Now Reading: NASA’s Lucy probe will fly by the asteroid Donaldjohanson on Easter Sunday
-
01
NASA’s Lucy probe will fly by the asteroid Donaldjohanson on Easter Sunday
NASA’s Lucy probe will fly by the asteroid Donaldjohanson on Easter Sunday
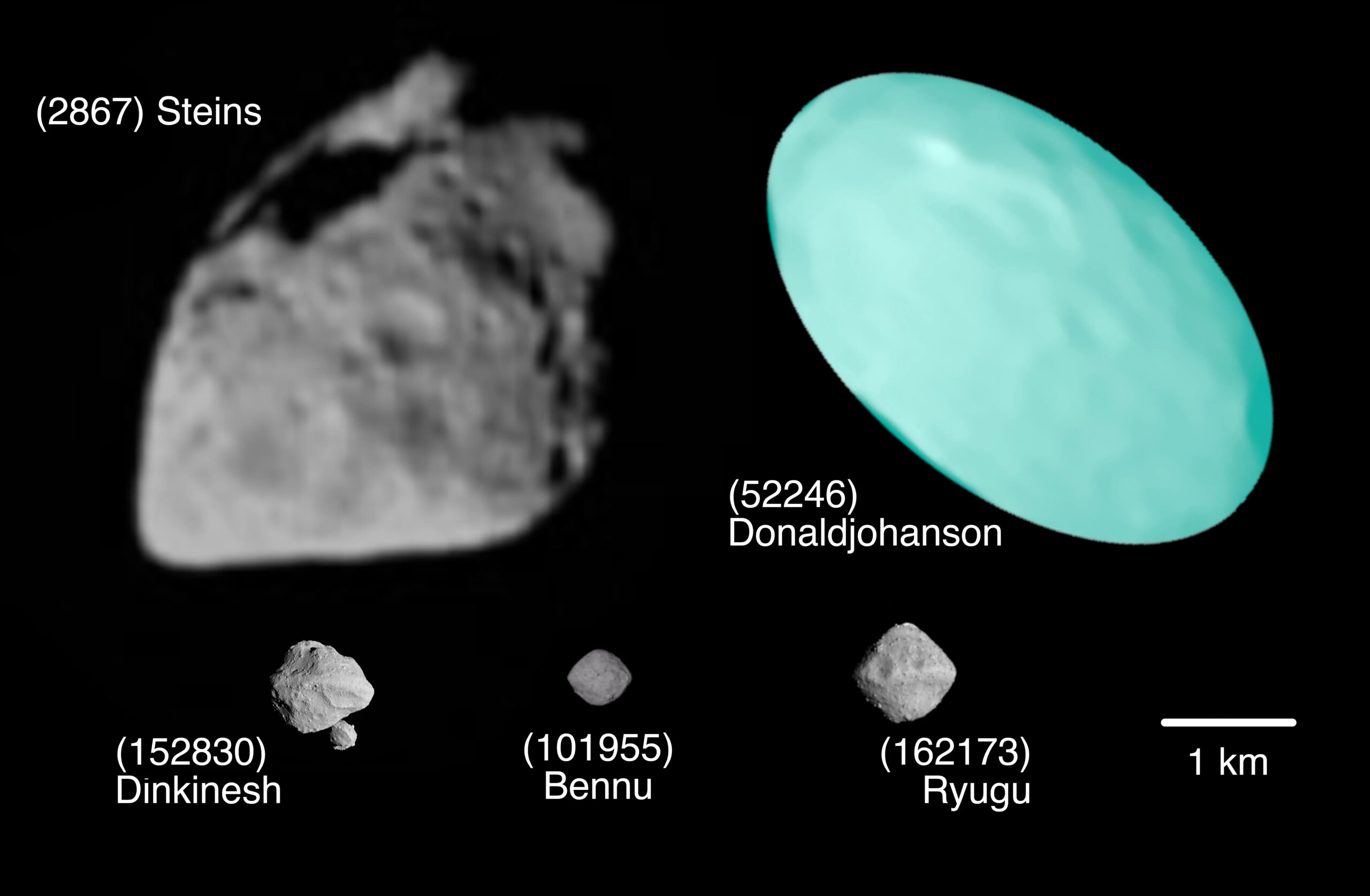
Easter Sunday certainly won’t be a day of rest for the astronomy community.
All eyes will be on NASA’s asteroid-studying Lucy spacecraft, which is due to have a close encounter at 1:51 p.m. EDT (1751 GMT) on April 20, 2025.
Launched in 2021, Lucy is on a 12-year journey to the orbit of Jupiter, during which the probe will perform flybys of eight Trojan asteroids in a quest to learn about the origins of the solar system, searching for elements that could spark the rise of life. But before Lucy gets there, the spacecraft will have time for a few dress rehearsals.
The first was a flyby of the asteroid Dinkinesh on Nov. 1, 2023. This coming Sunday, Lucy will zip past her second target, the asteroid Donaldjohanson. Lucy will pass by the asteroid at a distance of about 620 miles (1,000 kilometers), test its science instruments in the process.
Those tools include L’Ralph, a color camera and an infrared imaging spectrometer; L’LLORI, the high-resolution Lucy Long Range Reconnaissance Imager; and L’TES, the far-infrared Lucy Thermal Emission Spectrometer.
“We’re going to observe [Donaldjohanson] as if it was one of the Trojan asteroids, because we wanted to have a complete practice run,” Arizona State University professor Phil Christensen, who designed L’TES, said in a video interview. The goal, he shares, is to figure out the asteroid’s composition.
Related stories:
Lucy and Donaldjohanson are connected by far more than their upcoming physical proximity. The NASA mission was named after the three-million-year-old fossil australopithecine skeleton discovered in Ethiopia 1974, which contributed to our understanding of human evolution. And who discovered those bones? Paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson, founder of Arizona State University’s Institute of Human Origins.
Johanson spoke with Christensen during the video interview to discuss the Lucy mission, and Christensen had one very important question to ask. If, as scientists predict, a secondary asteroid is discovered during the Donaldjohanson flyby — asteroids often travel in pairs — what would Johanson want to name it?
“Oh, I’m going to have to give that some real thought,” said Johanson.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly




















