Now Reading: NASA Reveals New Details About Dark Matter’s Influence on Universe
-
01
NASA Reveals New Details About Dark Matter’s Influence on Universe
NASA Reveals New Details About Dark Matter’s Influence on Universe

With the Webb telescope’s unprecedented sensitivity, scientists are learning more about dark matter’s influence on stars, galaxies, and even planets like Earth.
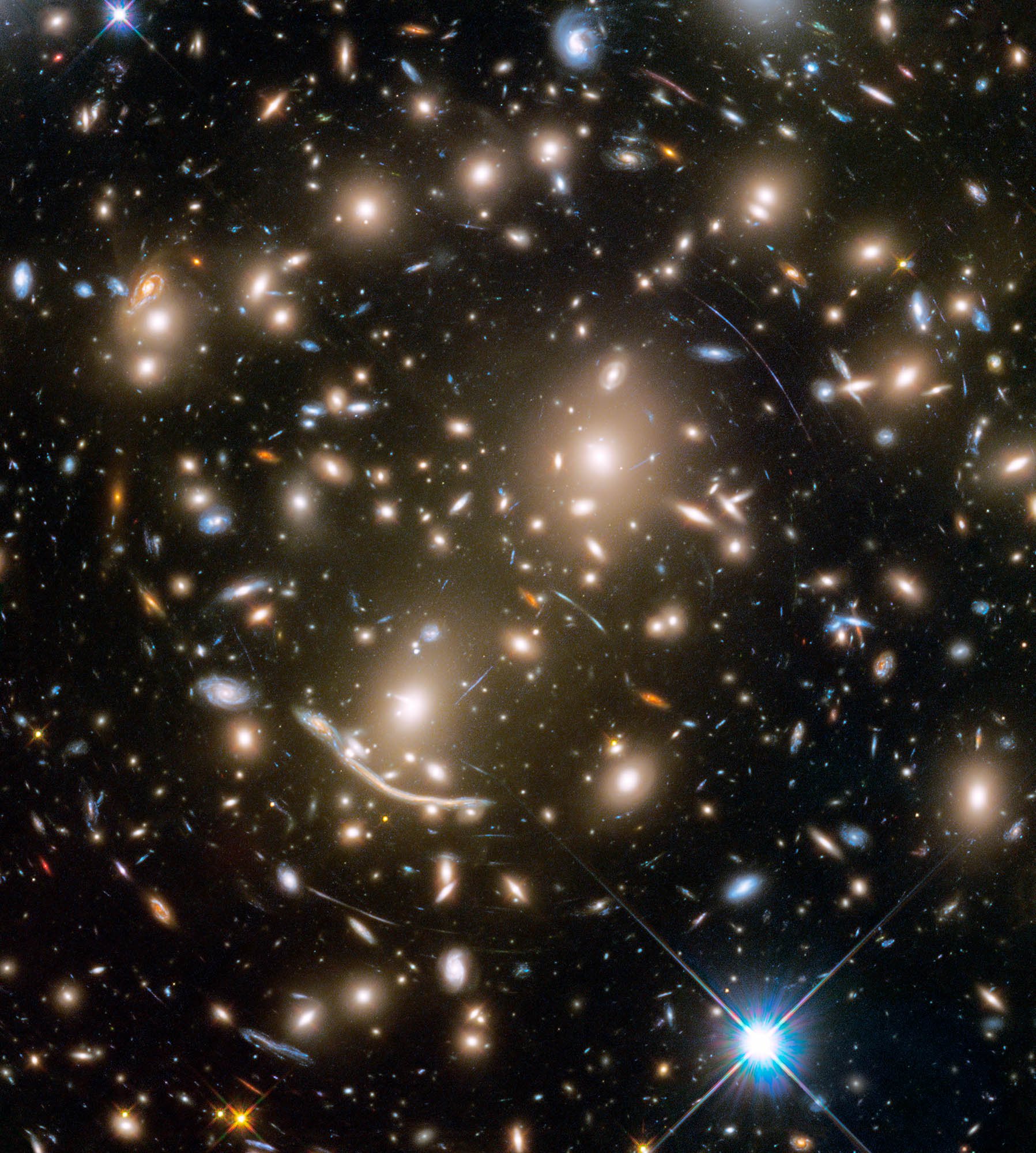
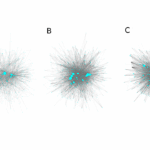
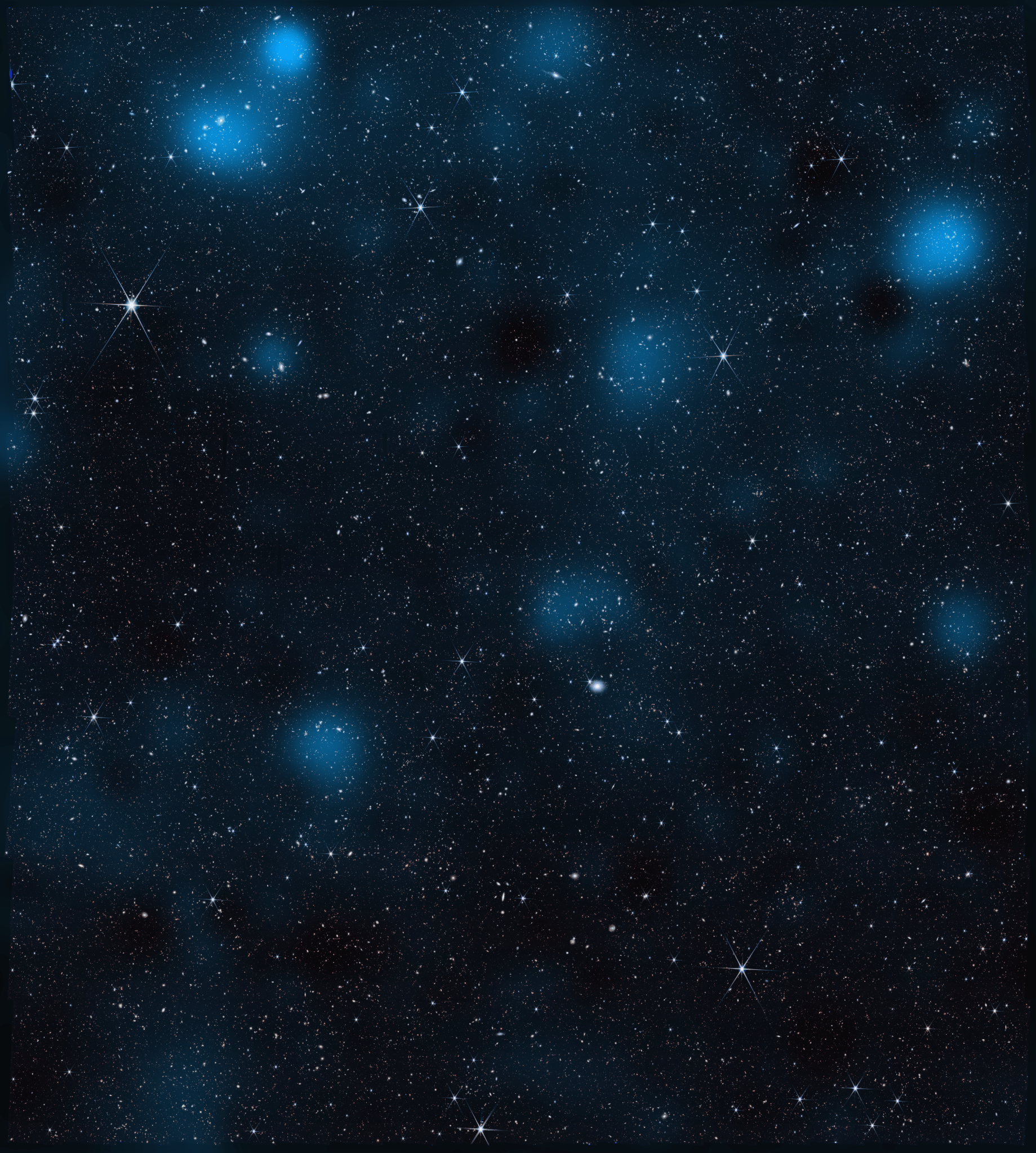
Scientists using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have made one of the most detailed, high-resolution maps of dark matter ever produced. It shows how the invisible, ghostly material overlaps and intertwines with “regular” matter, the stuff that makes up stars, galaxies, and everything we can see.
Published Monday, Jan. 26, in Nature Astronomy, the map builds on previous research to provide additional confirmation and new details about how dark matter has shaped the universe on the largest scales — galaxy clusters millions of light-years across — that ultimately give rise to galaxies, stars, and planets like Earth.
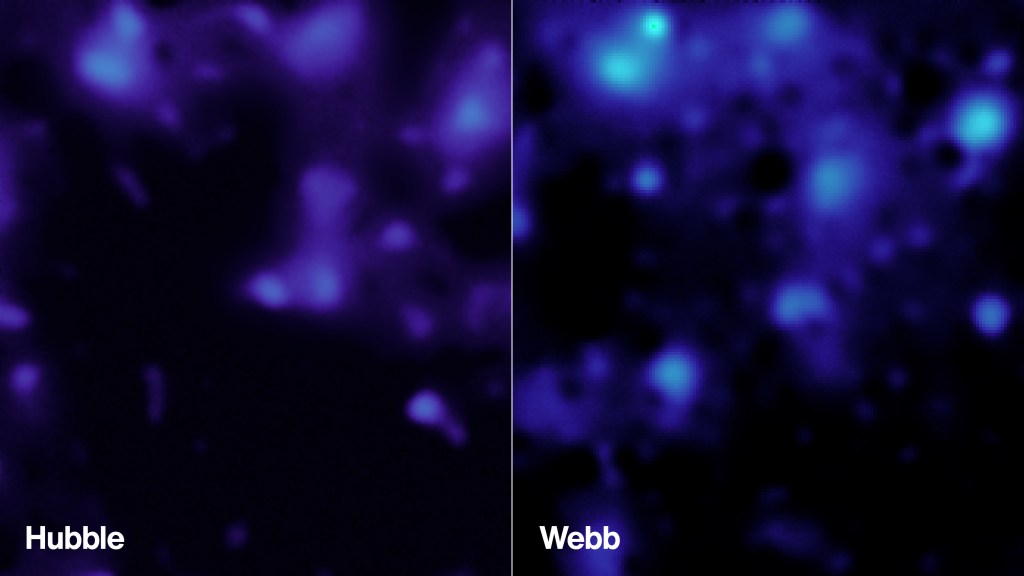
“This is the largest dark matter map we’ve made with Webb, and it’s twice as sharp as any dark matter map made by other observatories,” said Diana Scognamiglio, lead author of the paper and an astrophysicist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “Previously, we were looking at a blurry picture of dark matter. Now we’re seeing the invisible scaffolding of the universe in stunning detail, thanks to Webb’s incredible resolution.”
Dark matter doesn’t emit, reflect, absorb, or even block light, and it passes through regular matter like a ghost. But it does interact with the universe through gravity, something the map shows with a new level of clarity. Evidence for this interaction lies in the degree of overlap between dark matter and regular matter. According to the paper’s authors, Webb’s observations confirm that this close alignment can’t be a coincidence but, rather, is due to dark matter’s gravity pulling regular matter toward it throughout cosmic history.
“Wherever we see a big cluster of thousands of galaxies, we also see an equally massive amount of dark matter in the same place. And when we see a thin string of regular matter connecting two of those clusters, we see a string of dark matter as well,” said Richard Massey, an astrophysicist at Durham University in the United Kingdom and a coauthor of the new study. “It’s not just that they have the same shapes. This map shows us that dark matter and regular matter have always been in the same place. They grew up together.”
Closer look
Found in the constellation Sextans, the area covered by the new map is a section of sky about 2.5 times larger than the full Moon. A global community of scientists have observed this region with at least 15 ground- and space-based telescopes for the Cosmic Evolution Survey (COSMOS). Their goal: to precisely measure the location of regular matter here and then compare it to the location of dark matter. The first dark matter map of the area was made in 2007 using data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, a project led by Massey and JPL astrophysicist Jason Rhodes, a coauthor of the paper.
Webb peered at this region for a total of about 255 hours and identified nearly 800,000 galaxies, some of which were detected for the first time. Scognamiglio and her colleagues then looked for dark matter by observing how its mass curves space itself, which in turn bends the light traveling to Earth from distant galaxies. When observed by researchers, it’s as if the light of those galaxies has passed through a warped windowpane.
The Webb map contains about 10 times more galaxies than maps of the area made by ground-based observatories and twice as many as Hubble’s. It reveals new clumps of dark matter and captures a higher-resolution view of the areas previously seen by Hubble.
To refine measurements of the distance to many galaxies for the map, the team used Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), designed and managed through launch by JPL, along with other space- and ground-based telescopes. The wavelengths that MIRI detects also make it adept at detecting galaxies obscured by cosmic dust clouds.
Why it matters
When the universe began, regular matter and dark matter were probably sparsely distributed. Scientists think dark matter began to clump together first and that those dark matter clumps then pulled together regular matter, creating regions with enough material for stars and galaxies to begin to form.
In this way, dark matter determined the large-scale distribution of galaxies in the universe. And by prompting galaxy and star formation to begin earlier than they would have otherwise, dark matter’s influence also played a role in creating the conditions for planets to eventually form. That’s because the first generations of stars were responsible for turning hydrogen and helium — which made up the vast majority of atoms in the early universe — into the rich array of elements that now compose planets like Earth. In other words, dark matter provided more time for complex planets to form.
“This map provides stronger evidence that without dark matter, we might not have the elements in our galaxy that allowed life to appear,” said Rhodes. “Dark matter is not something we encounter in our everyday life on Earth, or even in our solar system, but it has definitely influenced us.”
Scognamiglio and some of her coauthors will also map dark matter with NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope over an area 4,400 times bigger than the COSMOS region. Roman’s primary science goals include learning more about dark matter’s fundamental properties and how they may or may not have changed over cosmic history. But Roman’s maps won’t beat Webb’s spatial resolution. More detailed looks at dark matter will be possible only with a next-generation telescope like the Habitable Worlds Observatory, NASA’s next astrophysics flagship concept.
More about Webb
The James Webb Space Telescope is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
To learn more about Webb, visit:
Media Contacts
Calla Cofield / Ian O’Neill
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469 / 818-354-2649
calla.e.cofield@jpl.nasa.gov / ian.j.oneill@jpl.nasa.gov
2026-002
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly -
 07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits