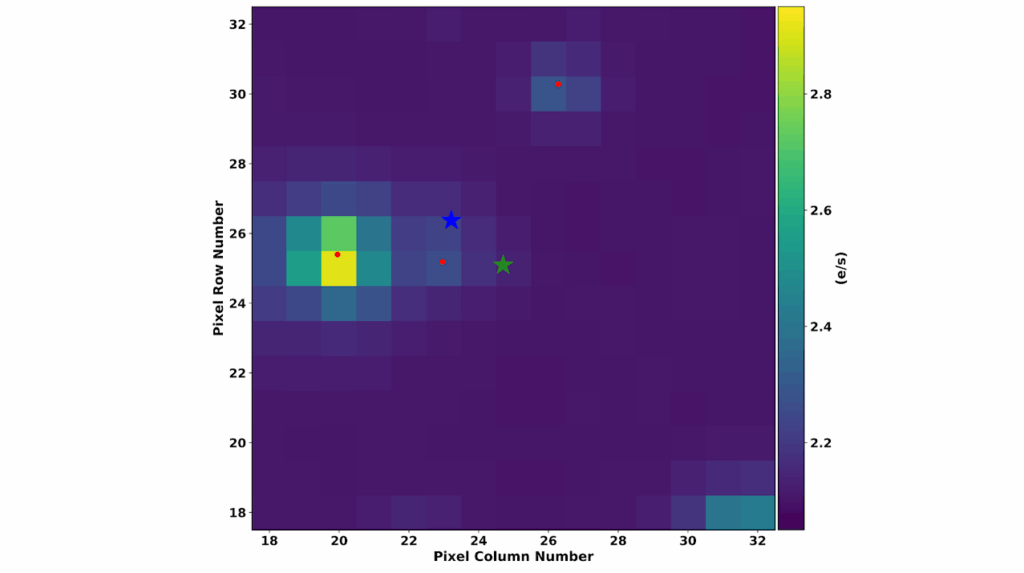
Now Reading: A Next-Generation Exoplanet Atmospheric Retrieval Framework for Transmission Spectroscopy (NEXOTRANS): Comparative Characterization for WASP-39 b Using JWST NIRISS, NIRSpec PRISM, and MIRI Observations
-
01
A Next-Generation Exoplanet Atmospheric Retrieval Framework for Transmission Spectroscopy (NEXOTRANS): Comparative Characterization for WASP-39 b Using JWST NIRISS, NIRSpec PRISM, and MIRI Observations
A Next-Generation Exoplanet Atmospheric Retrieval Framework for Transmission Spectroscopy (NEXOTRANS): Comparative Characterization for WASP-39 b Using JWST NIRISS, NIRSpec PRISM, and MIRI Observations
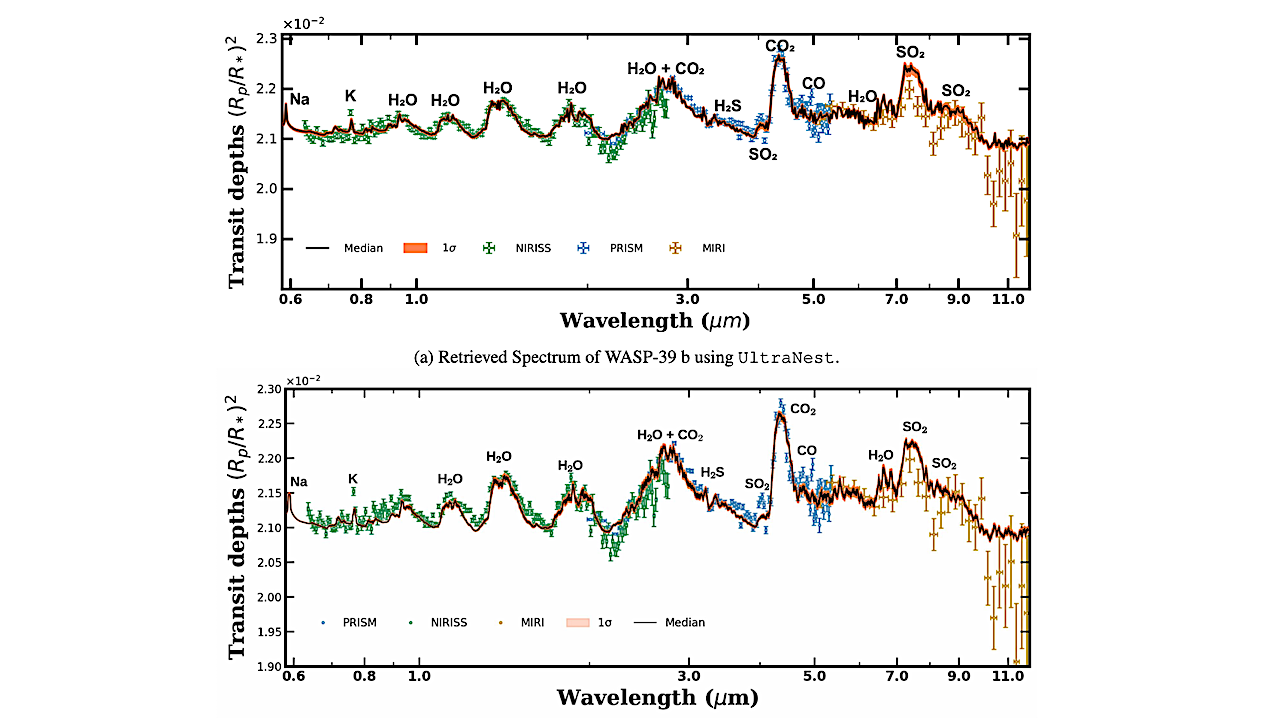

The retrieved spectra using the hybrid equilibrium chemistry model and machine learning approaches are shown. Observations from JWST instruments are illustrated with different colored error bars: green for NIRISS, blue for NIRSpec PRISM, and golden for MIRI. — astro-ph.EP
The advent of JWST has marked a new era in exoplanetary atmospheric studies, offering higher-resolution data and greater precision across a broader spectral range than previous space-based telescopes.
Accurate analysis of these datasets requires advanced retrieval frameworks capable of navigating complex parameter spaces. We present NEXOTRANS, an atmospheric retrieval framework that integrates Bayesian inference using UltraNest/PyMultiNest with four machine learning algorithms: Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, K-Nearest Neighbor, and Stacking Regressor.
This hybrid approach enables a comparison between traditional Bayesian methods and computationally efficient machine learning techniques. Additionally, NEXOTRANS incorporates NEXOCHEM, a module for solving equilibrium chemistry. We applied NEXOTRANS to JWST observations of the Saturn-mass exoplanet WASP-39 b, spanning wavelengths from 0.6 microns to 12.0 microns using NIRISS, NIRSpec PRISM, and MIRI.
Four chemistry models-free, equilibrium, modified hybrid equilibrium, and modified equilibrium-offset chemistry-were explored to retrieve precise Volume Mixing Ratios (VMRs) for H2O, CO2, CO, H2S, and SO2. Absorption features in both NIRSpec PRISM and MIRI data constrained SO2 log VMRs to values between -6.67 and -5.31 for all models except equilibrium chemistry.
High-altitude aerosols, including ZnS and MgSiO3, were inferred, with constraints on their VMRs, particle sizes, and terminator coverage fractions, providing insights into cloud composition. For the best-fit modified hybrid equilibrium model, we derived super-solar elemental abundances of O/H = 7.94 (+0.18/-0.18) x solar, C/H = 10.96 (+0.42/-0.41) x solar, and S/H = 3.98 (+0.29/-0.35) x solar, along with a C/O ratio of 1.17 (+0.03/-0.03) x solar, demonstrating NEXOTRANS’s potential for atmospheric characterization in the JWST era and beyond.
Tonmoy Deka, Tasneem Basra Khan, Swastik Dewan, Priyankush Ghosh, Debayan Das, Liton Majumdar
Comments: Accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal; 37 Pages, 17 Figures & 5 Tables
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP); Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM)
Cite as: arXiv:2504.18815 [astro-ph.EP] (or arXiv:2504.18815v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.18815
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Liton Majumdar
[v1] Sat, 26 Apr 2025 06:06:38 UTC (24,219 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.18815
Astrobiology
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly