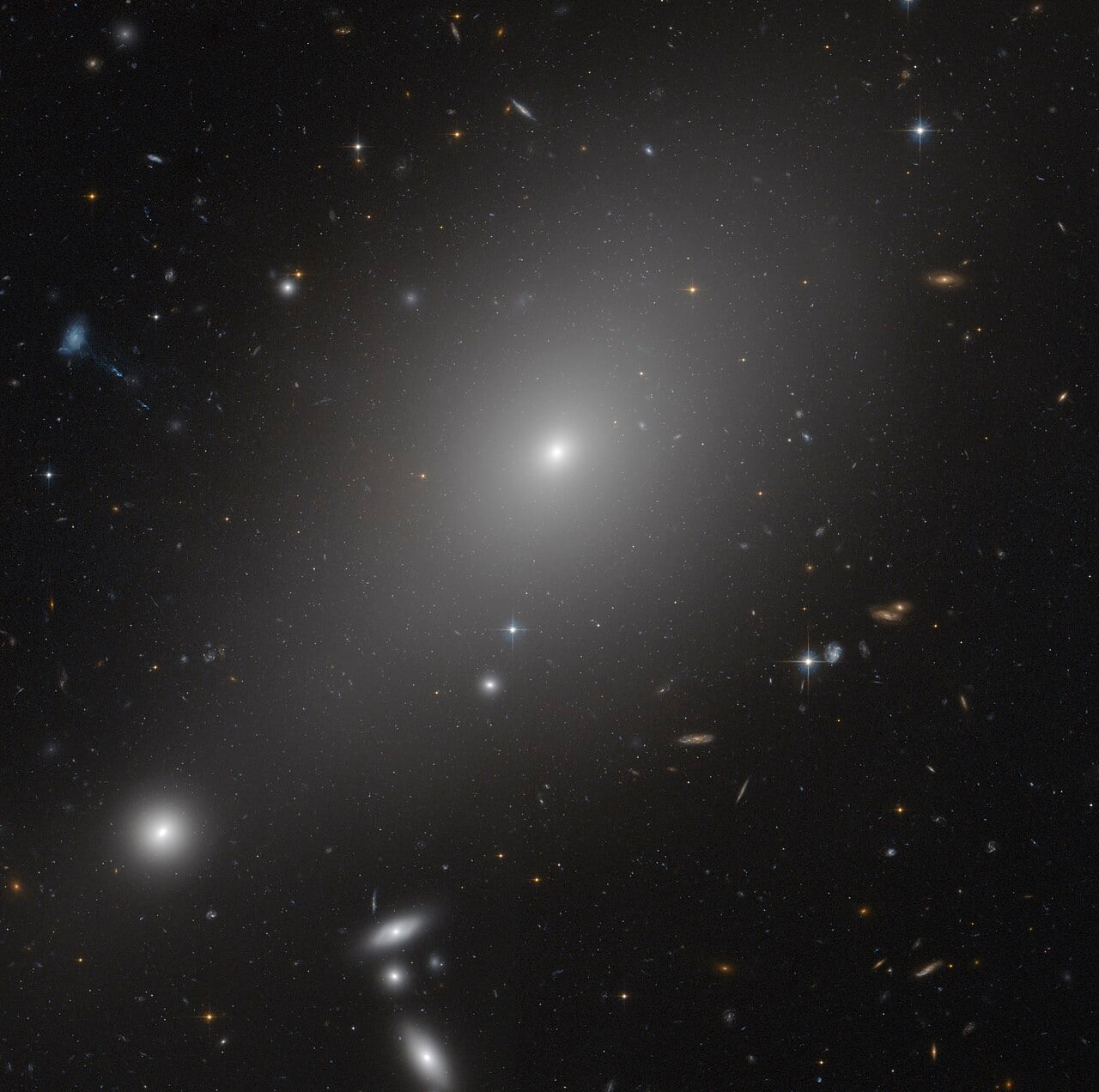


Astronomers have revealed a surprising diversity in the evolutionary paths of the universe’s most massive galaxies. Using multi-wavelength observations combining Keck Observatory spectroscopy with far infrared and radio data, researchers found that less than two billion years after the Big Bang, some ultramassive galaxies had already shut down star formation and shed their dust, while others continued building stars behind thick dusty veils.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
[mc4wp_form id=314]
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...
Popular Now
-
 01From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
01From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 02Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
02Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 03How New NASA, India Earth Satellite NISAR Will See Earth
03How New NASA, India Earth Satellite NISAR Will See Earth -
 04Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
04Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
Scroll to Top