Now Reading: Turquoise Waters of Failaka Island Highlight Environmental Significance and Technological Innovations
-
01
Turquoise Waters of Failaka Island Highlight Environmental Significance and Technological Innovations
Turquoise Waters of Failaka Island Highlight Environmental Significance and Technological Innovations
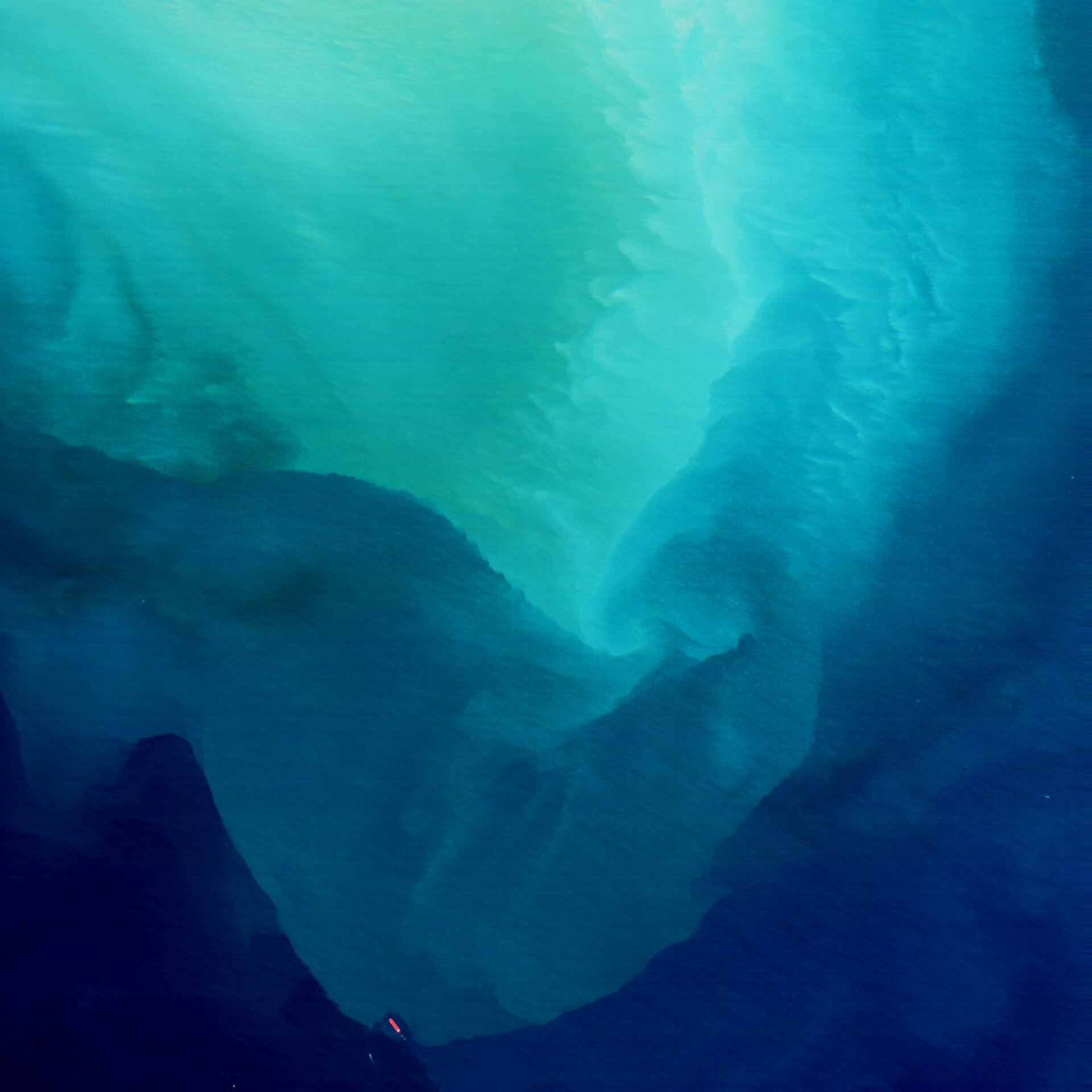


The mesmerizing turquoise waters that grace the southeast of the Kuwaiti island of Failaka are a visual testament to the intricate interplay of natural forces shaping our planet. Situated approximately 20 kilometers off the coast of Kuwait at the northern tip of the Persian Gulf, Failaka Island is not just a geographical landmark but a vibrant ecosystem pulsating with life and color. The striking hues of blue and green that adorn the waters surrounding Failaka result from a fascinating combination of environmental factors, including prevailing wind patterns and sediment dynamics.
Throughout the year, the winds sweep across the Gulf, carrying fine particles of sand and dust from various soil disposal activities, which become re-suspended and contribute to the sediment found in the water. This process creates a dynamic marine landscape, where the variations in sediment concentration alter the water’s appearance, creating swirling patterns reminiscent of an artist’s brushstrokes. Such rich visual diversity is not only a delight for the eyes but also serves as a valuable indicator of the region’s ecological health.
Failaka Island has been a focal point for researchers and visitors alike, offering insights into both historical and environmental aspects of the region. Once a thriving center of civilization, its archaeological sites tell tales of human settlements and interactions with the natural world. However, the contemporary narrative is reshaped by the environmental challenges and opportunities presented by its proximity to urban development in Kuwait.
In addition to its natural beauty, Failaka very important for marine biodiversity. The surrounding waters support a variety of marine species, from vibrant coral reefs to schools of fish that thrive in the nutrient-rich currents. This biodiversity is essential not only for ecological balance but also for local fisheries that sustain communities in the region. Understanding these ecosystems becomes increasingly important as pressures from pollution and climate change mount.
The ecological significance of the turquoise waters can be highlighted by initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. For instance, local organizations are focusing on marine conservation efforts to monitor and protect marine habitats. Such activities include:
- Coral Reef Restoration: Efforts to rehabilitate damaged reefs enhance the biodiversity of the waters and create a more resilient marine ecosystem.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Regular assessments of sediment and pollution levels help in understanding the health of the marine environment.
- Community Engagement: Programs aimed at educating local fishermen about sustainable fishing practices contribute to the long-term viability of marine resources.
The region’s vibrant waters are also a reminder of the broader implications of environmental stewardship. By using advanced technologies like remote sensing, scientists can gain deeper insights into the health of marine ecosystems, making it possible to respond proactively to changing conditions. The satellite images captured during missions like Φsat-2 provide a glimpse into the dynamic and ever-changing nature of the Gulf’s waters, revealing patterns that are both beautiful and essential for understanding our planet’s ecological systems.
The turquoise hues of Failaka’s waters are more than a stunning visual; they embody the intricate connections between wind, sediment, and marine life, presenting a microcosm of the Earth’s ecological tapestry. As we continue to study and cherish these waters, the lessons learned can guide future efforts to protect and sustain the natural beauty that defines this unique region.
The Φsat-2 mission represents a significant leap forward in our understanding of Earth observation through the integration of cutting-edge technologies, particularly in the domain of artificial intelligence (AI). Launched in August 2024, this state-of-the-art cubesat has quickly established itself as a pivotal tool in gathering and analyzing vast amounts of data from our planet’s surface. Orbiting at an altitude of 510 kilometers, Φsat-2 employs seven multispectral bands, ranging from visible to near-infrared wavelengths, allowing it to capture images with remarkable detail, boasting a ground sampling distance of approximately 5 meters.
One of the most exciting features of the Φsat-2 mission is its AI capabilities, which transform the satellite into an intelligent observer of Earth. This onboard AI is designed to not only capture stunning images of the Earth’s surface but also to autonomously interpret and classify that data. For example, the AI can discern between ocean and land, detect the presence of clouds, and even identify various types of vessels navigating the waters. Such capabilities are invaluable for marine monitoring and environmental management, providing data that can inform policies and practices to protect vital ecosystems.
The true potential of the Φsat-2 mission is highlighted when considering its applications in environmental monitoring. The onboard AI processes the images in real-time, enabling it to identify areas that require further investigation. For instance, if the satellite detects an unusual concentration of pollutants in the water, it can flag that area for additional scrutiny, allowing scientists and environmentalists to respond swiftly to potential ecological threats.
Moreover, the AI not only assists in identifying environmental issues but also contributes to improving disaster response strategies. In instances of natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes, Φsat-2 can analyze affected areas and generate street maps, providing crucial data for emergency response teams. This capability enhances situational awareness during crises, enabling a faster and more coordinated response to help impacted communities.
Another fascinating application of Φsat-2’s AI technology is its ability to detect marine pollution. By analyzing spectral data, the AI can identify oil spills, algal blooms, and other forms of contamination. This feature is particularly important for regions like the Persian Gulf, where oil exploration and marine traffic pose significant risks to water quality and ecosystem health.
In addition to monitoring pollution and providing disaster relief, the AI capabilities of Φsat-2 are being used to enhance our understanding of marine biodiversity. The satellite can track changes in marine habitats over time, helping researchers identify patterns in species movements and habitat shifts that may be driven by climate change or human activity. This kind of data very important for developing conservation strategies aimed at protecting vulnerable species and ecosystems.
As we look toward the future, the Φsat-2 mission sets a new standard for the integration of AI in Earth observation. Its advanced capabilities exemplify how technology can be harnessed to not only observe but also interpret the complex systems that govern our planet. The data generated from this mission will undoubtedly support a wide range of applications, from environmental management to urban planning, illustrating the power of innovation in addressing some of the most pressing challenges faced by our world today.
In essence, Φsat-2 is a game-changer in the sphere of remote sensing, providing unprecedented insights into the Earth’s environment while using artificial intelligence to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of data collection and analysis. As we continue to harness the power of technology in understanding our planet, missions like Φsat-2 will play a critical role in shaping a more sustainable and informed future.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly