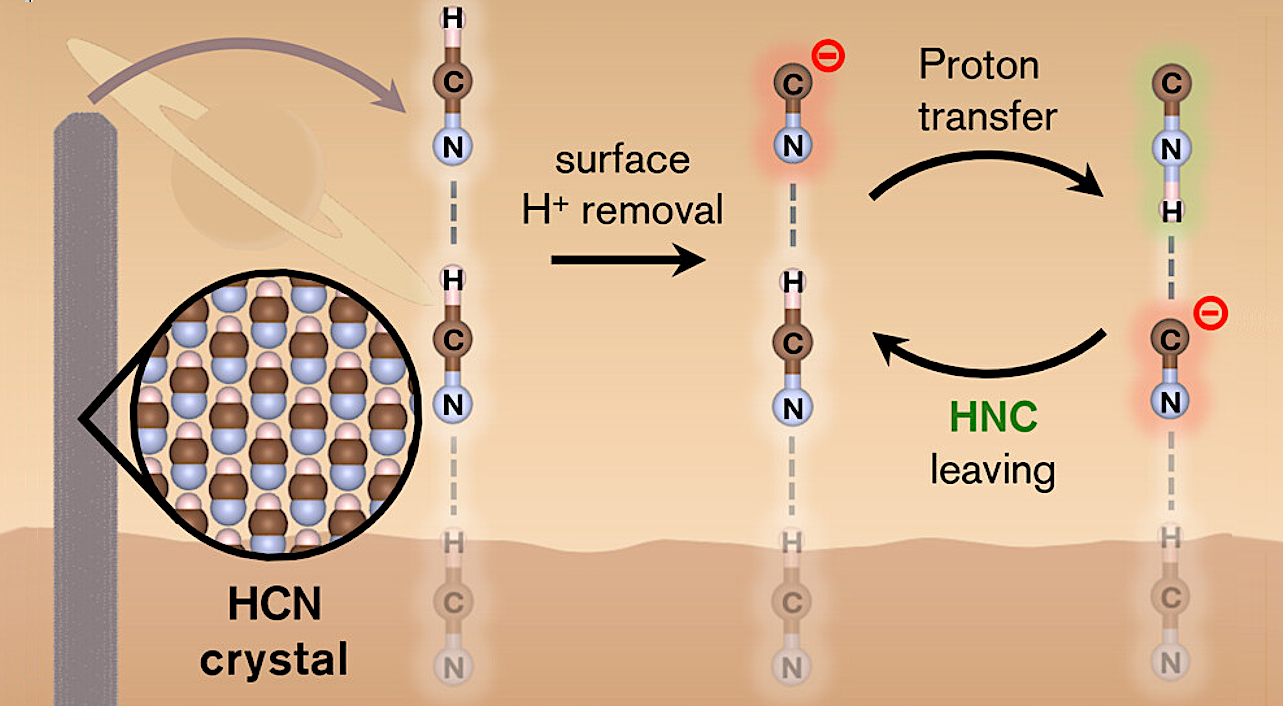
Graphical Abstract — American Chemical Society A substance poisonous to humans — hydrogen cyanide — may have helped create the seeds of life on Earth. At cold temperatures, hydrogen cyanide
Astrobiology29- Page
NASA DARES AGU Community Update In case you missed it, the recording of the NASA-DARES Community Update, held during the AGU Fall Meeting on December 18, 2025, is now available
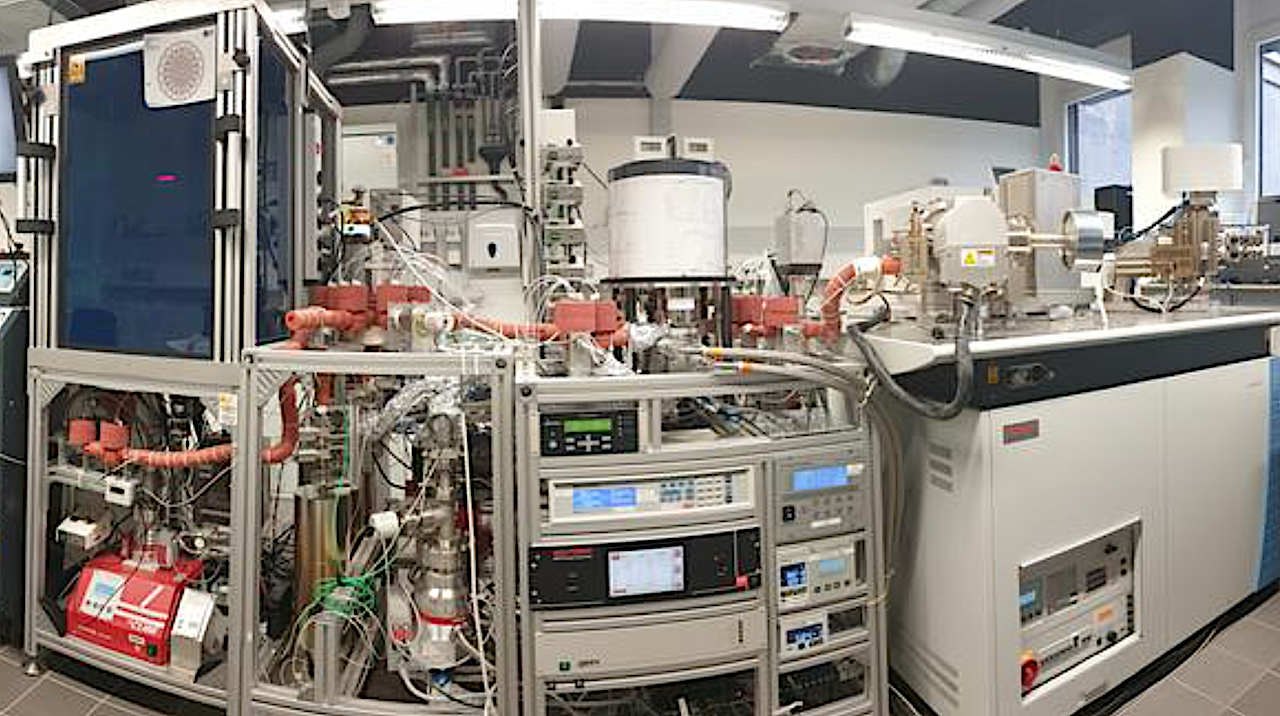
The noble gas laboratory in Cologne used to analyse the crypton for the study. Credit Tibor Dunai – University of Cologne An international research team involving the University of Cologne
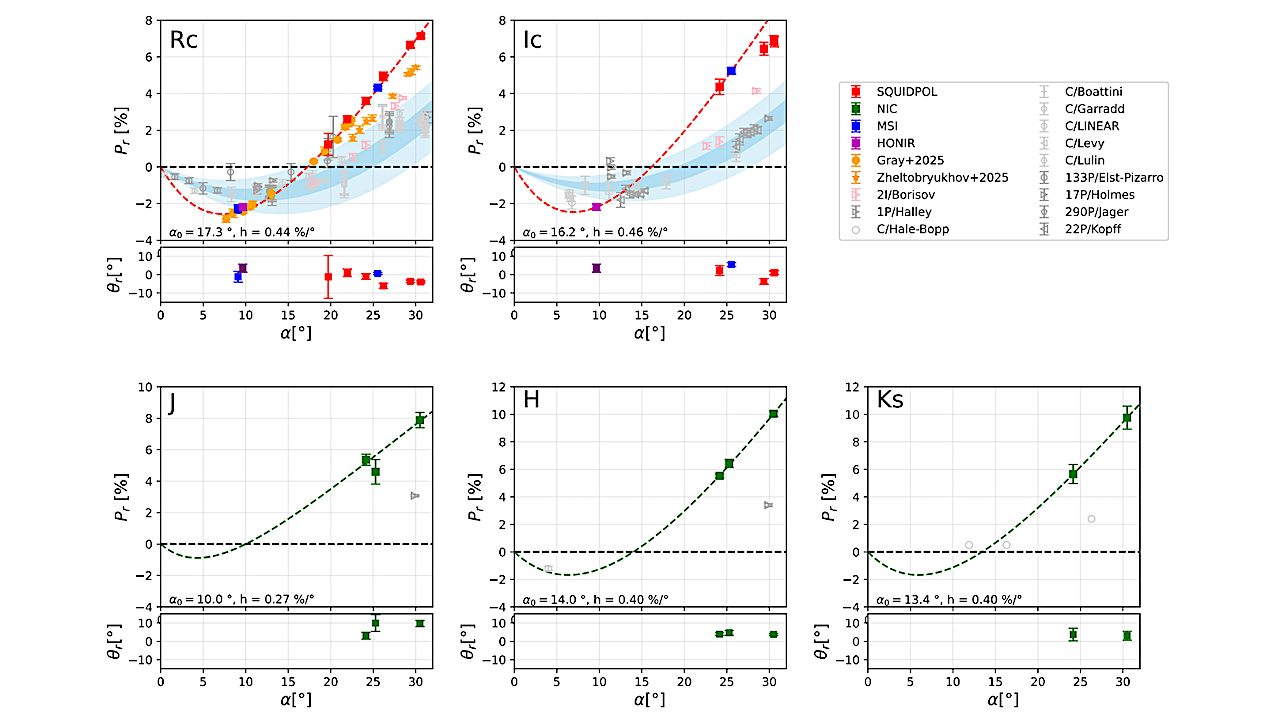
Polarization degree (Pr) and polarization position angle (θr) of 3I/ATLAS as a function of phase angle, measured in five bands (RC, IC, J, H, and Ks). Colored symbols denote our
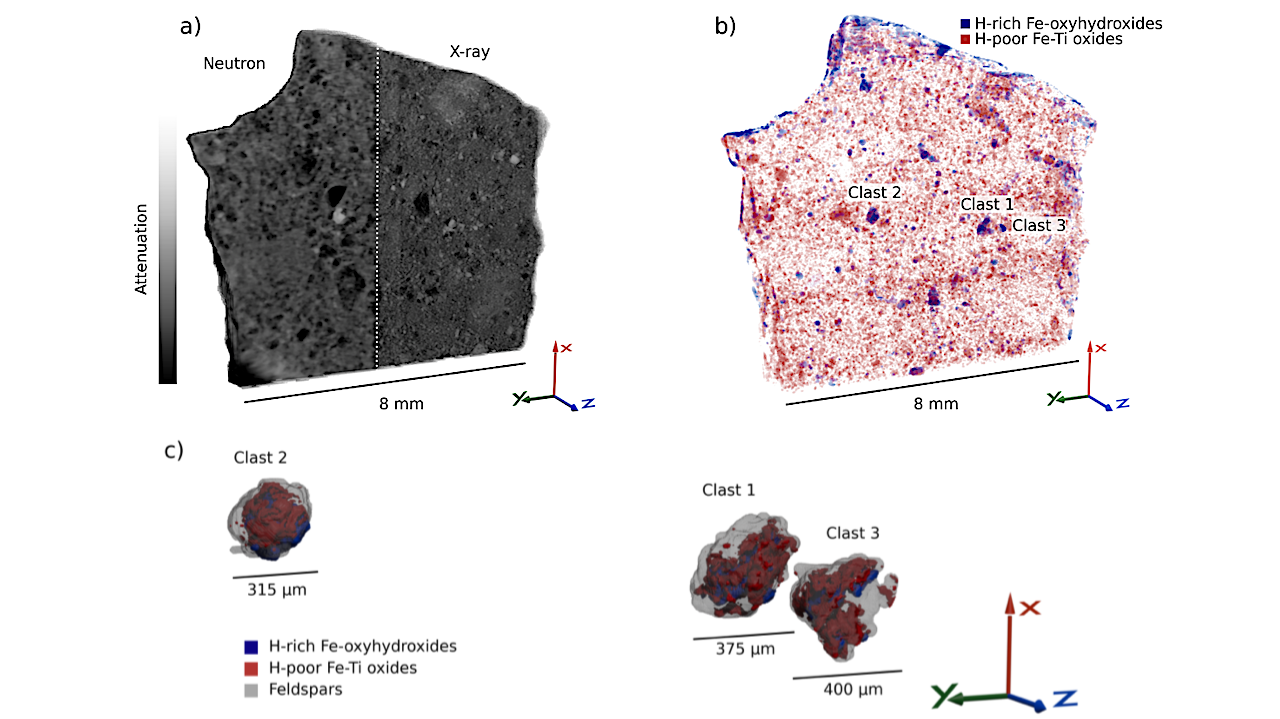
3D rendering of meteorite and clasts. a) 3D rendering of the attenuation tomograms cut in half in z to show two H-Fe-ox clasts, showing neutron attenuation on the left and
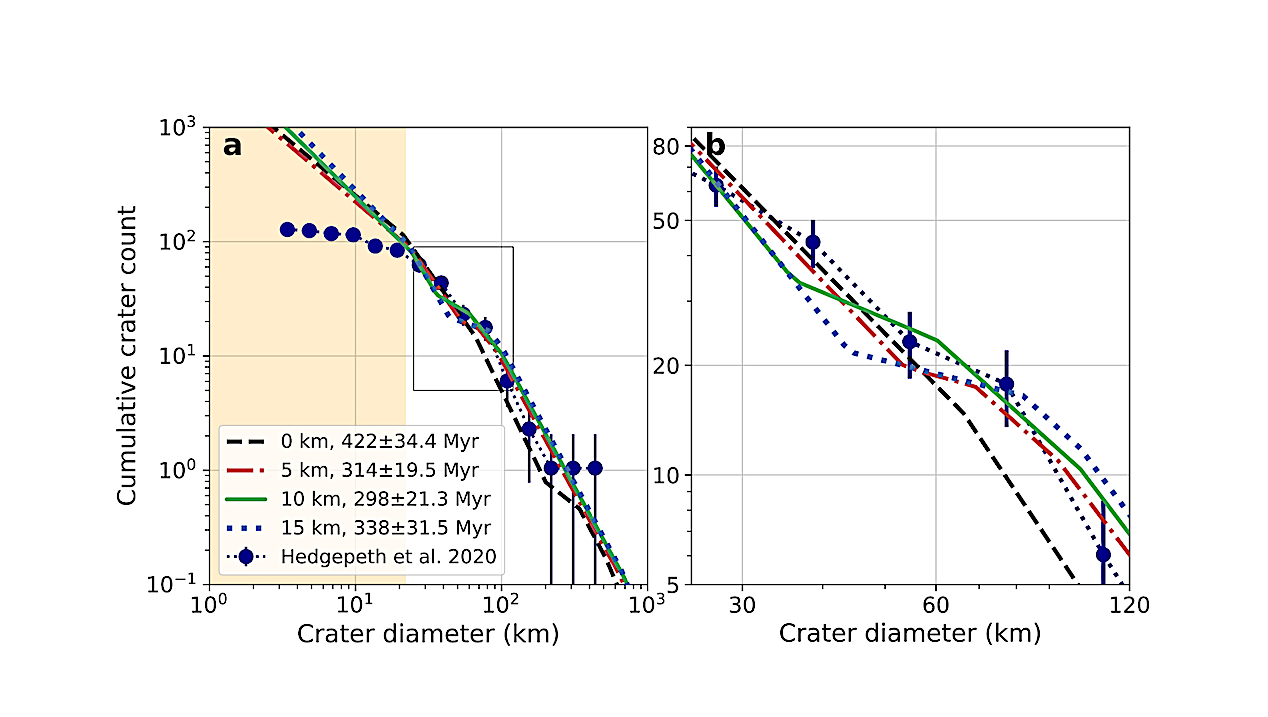
Status Report astro-ph.EP January 15, 2026 Cumulative crater count as a function of crater diameter. Each symbol and line depicts a fit to a different methane-clathrate thickness (see legend). The
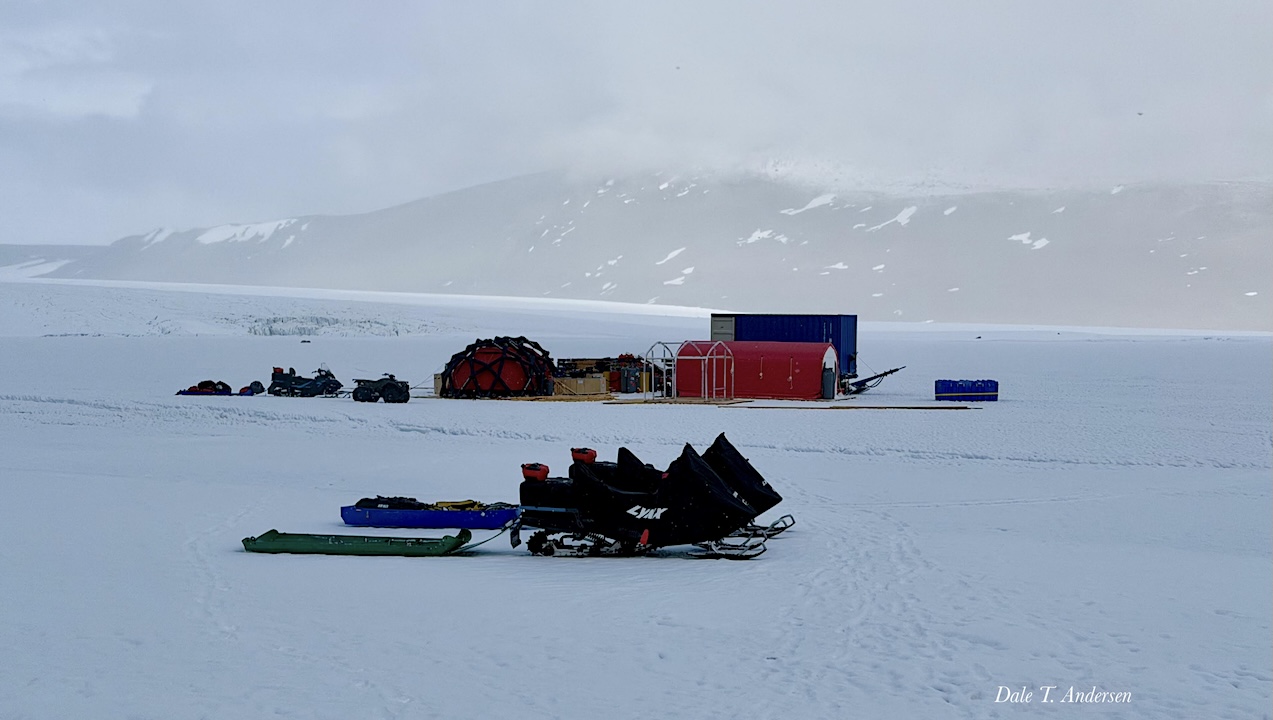
Lake Untersee Base Camp as of 14 January 2026 — Dale T. Andersen Hi Keith, Since our arrival we have been working hard to get shelter in place. That is
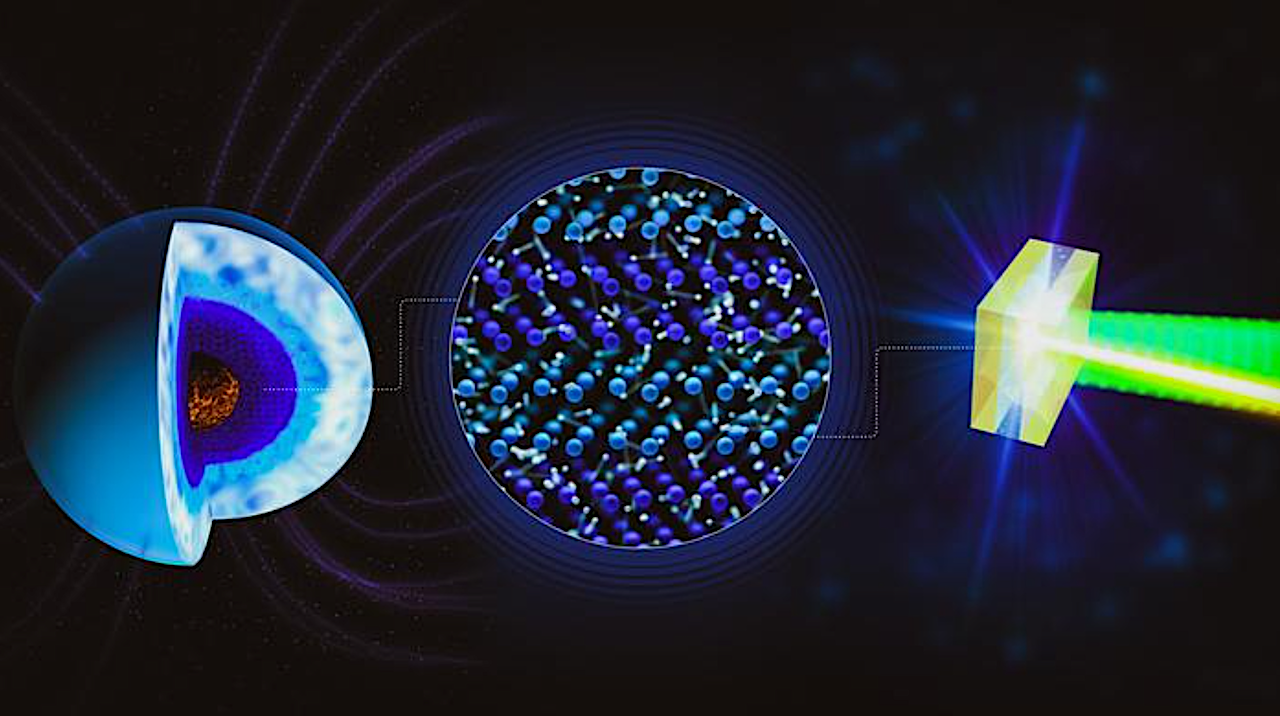
Schematic representation of the microscopic structure of superionic water, in which the oxygen atoms form a solid crystal lattice, while hydrogen ions are virtually free to move within it. With
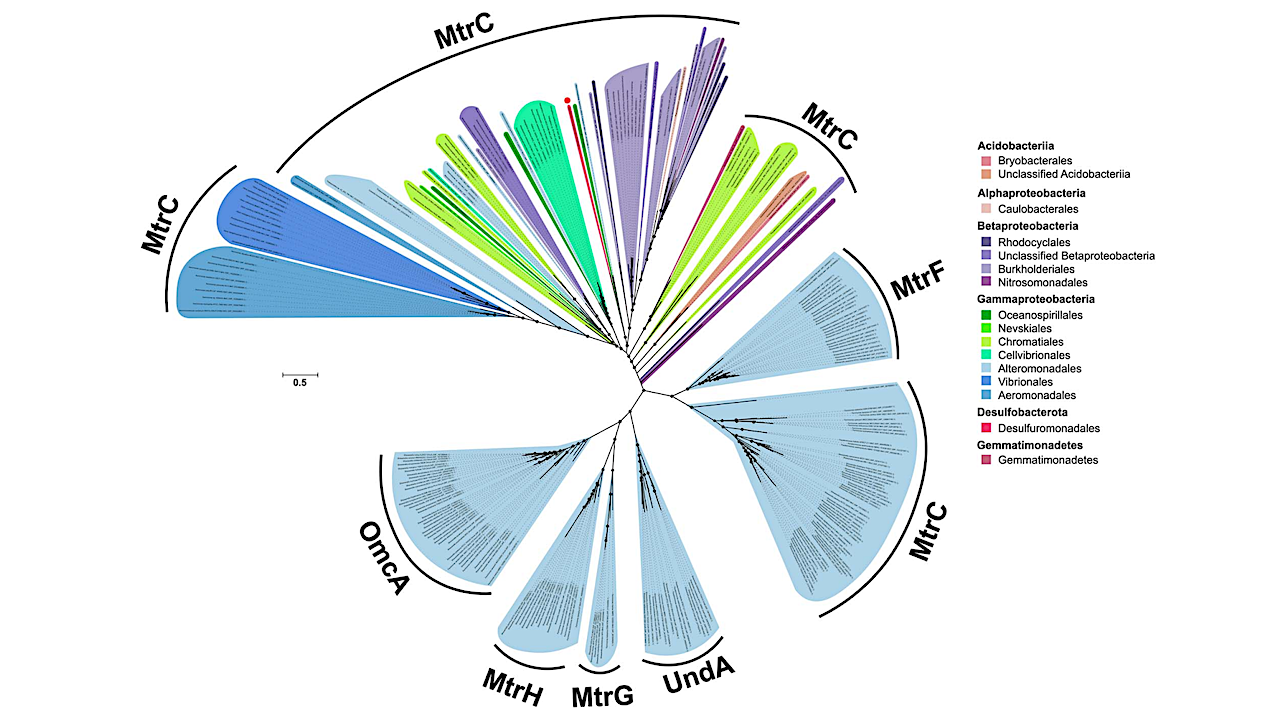
Phylogenetic relationship among known OmcA/MtrC decaheme c-type cytochromes from diverse bacteria and the newly identified D. acetexigens MtrC detected in this study. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree constructed from a concatenated alignment
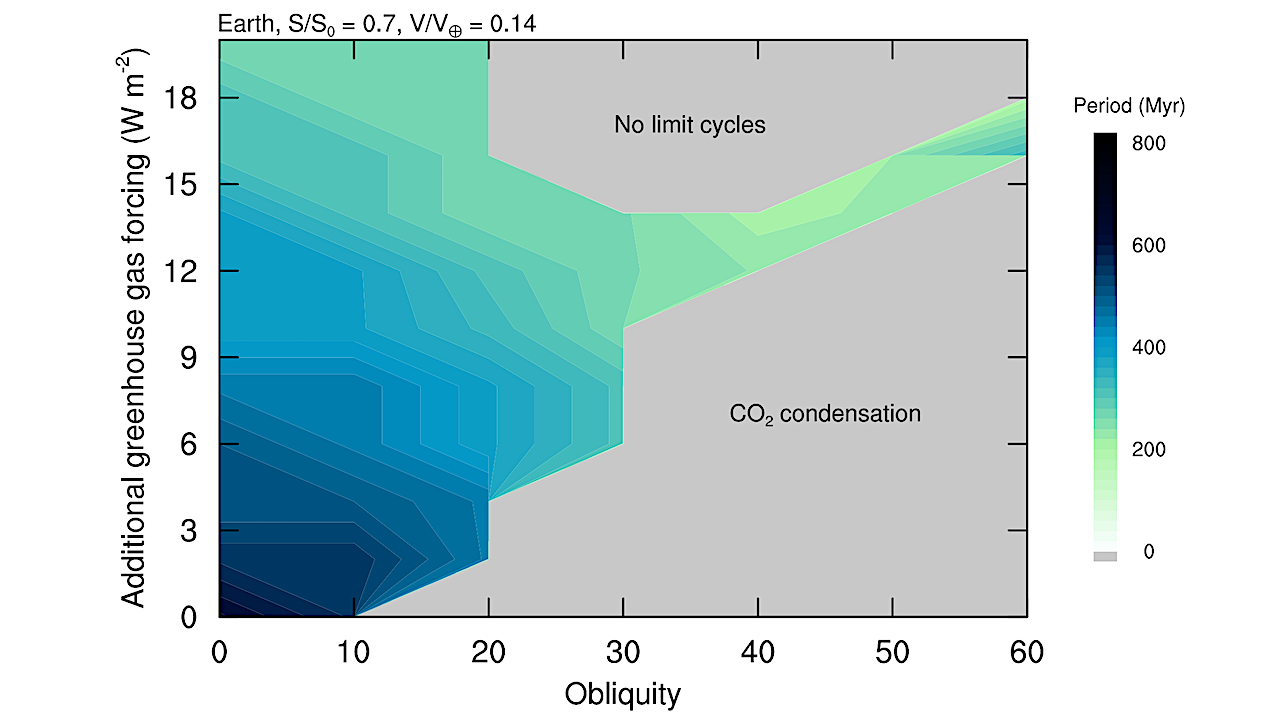
The period of limit cycle events (color contours) depends on planetary obliquity and the magnitude of any additional greenhouse gas warming Fadd. Limit cycling is assumed to halt when CO2
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly