Now Reading: Earth-mass Planets With He Atmospheres In The Habitable Zone Of Sun-like Stars
-
01
Earth-mass Planets With He Atmospheres In The Habitable Zone Of Sun-like Stars
Earth-mass Planets With He Atmospheres In The Habitable Zone Of Sun-like Stars
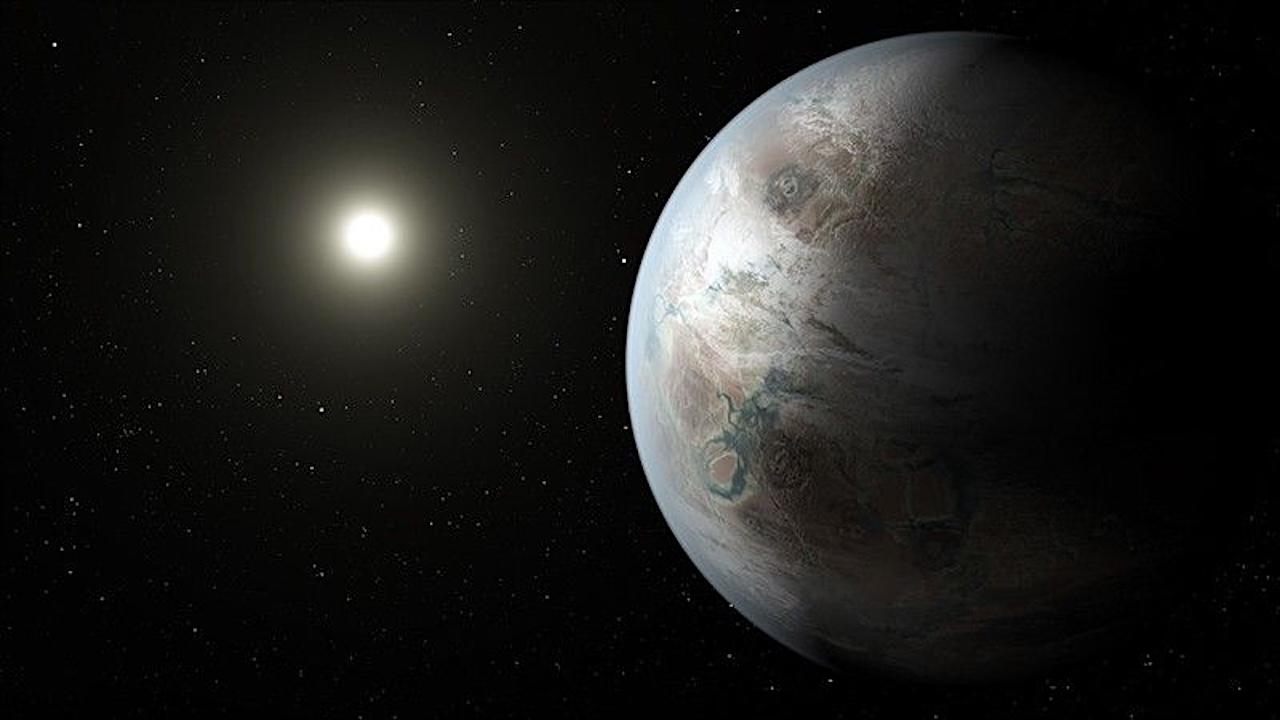


Earth-mass planet orbiting a sun-like star — NASA
The discovery of many low-mass exoplanets, including several planets within the habitable zone of their host stars, has led to the question of which kind of atmosphere surrounds them.
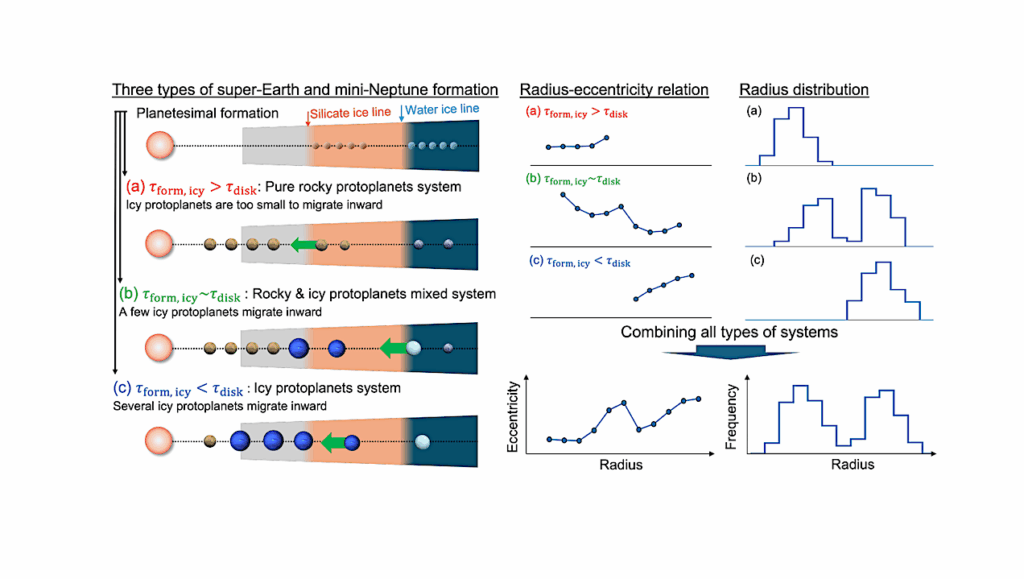
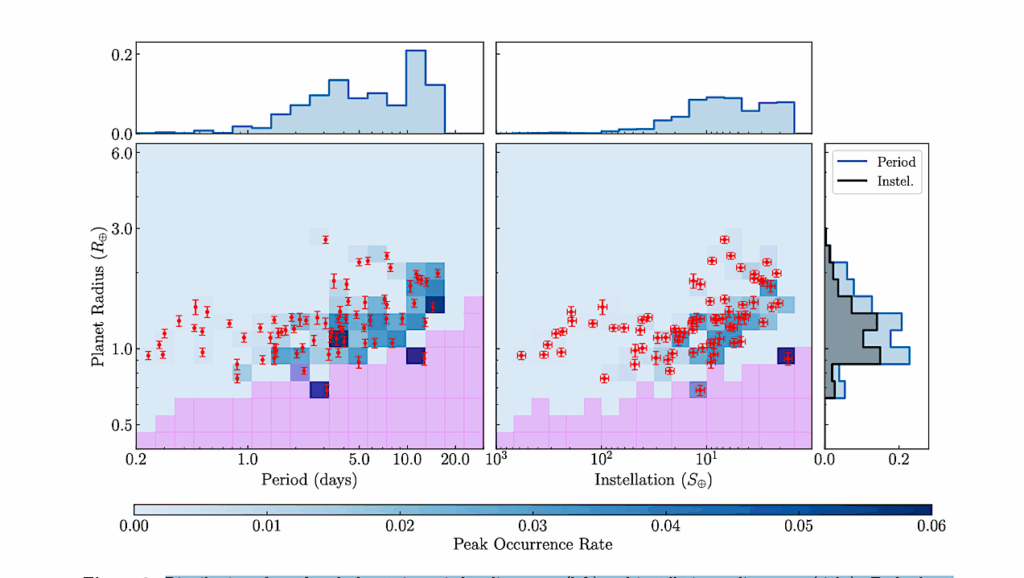
Recent exoplanet detections have revealed the existence of a large population of low-mass planets (<3 M⊕) with H2-dominated atmospheres that must have been accreted from the protoplanetary disk.
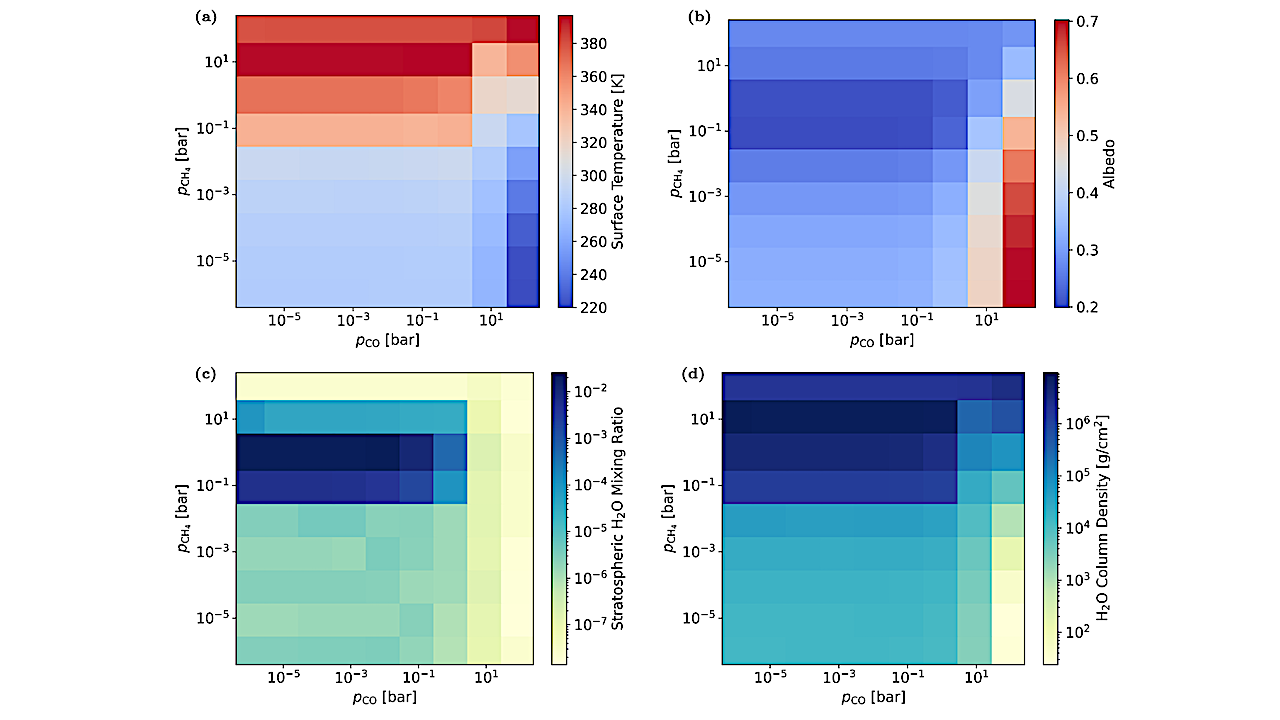
As the gas disk usually has an ~10% fraction of helium, we model the possible enrichment of the primordial He fraction in the atmosphere of planets with mass between 0.75 M⊕ and 3.0 M⊕ that orbit in the classical habitable zone of Sun-like stars.
Depending on the mass accreted by the planet during the gas disk phase and the stellar high-energy flux between ~10 and 120 nm, we find that Earth-like planets with masses between ~0.95 M⊕ and 1.25 M⊕ inside the habitable zone of Sun-like stars can end up with He-dominated primordial atmospheres.
This finding has important implications for the evolution of Earth-like habitats, as these thick helium-enriched primordial atmospheres can inhibit the habitability of these planets. The upcoming generation of giant telescopes, such as the Extremely Large Telescope, may enable us to observe and explore these atmospheres.
Earth-mass planets with He atmospheres in the habitable zone of Sun-like stars, Nature Astronomy via PubMed
Astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly