Now Reading: CO Detected in CI Tau b: Hot Start Implied by Planet Mass and MK
-
01
CO Detected in CI Tau b: Hot Start Implied by Planet Mass and MK
CO Detected in CI Tau b: Hot Start Implied by Planet Mass and MK
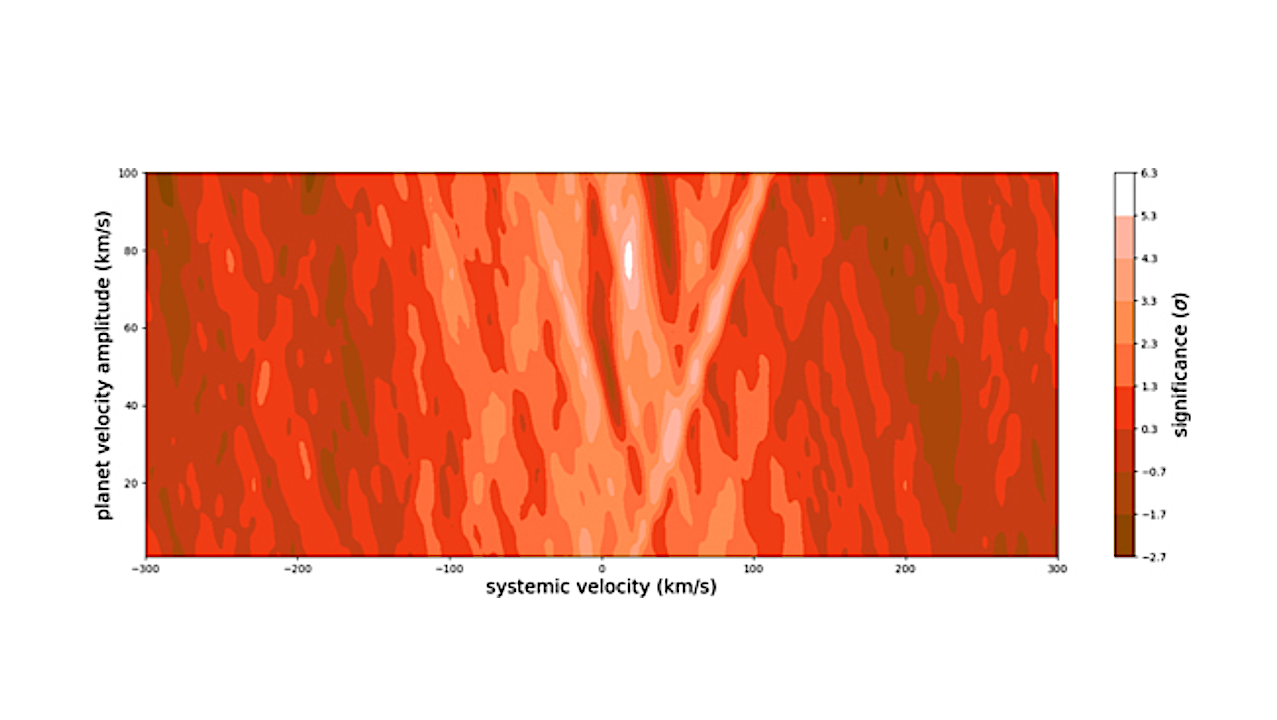

Cross-correlation function significance plotted as a function of planet velocity amplitude and systemic radial velocity. The significance is the number of standard deviations above the mean for those parameters, peaking at 5.7σ. — The Astrophysical Journal
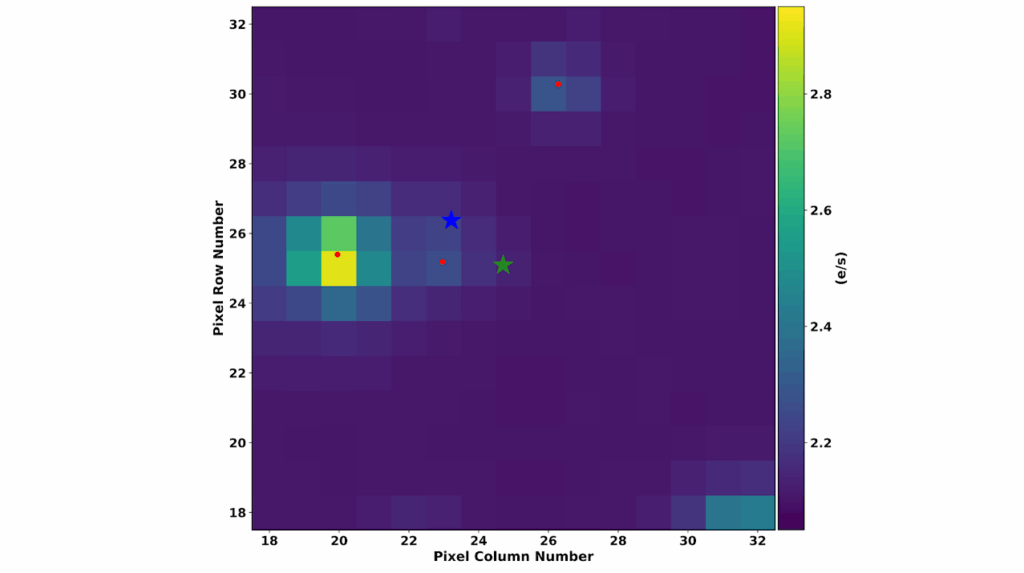
We acquired high-resolution infrared spectra of CI Tau, the host star of one of the few young planet candidates amenable to direct spectroscopic detection.
We confirm the planet’s existence with a direct detection of CO in the planet’s atmosphere. We also calculate a mass of 11.6 MJ based on the amplitude of its radial velocity variations.
We estimate its flux contrast with its host star to get an absolute magnitude estimate for the planet of 8.17 in the K-band. This magnitude implies the planet formed via a “hot start” formation mechanism.
This makes CI Tau b the youngest confirmed exoplanet as well as the first exoplanet around a T Tauri star with a directly determined, model-independent dynamical mass.
CO Detected in CI Tau b: Hot Start Implied by Planet Mass and MK, The Astrophysical Journal (open access)
Astrobiology, Astrochemistry,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly