Exploring Tatooine — ESA ESAC, Madrid, Spain10-12 December 2025 This event aims to bring together experts in the field to discuss the latest advancements, share insights, and foster collaborations with
Astrobiology80- Page
The abstract in PubMed or at the publisher’s site is linked when available and will open in a new window. Ferraro S, Sengupta S, Shaw J, Dave A, Cheli M,
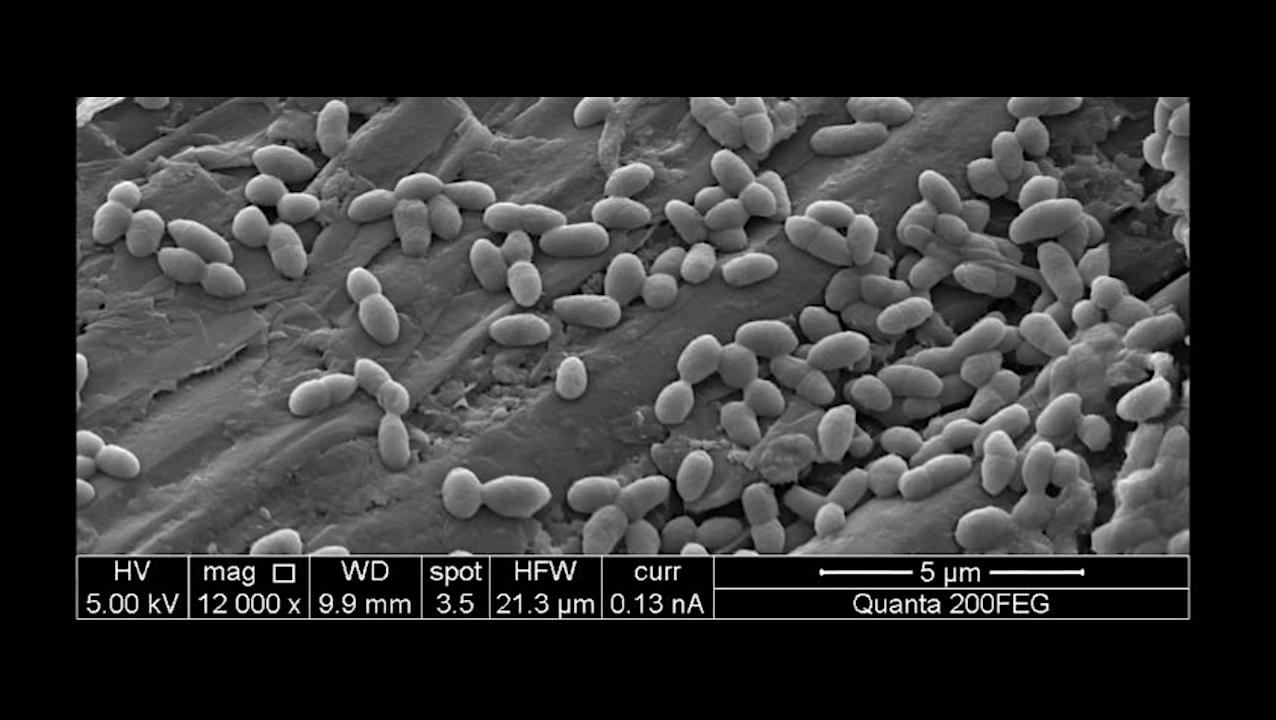
Desulfuromonas acetexigens on a metal electrod surface. Credits: KAUST. Microbes are masters of survival, evolving ingenious strategies to capture energy from their surroundings. For decades, scientists believed that only a
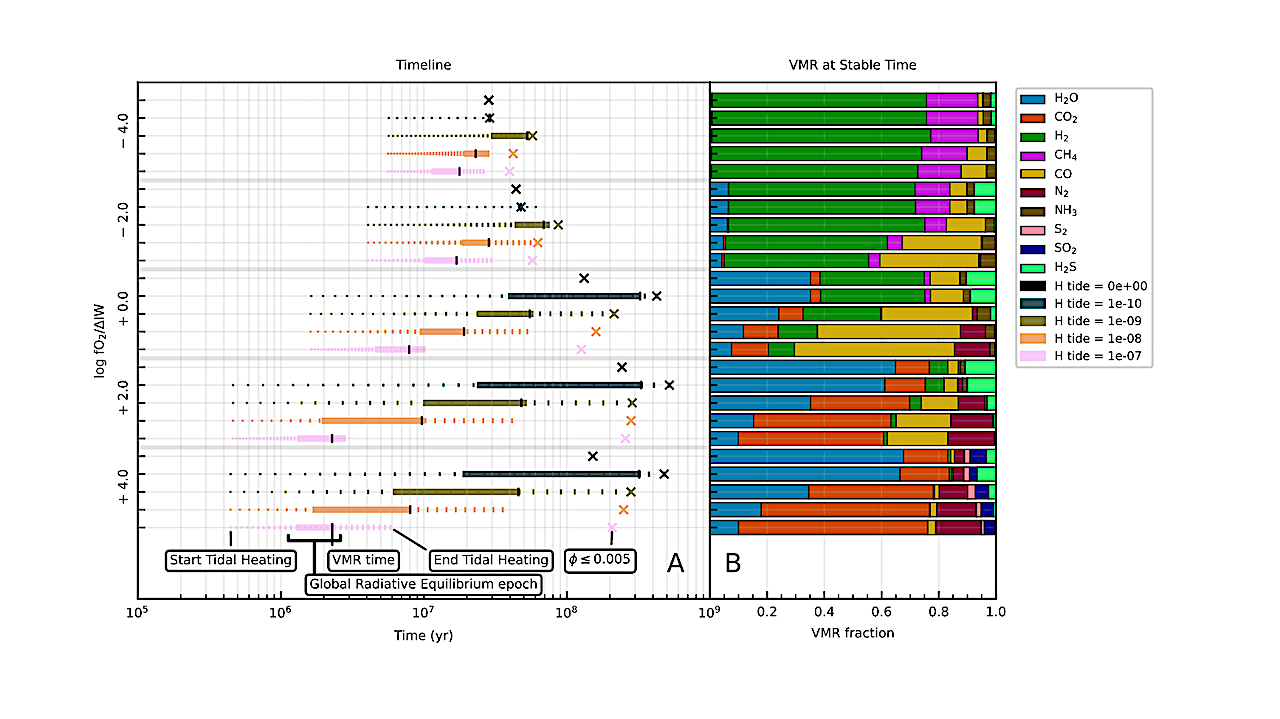
Evolution of nominal-composition cases across the full range of fO2 and tidal power densities simulated (see Section 2.3). Panel A (left): stages in planet’s lifetime after model initialization. Dotted lines
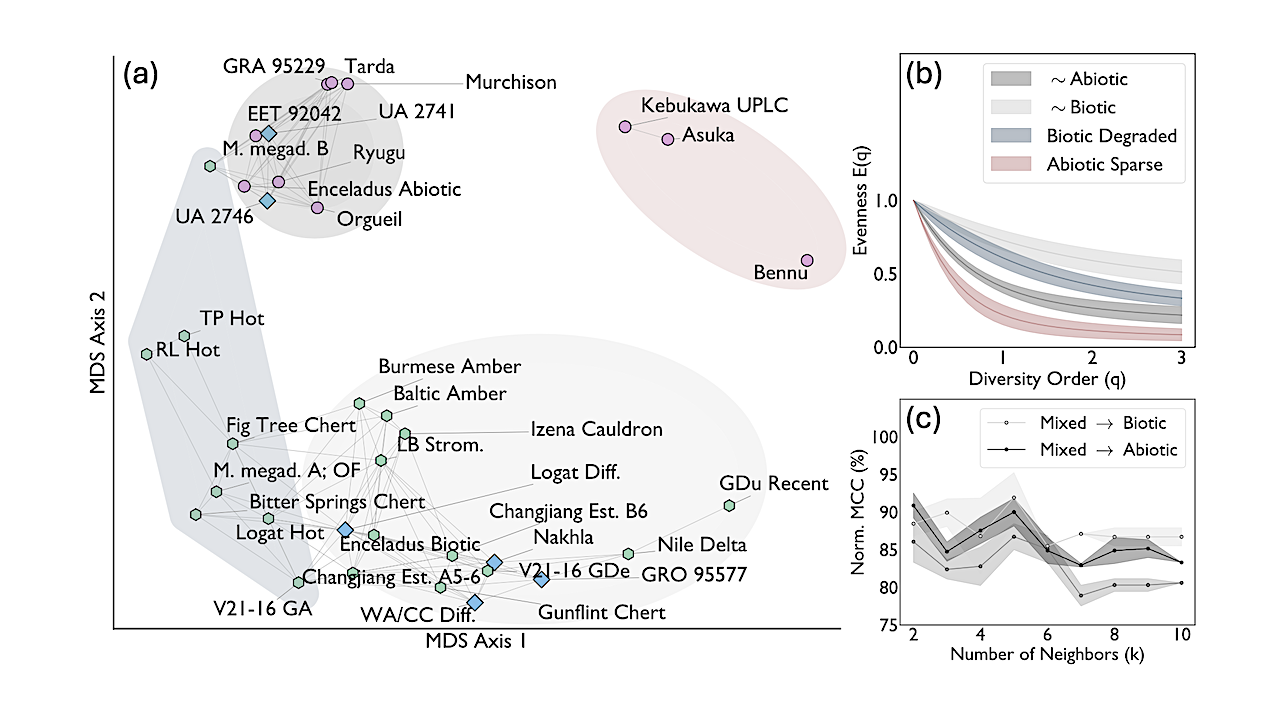
Dissimilarity analysis of evenness curves of amino acid assemblages. (a): Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) projection of dissimilarities between evenness curves, E(q). Points represent samples; distances between samples grow with dissimilarity. Edges
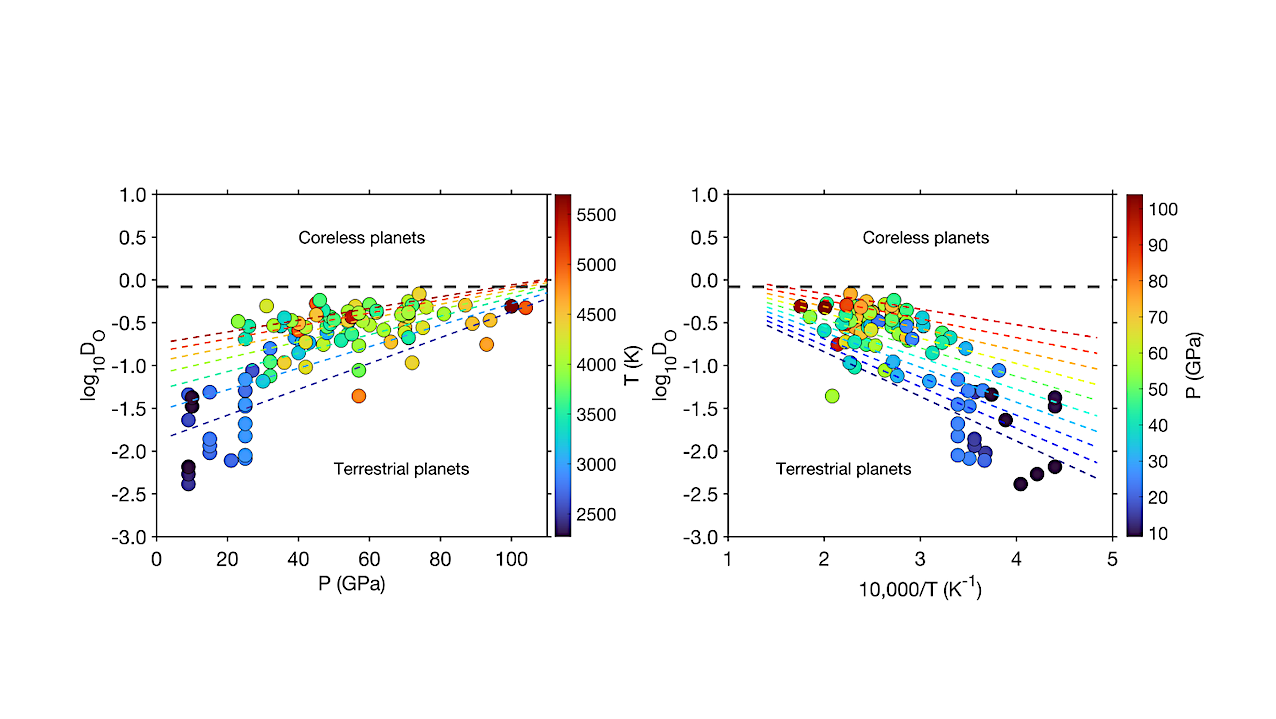
TRAPPIST-1 Status Report astro-ph.EP November 4, 2025 Filed under astro-ph.EP, astrogeology, exoplanet, M-dwarf, TRAPPIST-1, TRAPPIST-1 b, TRAPPIST-1 c, TRAPPIST-1 d, TRAPPIST-1 e, TRAPPIST-1 f, TRAPPIST-1 g Core–mantle partition coefficient of
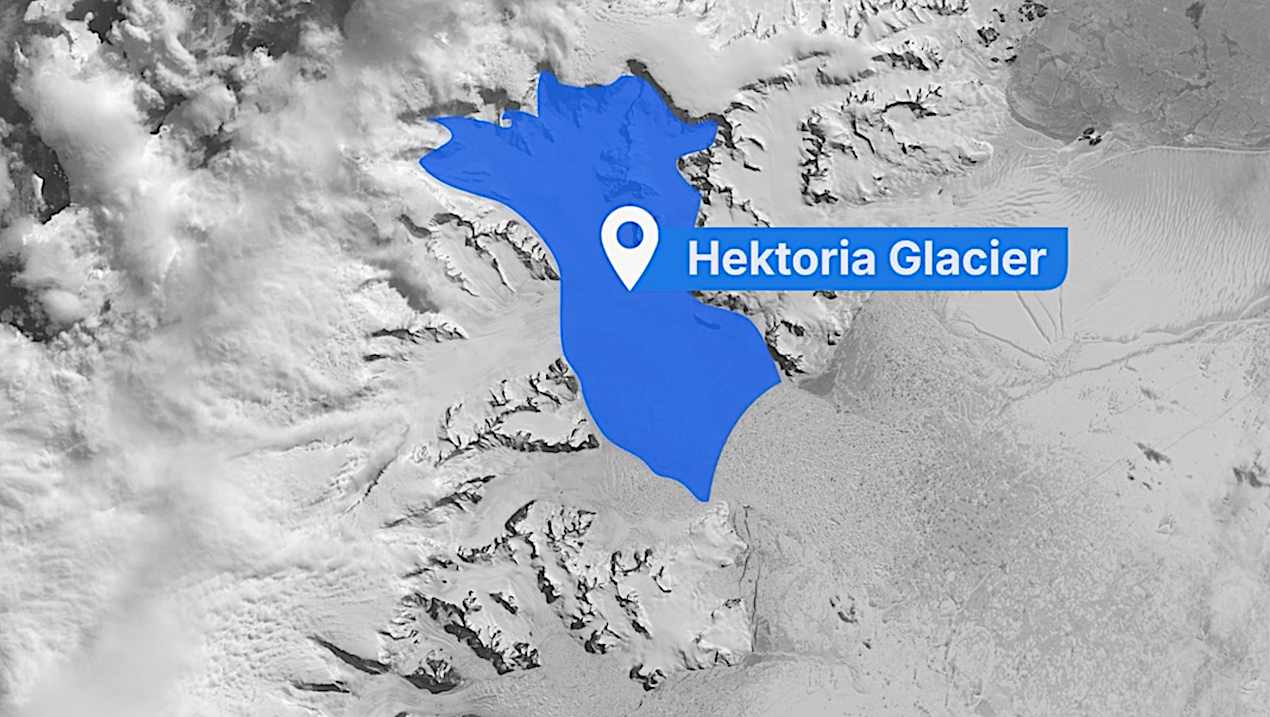
Hektoria Glacier on Antarctica’s Eastern Peninsula experienced the fastest retreat recorded in modern history—in just two months, nearly 50 percent of the glacier disintegrated. This video illustrates how and why
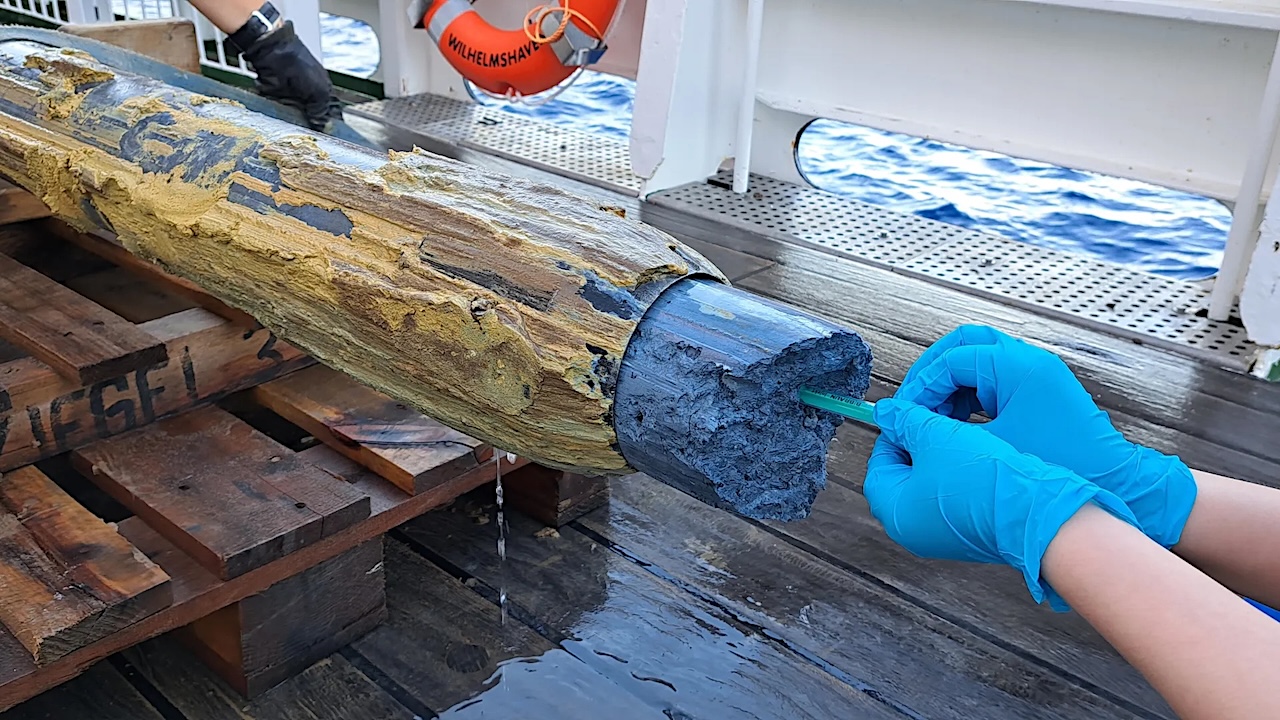
Blue serpentinite mud from a newly discovered mud volcano in a gravity core. The samples have been studied by a team in order to decipher the survival strategies of microorganisms.
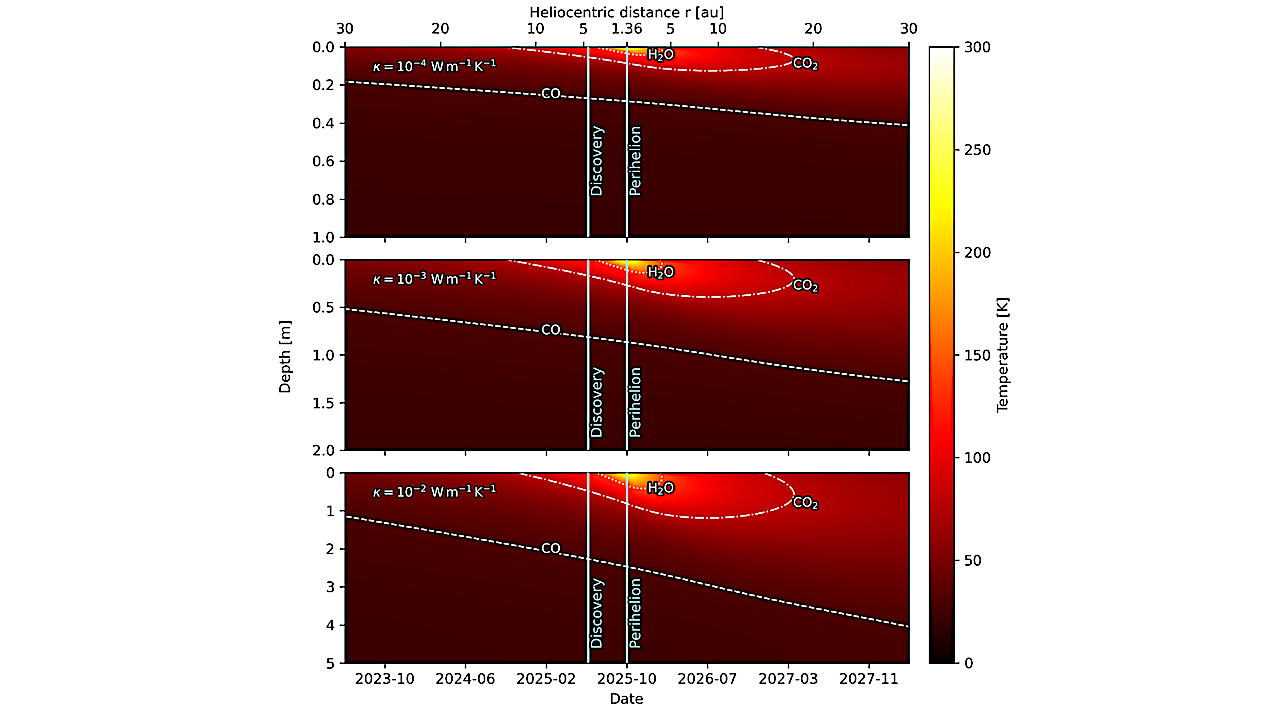
The temperature versus depth and time for 𝜅 = 10−4 W m−1 K−1 , 10−3 W m−1 K−1, and 10−2 W m−1 K−1 (top, middle, and bottom panels). The sublimation
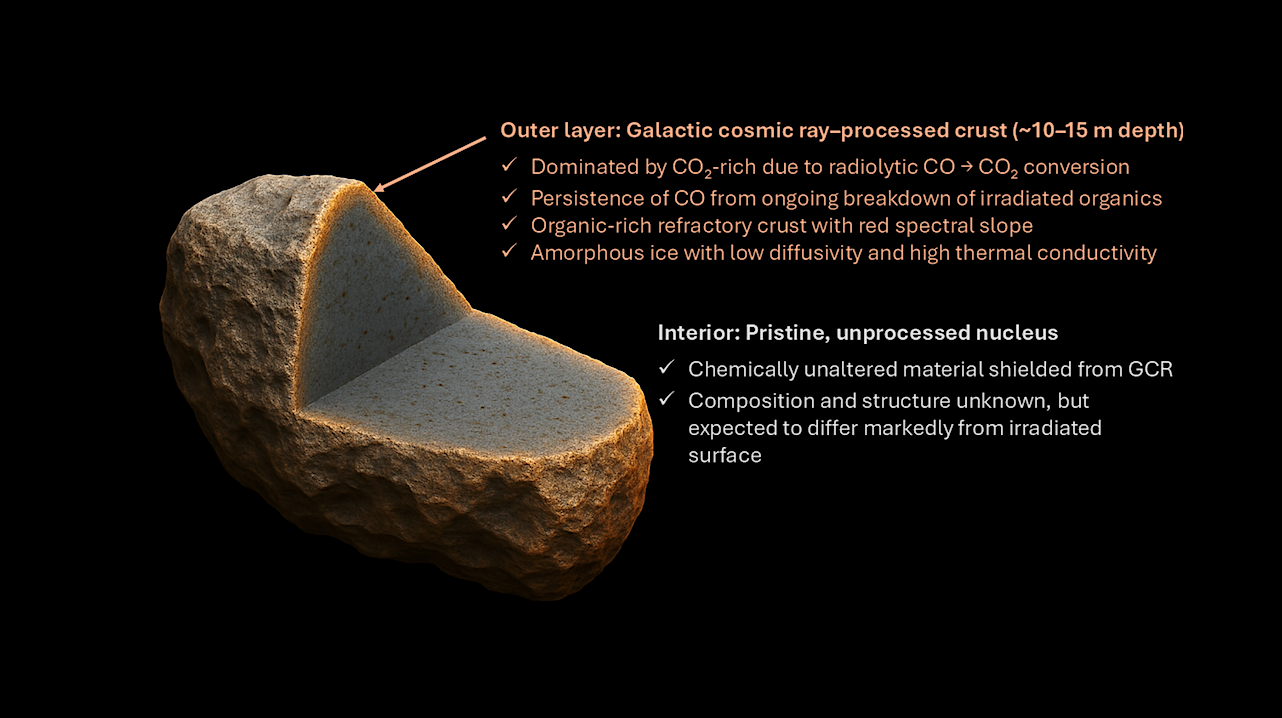
Schematic illustration of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS showing the expected stratigraphy of an irradiated nucleus. Galactic cosmic ray irradiation over several Gyr alters the outer ∼15–20 m, producing a CO2-rich crust
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors