Now Reading: A D/H Ratio Consistent With Earth’s Water In Halley-type Comet 12P From ALMA HDO Mapping
-
01
A D/H Ratio Consistent With Earth’s Water In Halley-type Comet 12P From ALMA HDO Mapping
A D/H Ratio Consistent With Earth’s Water In Halley-type Comet 12P From ALMA HDO Mapping
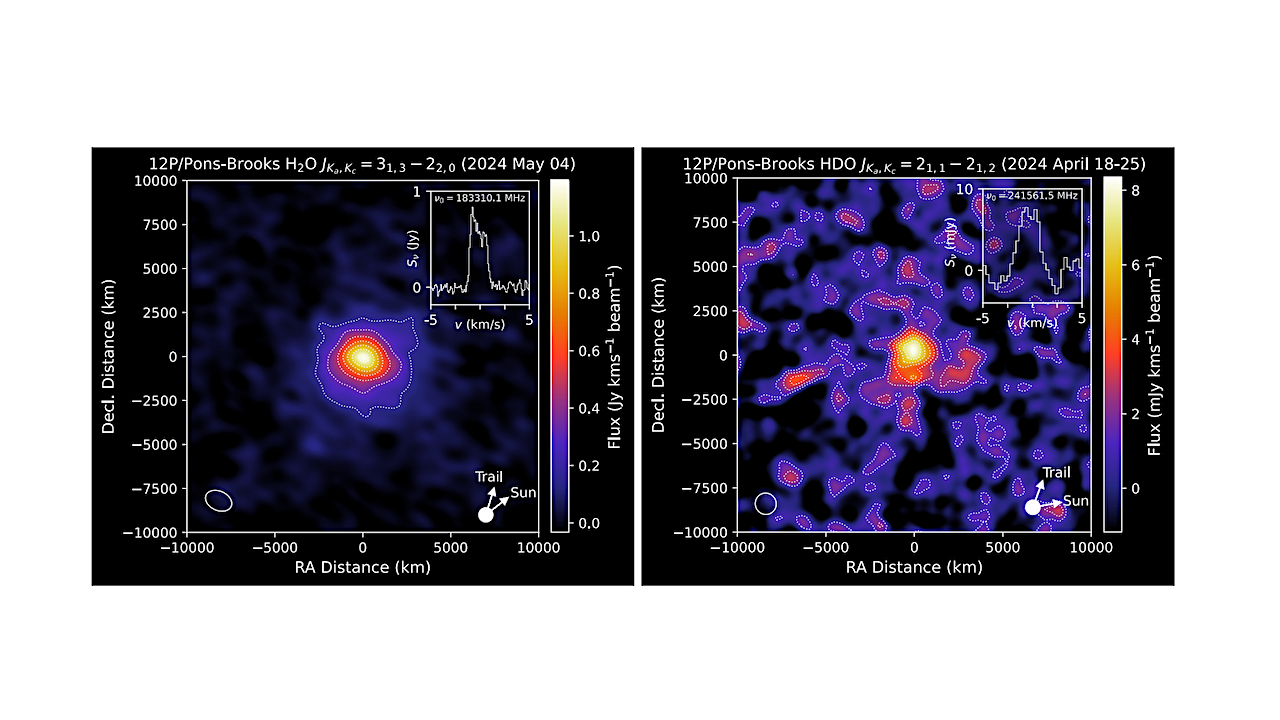

ALMA emission maps of H2O and HDO in comet 12P/Pons-Brooks. The image cubes have been spectrally integrated, continuum-subtracted, and are centered on the thermal continuum peak. The contour separation is 5 for H2O, and 1 for HDO, where is the RMS noise of each map. Inset panels (upper right) show the spectral line profiles extracted at the origin, as a function of cometocentric velocity (v). The spatial resolution (beam FWHM) is shown lower left, and the directions of the (sky-projected) comet-Sun and orbital trail vectors are shown lower right. The coordinate axes are sky-projected offsets (in kilometers) from the continuum peak, aligned with the celestial RA (right ascension) and Dec. (declination) grid. — astro-ph.EP
The D/H ratio in particular, helps reveal the relationship between (and heritage of) different H2O reservoirs within the Solar System. Here we present interferometric maps of water (H2O) and semiheavy water (HDO) in the gas-phase coma of a comet (Halley-type comet 12P/Pons-Brooks), obtained using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
The maps are consistent with outgassing of both H2O and HDO directly from the nucleus, and imply a coma D/H ratio (for water) of (1.71±0.44)×10−4.
This is at the lower end of the range of previously-observed values in comets, and is consistent with D/H in Earth’s ocean water. Our results suggest a possible common heritage between a component of the Oort cloud’s water ice reservoir, and the water that was delivered to the young Earth during the early history of the Solar System.
M. A. Cordiner, E. L. Gibb, Z. Kisiel, N. X. Roth, N. Biver, D. Bockelée-Morvan, J. Boissier, B. P. Bonev, S. B. Charnley, I. M. Coulson, J. Crovisier, M. N. Drozdovskaya, K. Furuya, M. Jin, Y.-J. Kuan, M. Lippi, D. C. Lis, S. N. Milam, C. Opitom, C. Qi, A. J. Remijan
Comments: Published in Nature Astronomy, 8 August 2025
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP)
Cite as: arXiv:2508.05925 [astro-ph.EP] (or arXiv:2508.05925v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2508.05925
Focus to learn more
Related DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-025-02614-7
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Martin Cordiner PhD
[v1] Fri, 8 Aug 2025 01:15:34 UTC (1,521 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.05925
Astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly