Now Reading: Curiosity Blog, Sols 4604-4606: Taking a Deep Breath of Martian Air
-
01
Curiosity Blog, Sols 4604-4606: Taking a Deep Breath of Martian Air
Curiosity Blog, Sols 4604-4606: Taking a Deep Breath of Martian Air


Written by Lauren Edgar, Planetary Geologist at USGS Astrogeology Science Center
Earth planning date: Friday, July 18, 2025
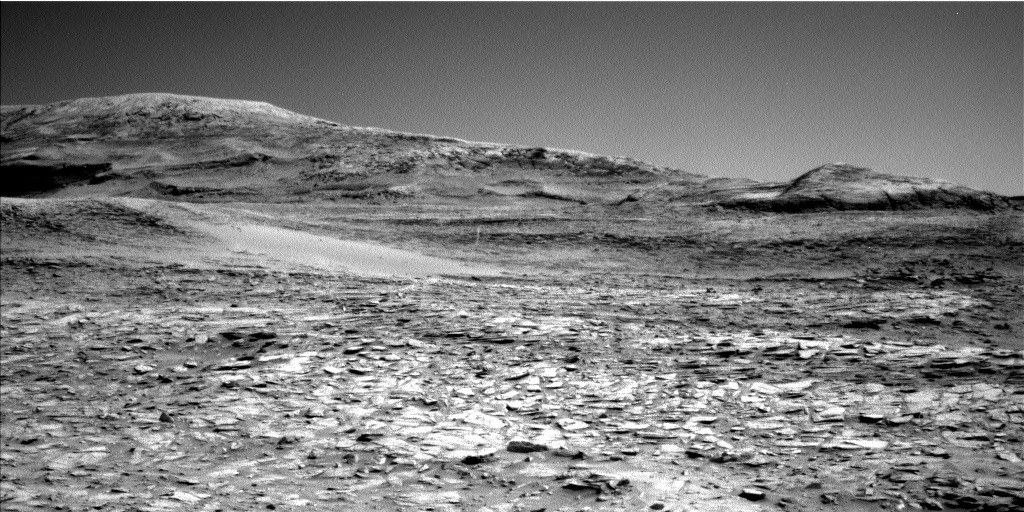
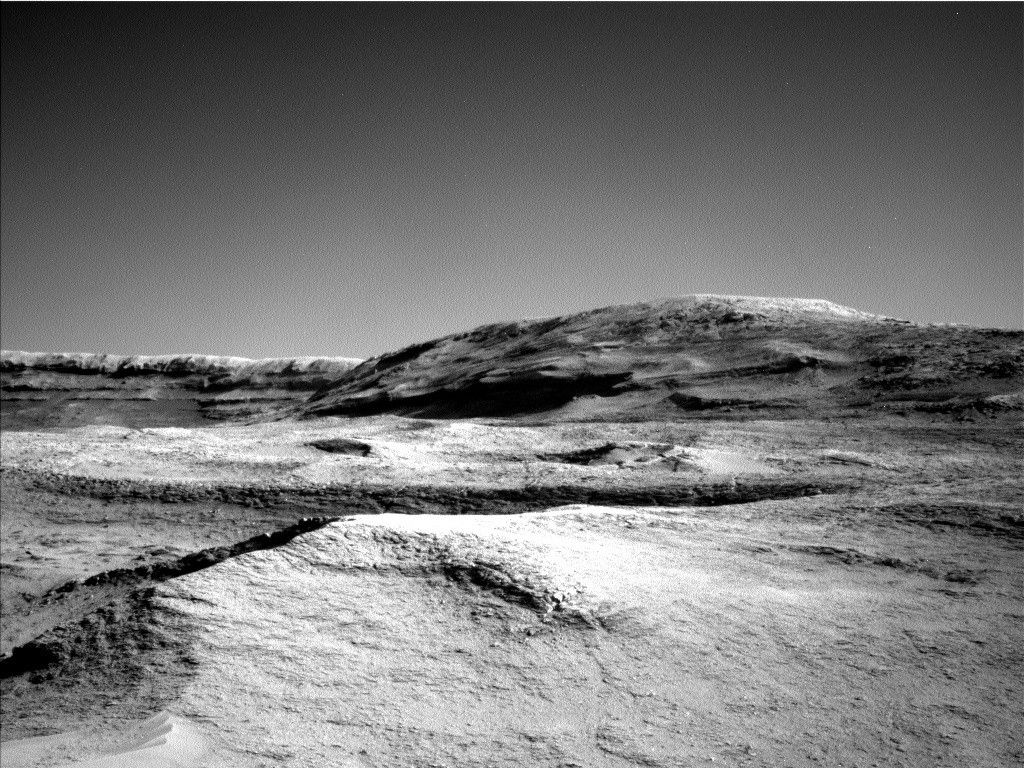
Curiosity has started to investigate the main exposure of the boxwork structures! What was once a distant target is now on our doorstep, and Curiosity is beginning to explore the ridges and hollows that make up this terrain, to better understand their chemistry, morphology, and sedimentary structures.
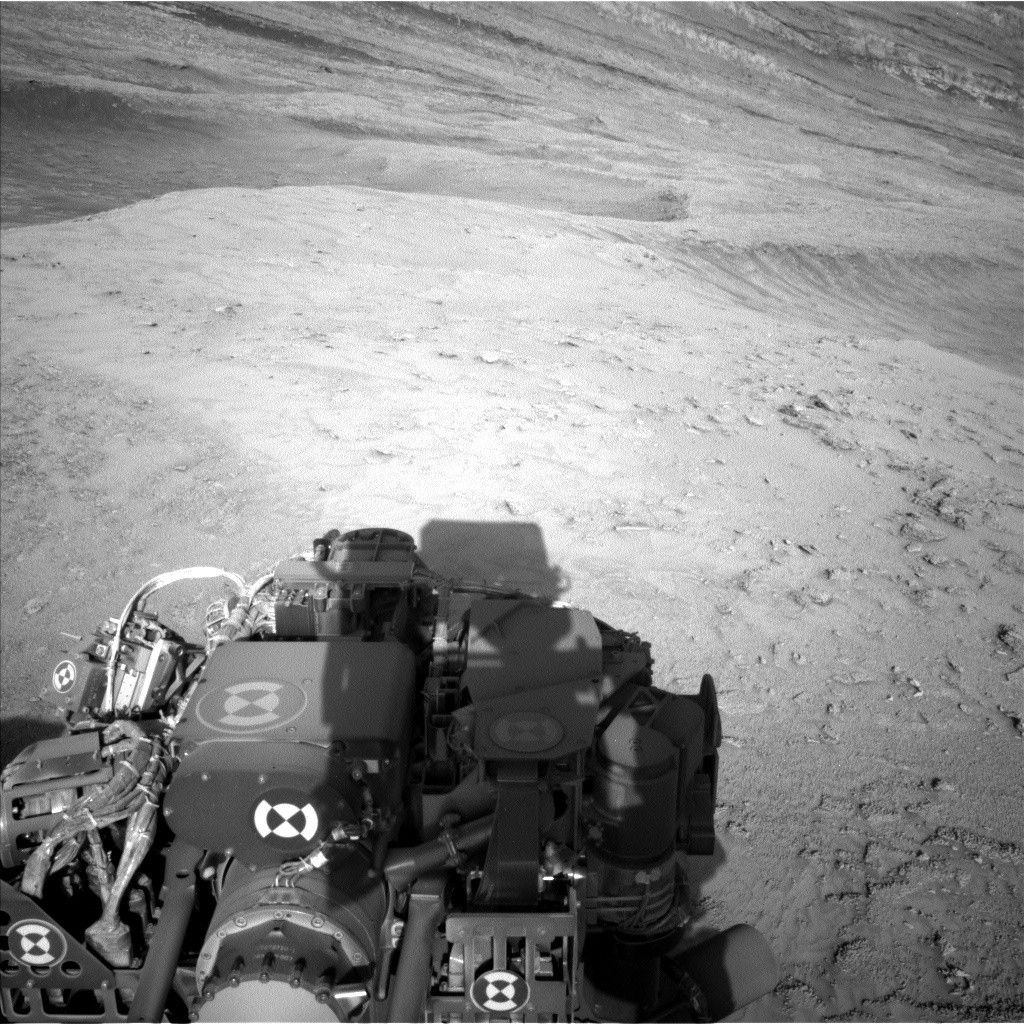
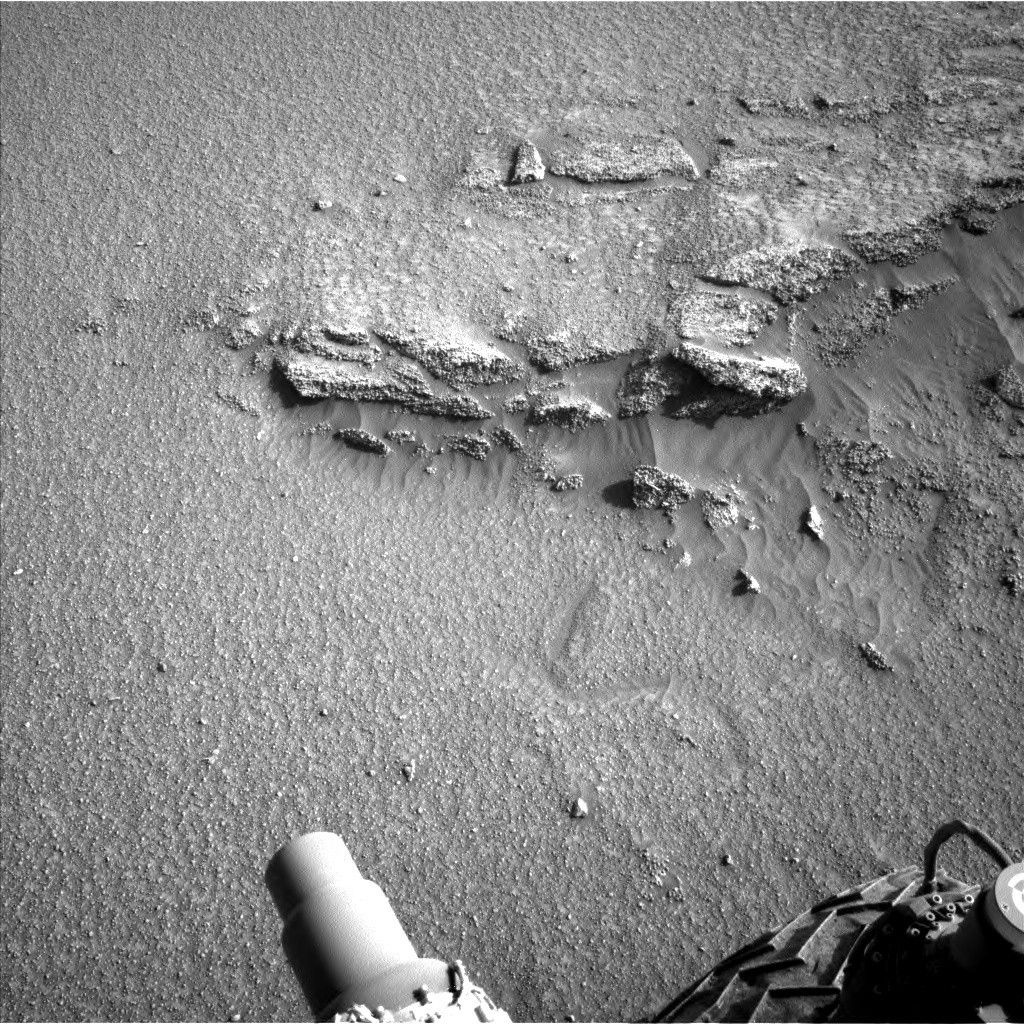
I was on shift as Long Term Planner during this three-sol weekend plan, and the team put together a very full set of activities to thoroughly investigate this site — from the sky to the sand. The plan starts with Navcam and Mastcam observations to assess the amount of dust in the atmosphere, followed by a large Mastcam mosaic to characterize the resistant ridge on which the rover is parked. ChemCam will also acquire a LIBS observation on a target named “Vicuna” to assess the chemistry of a well-exposed vein. The team chose this parking location to characterize the chemistry and textures of this topographic ridge (to compare with topographic lows), so the next part of the plan involves contact science using APXS and MAHLI to look at different parts of the nodular bedrock in our workspace, at targets named “Totoral” and “Sillar.” There’s also a MAHLI observation of the same vein that ChemCam targeted.
The second sol involves more Mastcam imaging to look at different parts of this prominent ridge, along with a ChemCam LIBS observation on top of the ridge, and a ChemCam RMI mosaic to document the sedimentary structures in a distant boxwork feature. Navcam will also be used to look for dust devils. Then Curiosity will take a short drive of about 5 meters (about 16 feet) to explore the adjacent hollow (seen as the low point in the foreground of the above Navcam image). After the drive we’ll take more images for context, and to prepare for targeting in Monday’s plan.
After all of this work it’s time to pause and take a deep breath… of Martian atmosphere. The weekend plan involves an exciting campaign to look for variations in atmospheric chemistry between night and day. So Curiosity will take an overnight APXS atmospheric observation at the same time that two instruments within SAM assess its chemical and isotopic abundance.
On the third sol Curiosity will acquire a ChemCam passive sky observation, leading to a great set of atmospheric data. These measurements will be compared to even more atmospheric activities in Monday’s plan to get the full picture. As you can imagine, this plan requires a lot of power, but it’s worth it for all of the exciting science that we can accomplish here.
The road ahead has many highs and lows (literally), but I can’t wait to see what Curiosity will accomplish. The distant buttes remind us that there’s so much more to explore, and I look forward to continuing to see where Curiosity will take us.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly