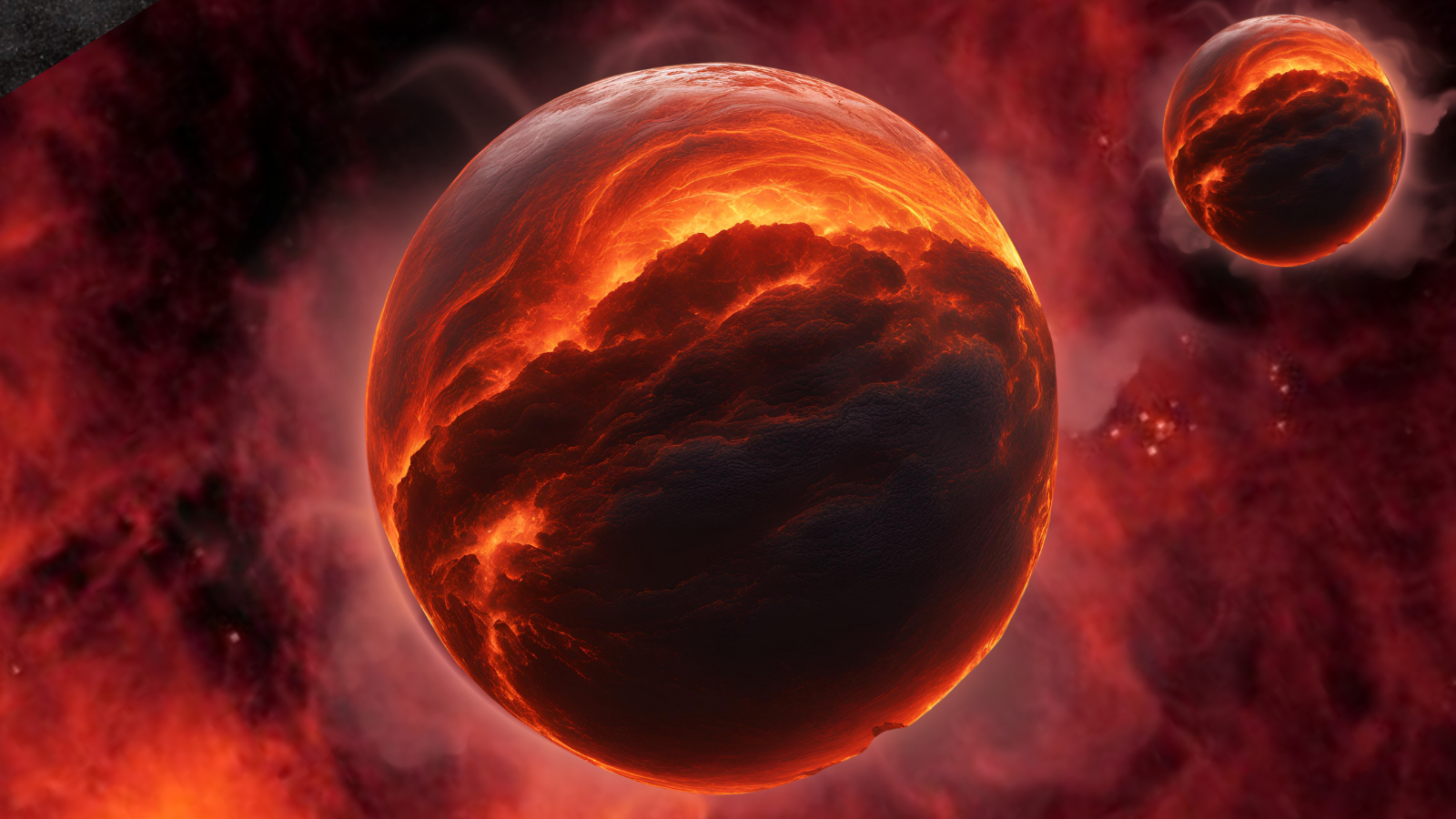
“Dark dwarfs” may sound like a new race of Sauron-worshipping Middle-Earth dwellers, but it’s actually a new type of stellar body proposed to exist at the hearts of galaxies. The
Hot Posts387- Page
Marvel Studios’ “The Fantastic Four: First Steps” is basking in the golden light of enthusiastic anticipation ahead of its July 25, 2025 release date. With Galactus positioned as the sci-fi
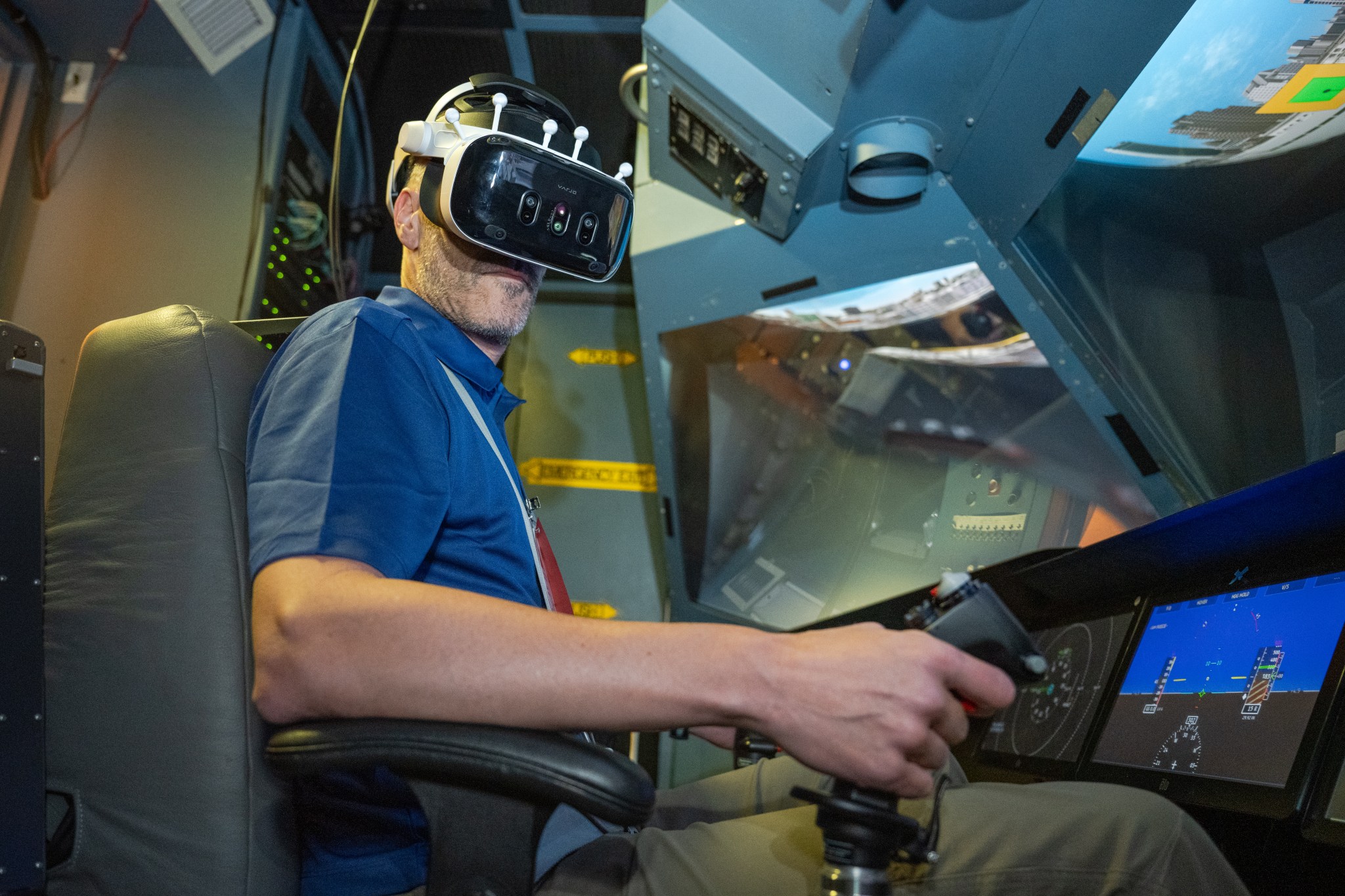
Damian Hischier of the National Test Pilot School in Mojave, California, takes part in testing of a virtual reality-infused pilot simulation in the Vertical Motion Simulator (VMS) at NASA’s Ames
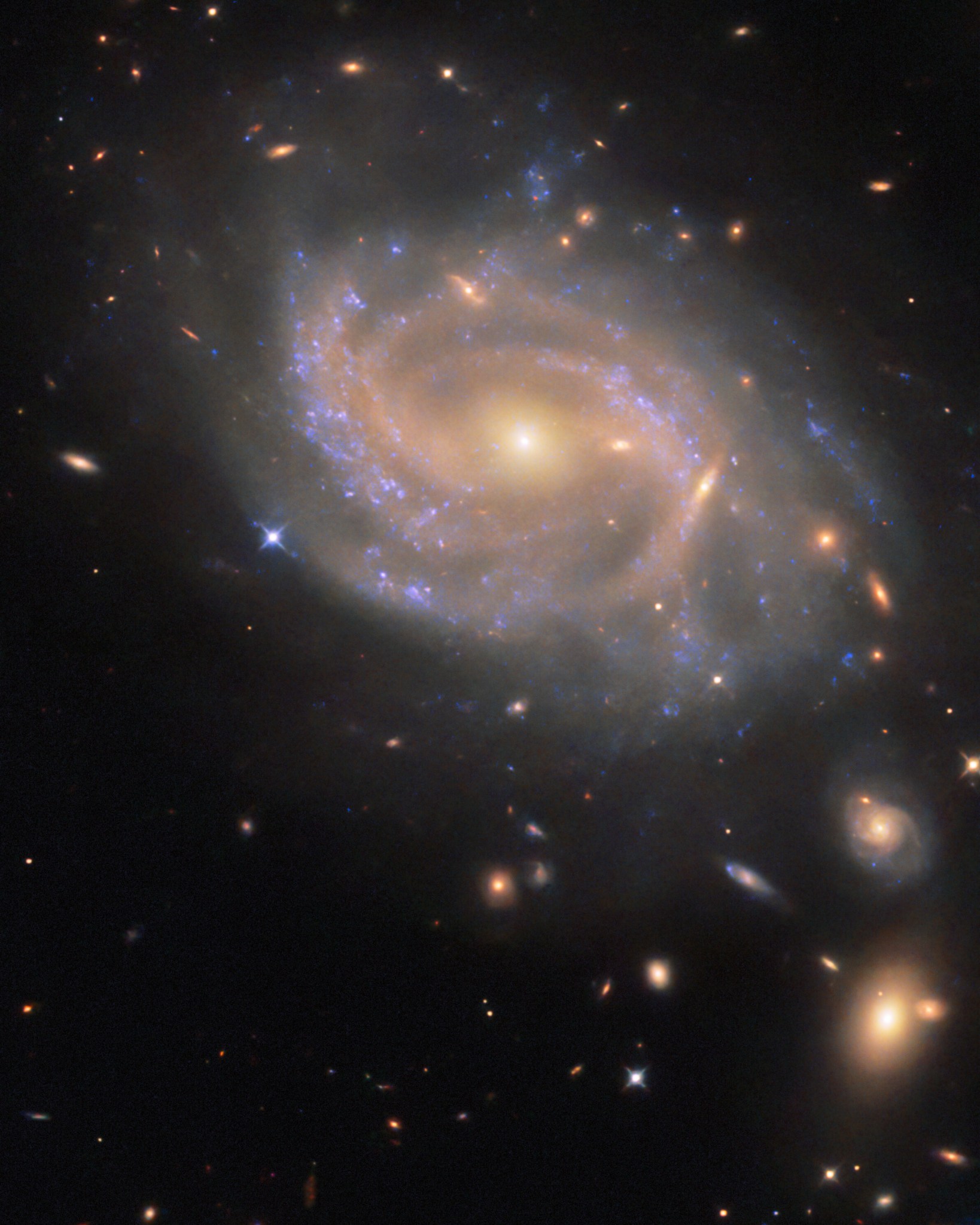
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the spiral galaxy NGC 3285B, a member of the Hydra I cluster of galaxies. ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. J. Foley (UC Santa Cruz)
Air sampling during a dust storm. Credit: Naama Lang-Yona How do living bacteria survive on the surface of dust particles carried by desert storms from the Sahara and Egypt to
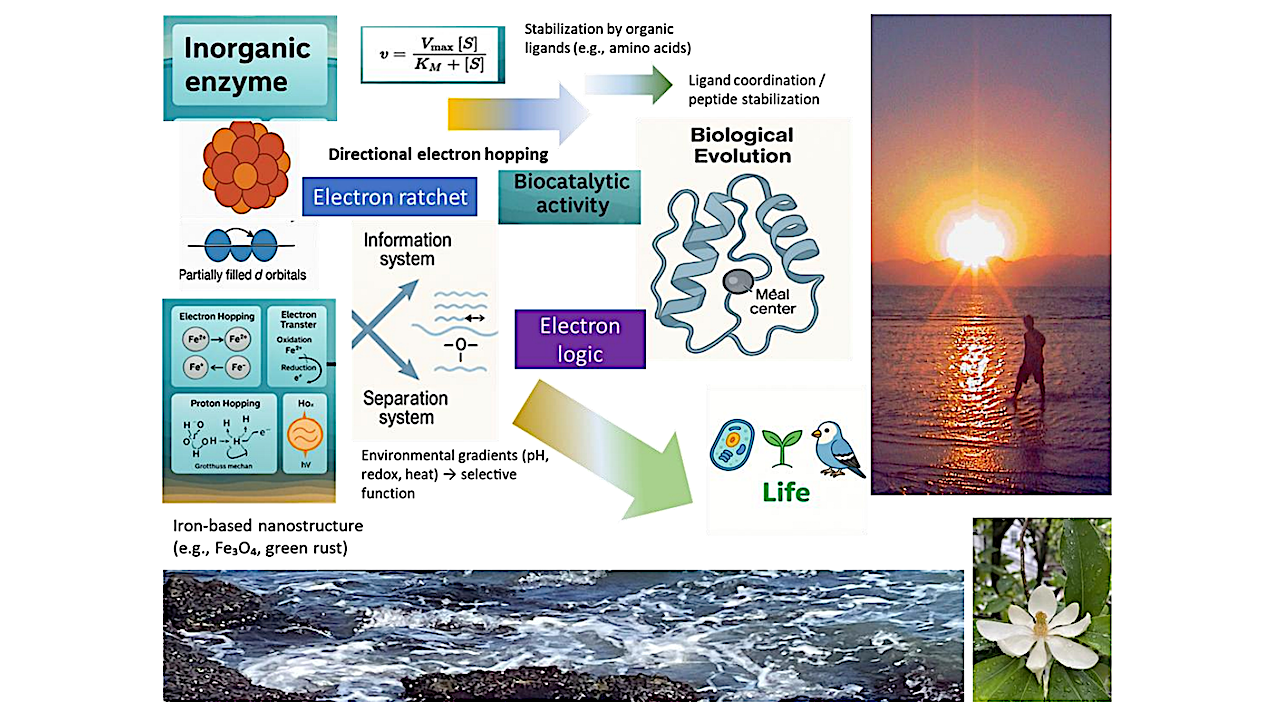
Graphical Abstract — chemrxiv.org We present a physicochemical framework for understanding the emergence of catalytic logic at the origin of life. In this view, early catalytic systems did not depend
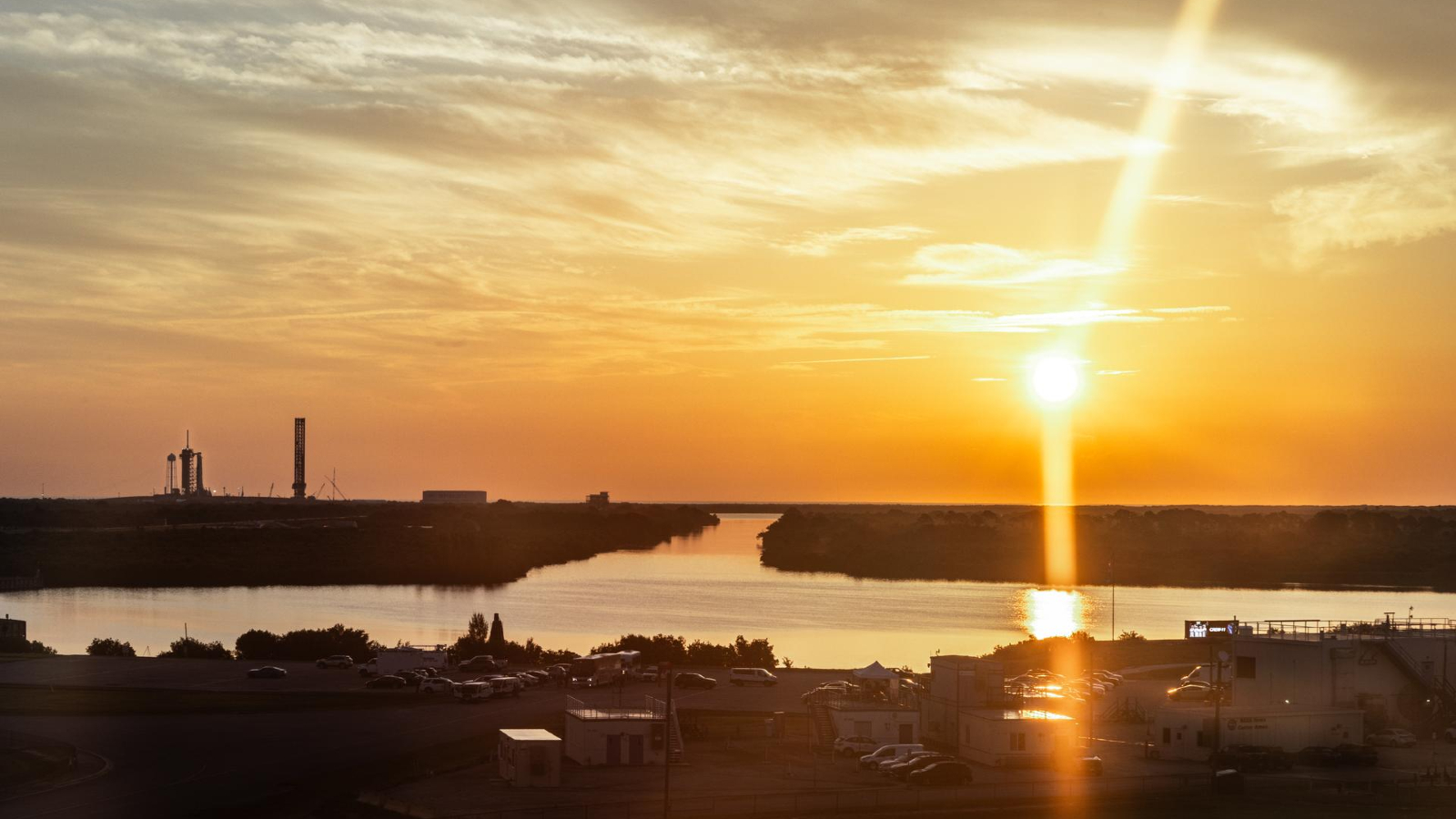
Crew-11 was the eleventh operational crewed mission that SpaceX has launched for NASA under the agency’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP), a partnership launched in the 2010s to return astronaut launches
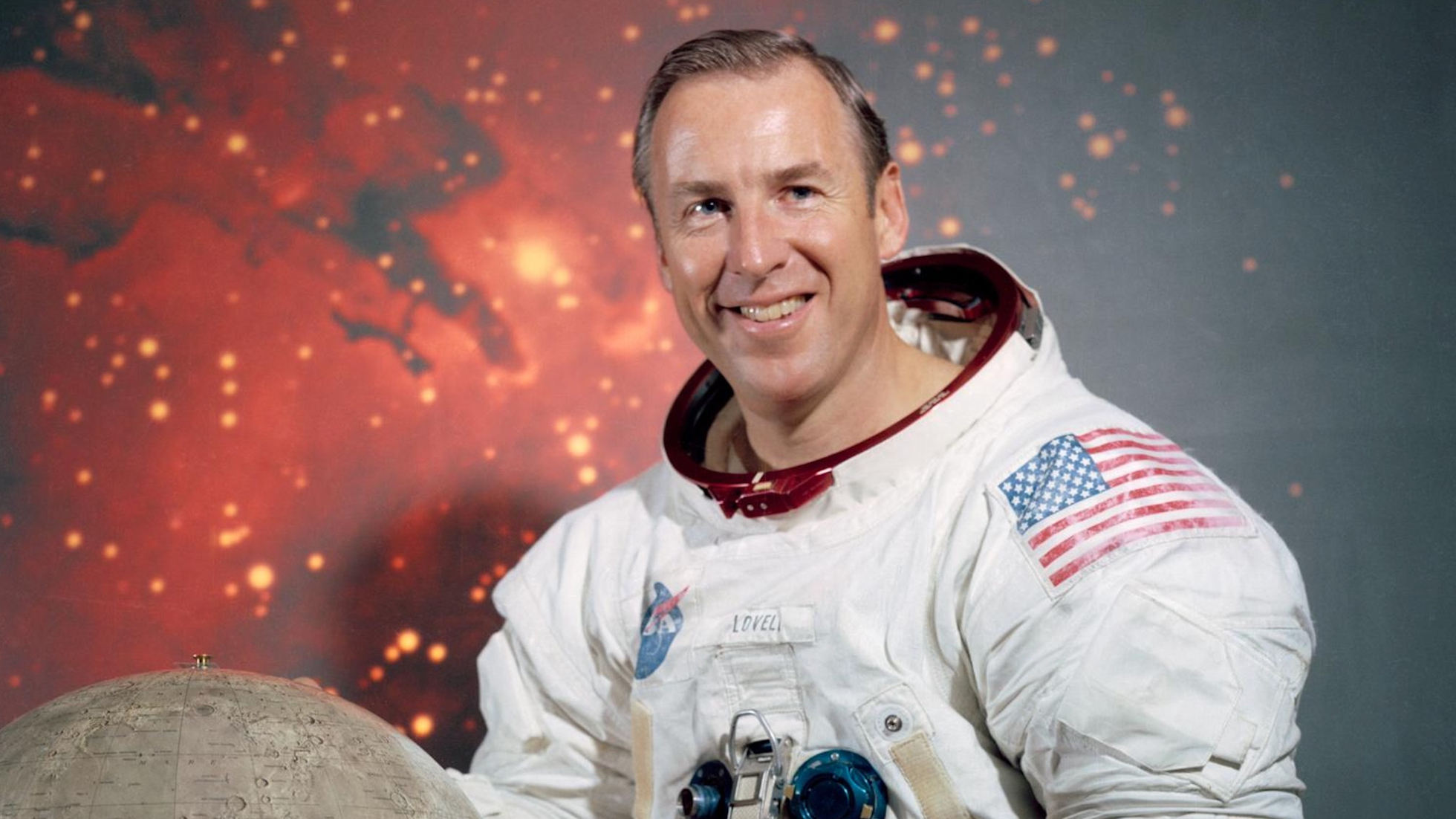
NASA astronaut Jim Lovell, who helped turn the near-disastrous Apollo 13 moon mission into an inspiring tale of ingenuity and survival, has died at the age of 97. Jim Lovell
Keith Cowing Explorers Club Fellow, ex-NASA Space Station Payload manager/space biologist, Away Teams, Journalist, Lapsed climber, Synaesthete, Na’Vi-Jedi-Freman-Buddhist-mix, ASL, Devon Island and Everest Base Camp veteran, (he/him) 🖖🏻 Follow on
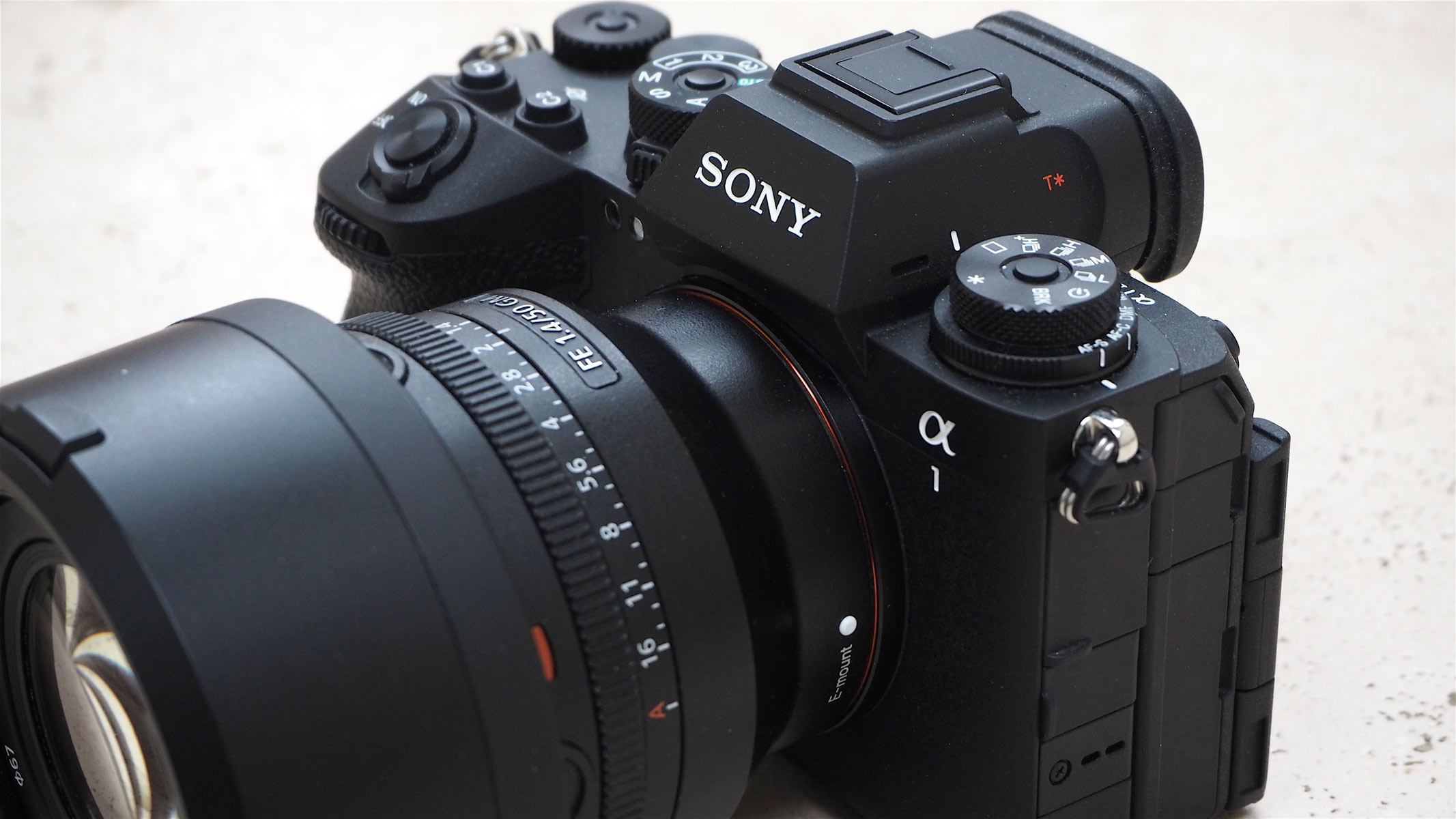
Sony A1 II: Key specs System: Sony Alpha E-mount mirrorless camera Sensor: 50.1 effective MP, full-frame CMOS ISO range: A core ISO 100-32,000; expandable to ISO 50-102,400 equivalent Burst shooting:
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
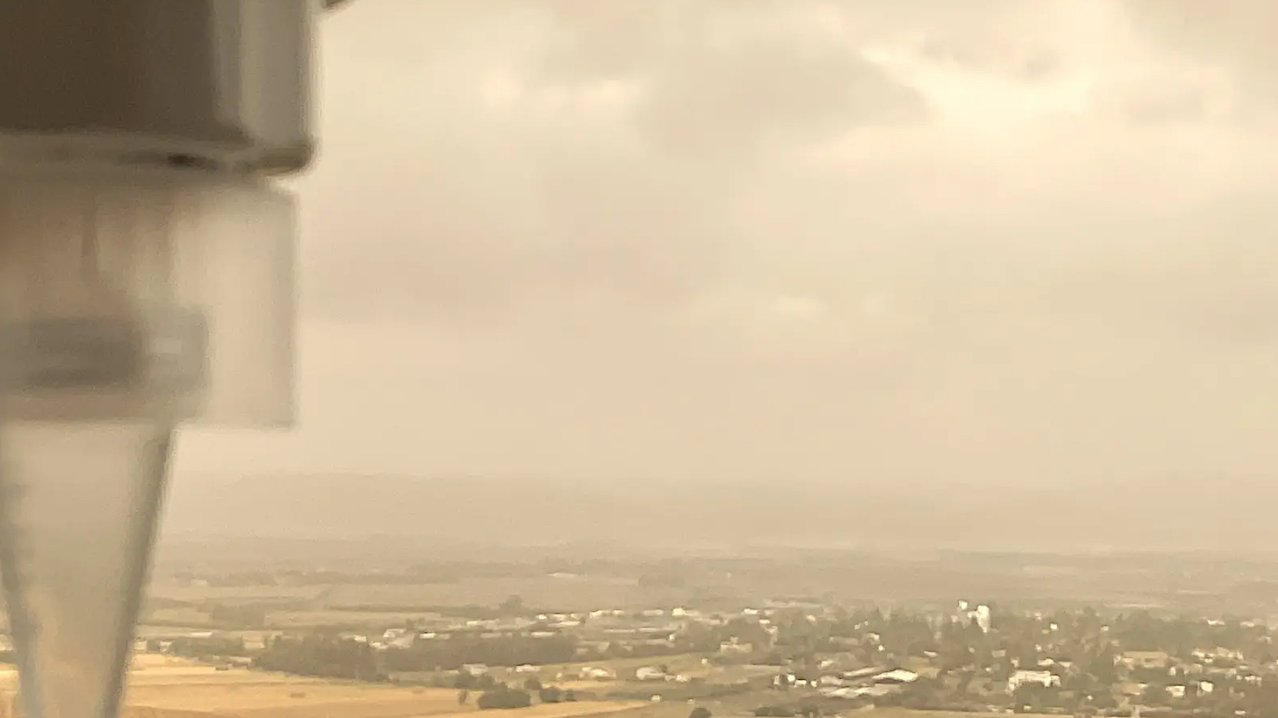
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly