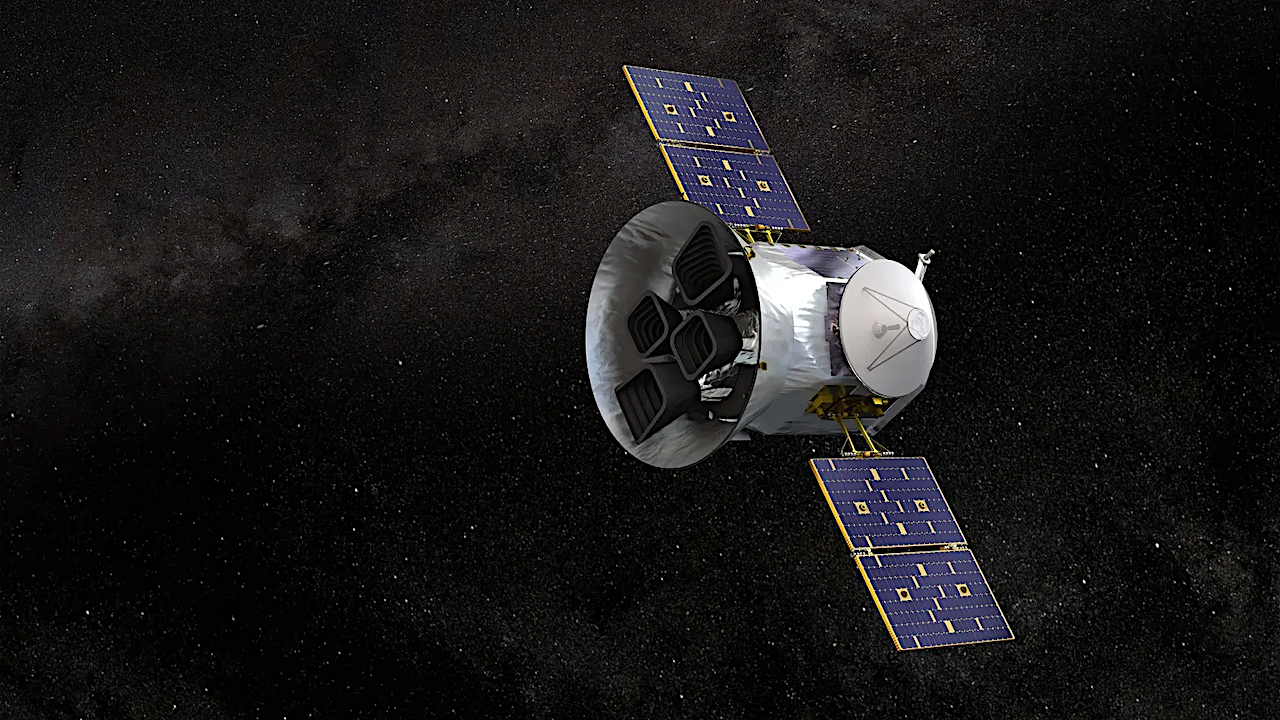
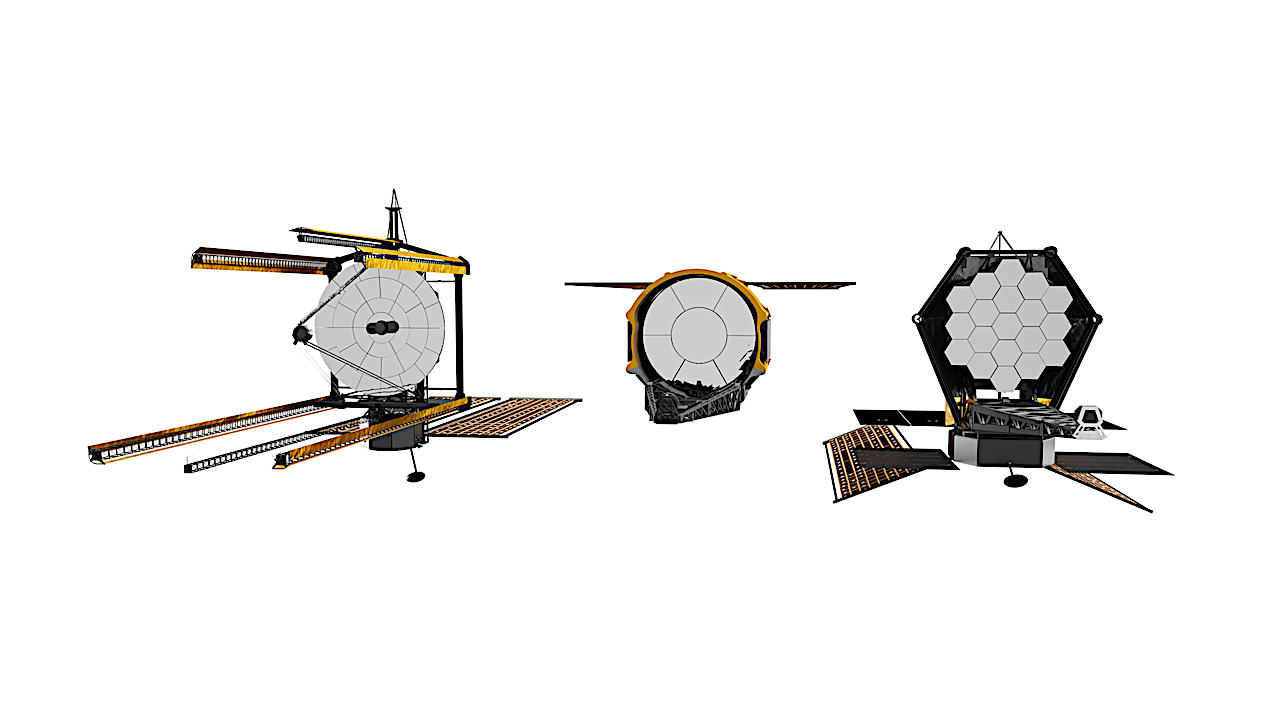
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) — NASA ROSES-25 Amendment 33: D.3D TESS General Investigator Final Text and Phase-1 Proposals Due March 10, 2026, via ARK/RPS. The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite
Astrobiology46- Page
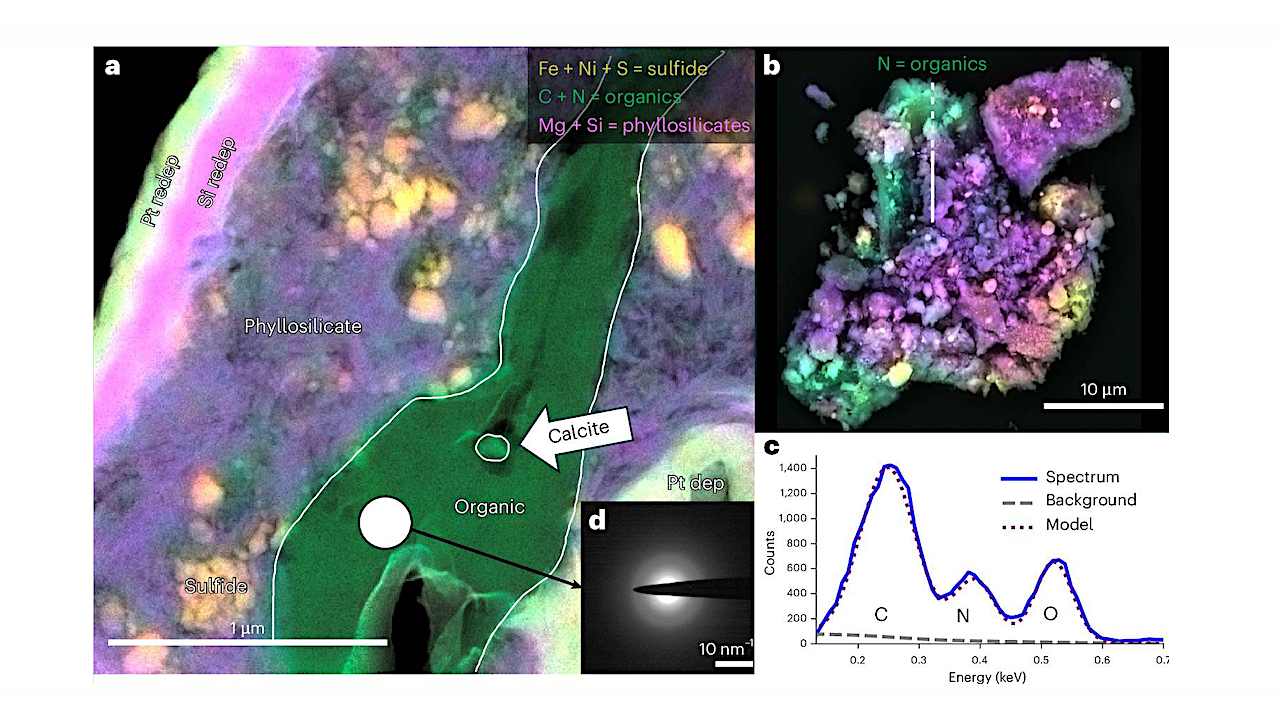
a, STEM high-angle annular dark field (HAADF) + EDS image of Particle 2. A nitrogenous vein (green) is sandwiched between phyllosilicate regions (purple). A circular region shows the location of a selected
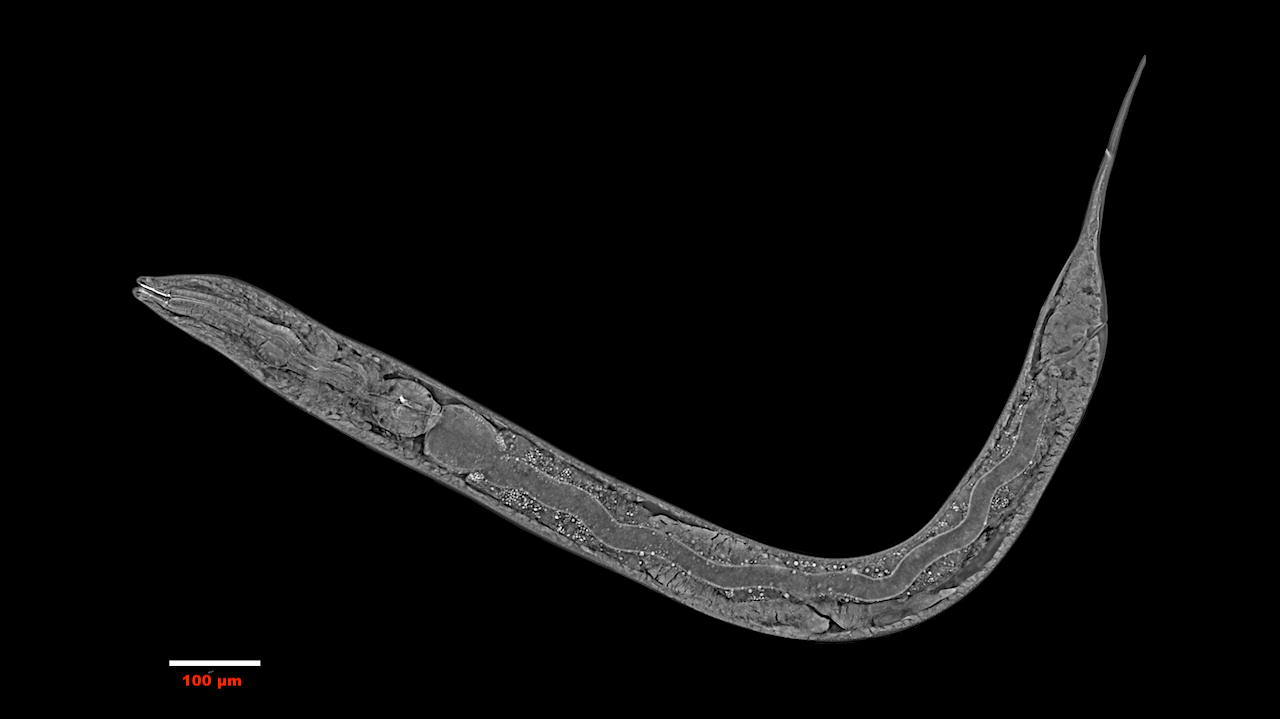
An image of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, showing internal structures including the intestine, pharynx, and body wall muscle. C. elegans is one of the simplest organisms with a nervous
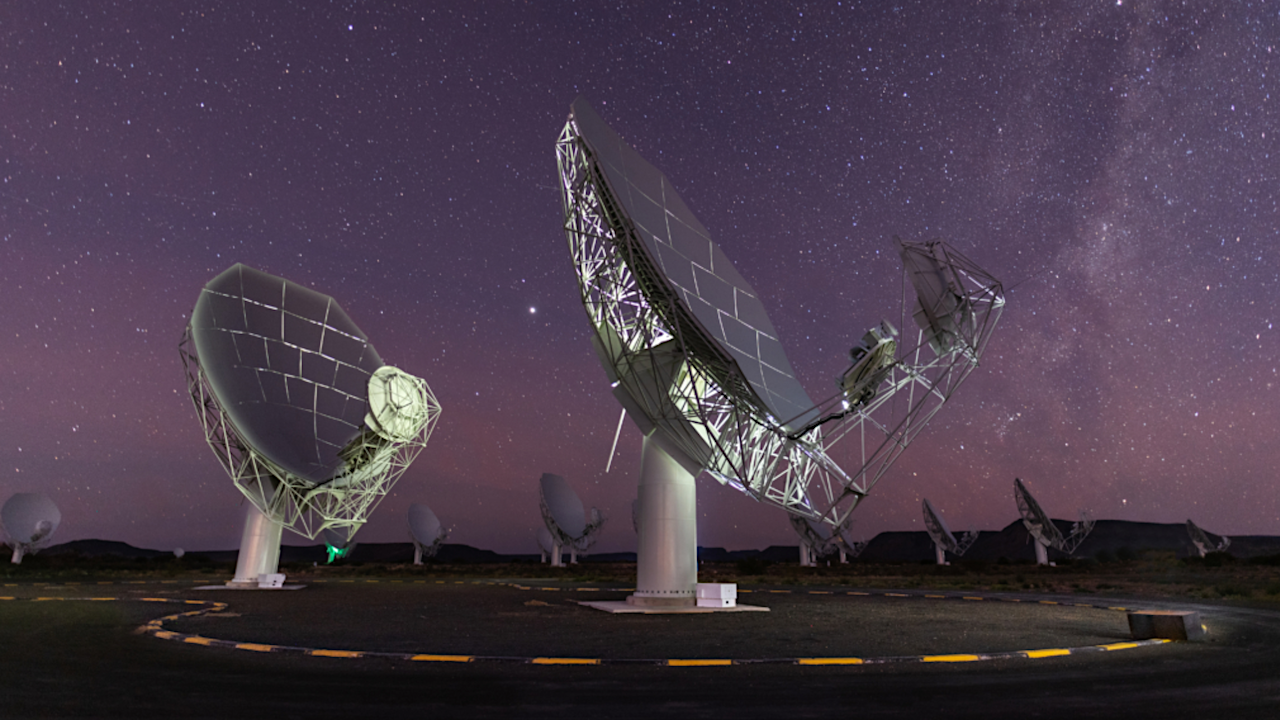
South Africa’s MeerKAT telescope. Credit: South African Radio Astronomy Observatory (SARAO). Since its discovery on 1 July 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), the object known as
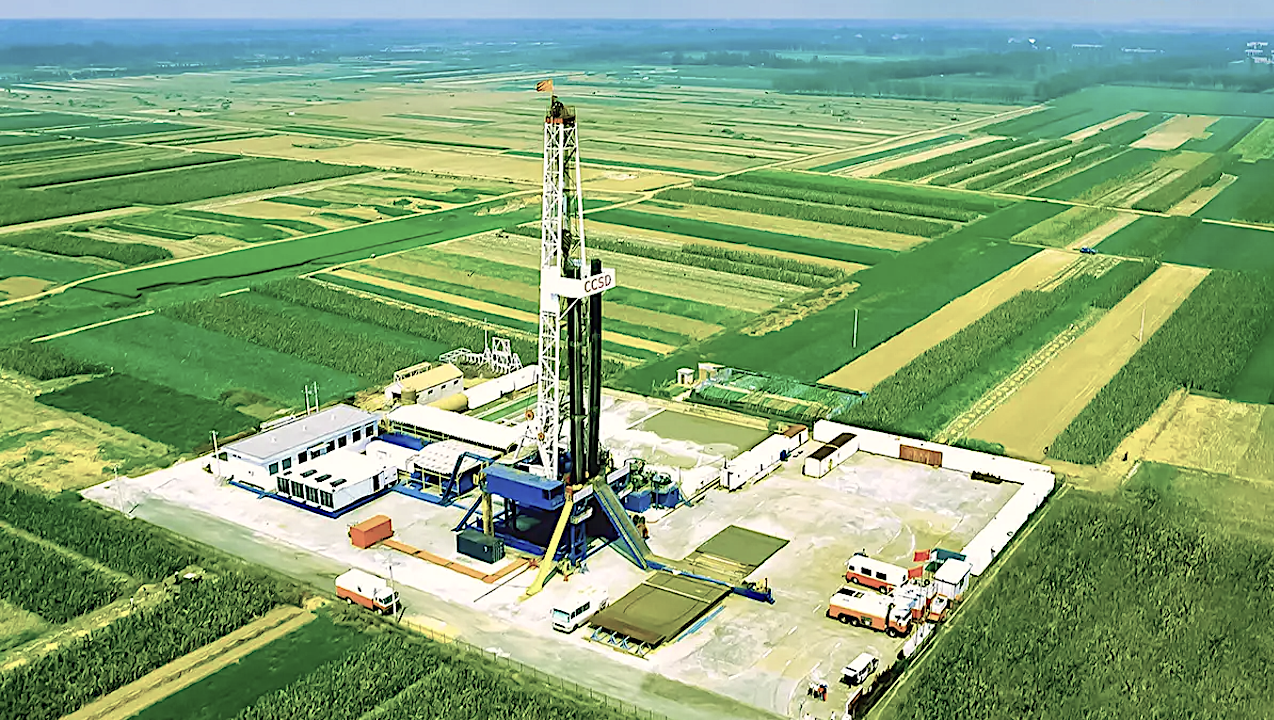
Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling project Facility — CCSD It is generally accepted that there is a vast, well-populated biosphere in the subsurface, but the depth limit of the terrestrial biosphere
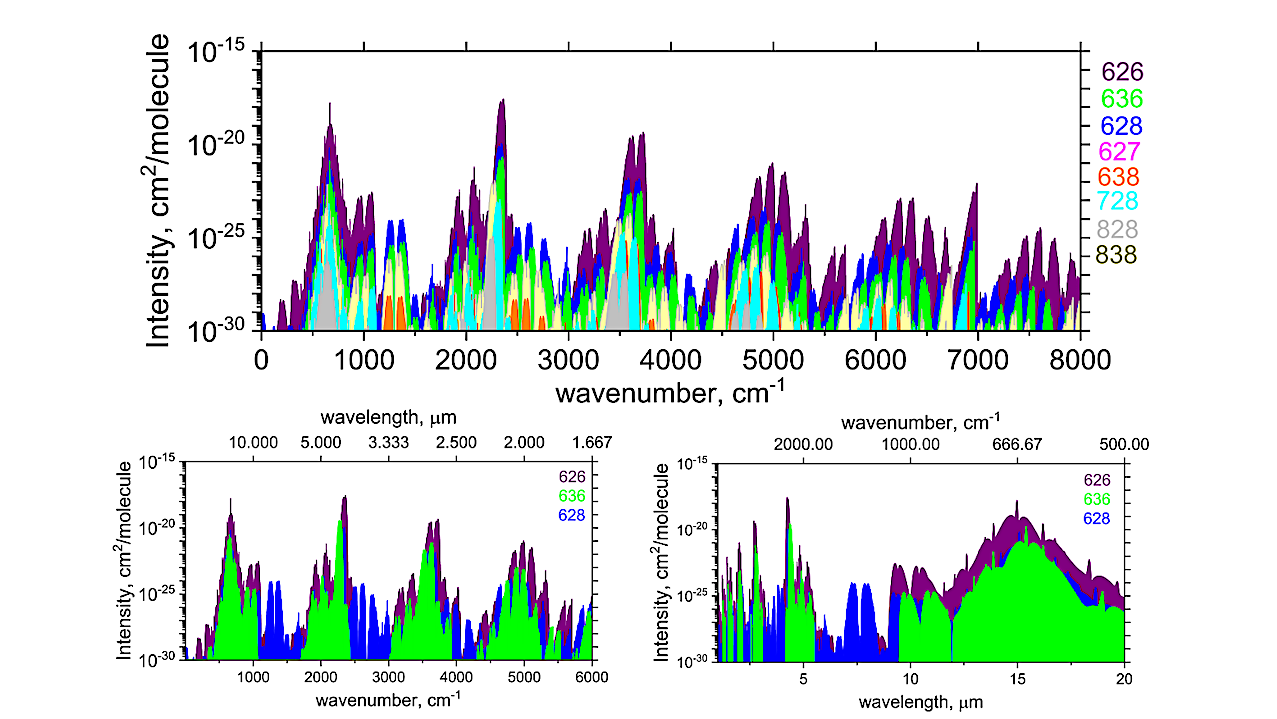
Spectra of selected CO2 isotopologues at T = 296 K, scaled by terrestrial isotopic abundances. In addition to 12C16O2, only 13C16O2 and 16O12C18O produce detectable IR features. — astro-ph.EP Extensive
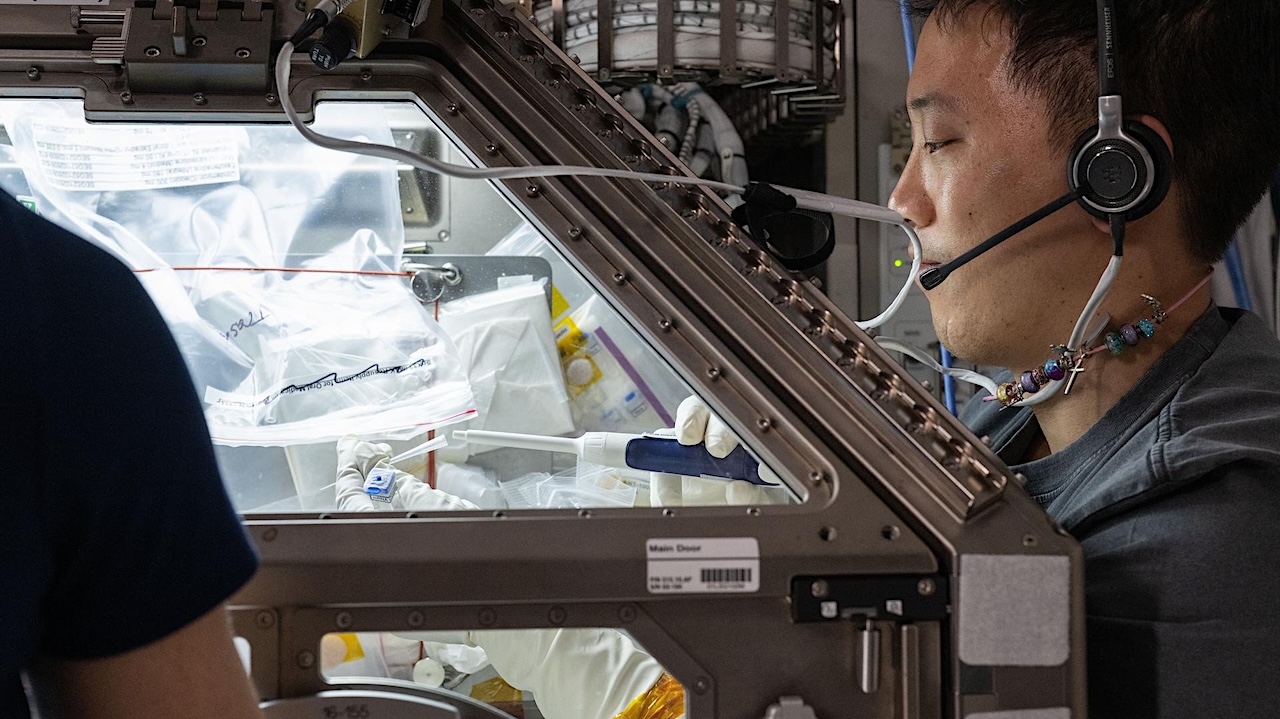
NASA ID: iss073e0025618 iss073e0025618 (May 8, 2025) larger image — NASA Working in the space station’s Microgravity Science Glovebox, NASA astronaut Jonny Kim mixes proteins with Janus base nanomaterials, small
Compilation of available Venus temperature profiles above 80 km both from spacecrafts, ground based telescopes and retrieved from CO non-LTE emissions observed by VIRTIS/VEx versus dayside (7-17 LT; LEFT) and
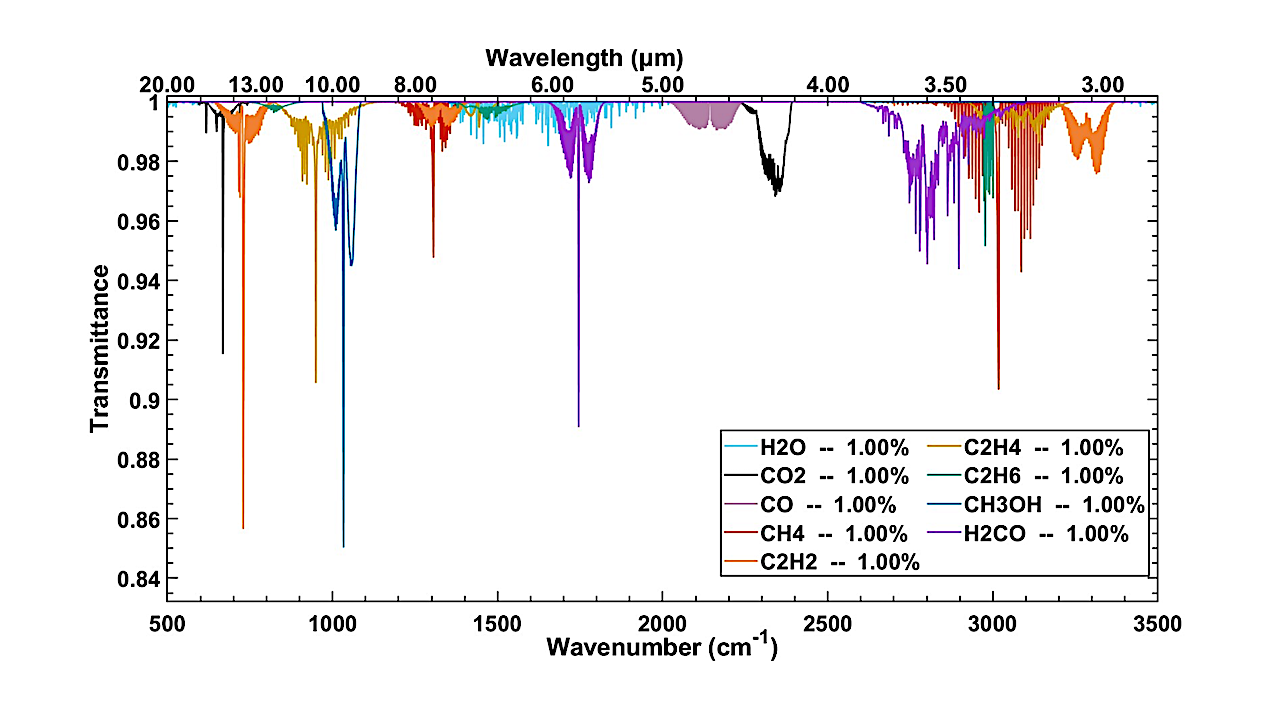
InfraRed features calculated from the HITRAN database for molecules with up to 2 carbon atoms studied in this study, with a fixed composition of 1% for each of them in
Three illustrations of what HWO may look like. From right to left, these are Engineering Architecture Concepts (EACs) 1, 2, and 3. Baffles to protect the mirror and reduce stray
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly