Now Reading: Hubble Spies Stellar Blast Setting Clouds Ablaze
-
01
Hubble Spies Stellar Blast Setting Clouds Ablaze
Hubble Spies Stellar Blast Setting Clouds Ablaze

2 min read
Hubble Spies Stellar Blast Setting Clouds Ablaze
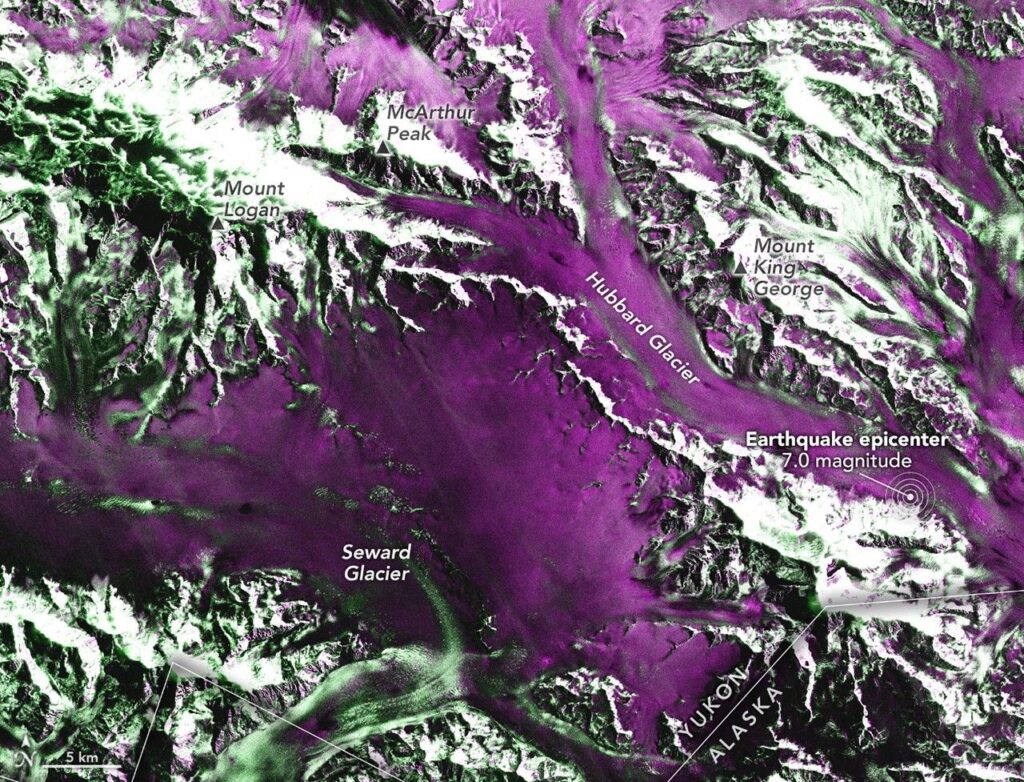
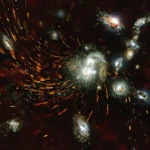
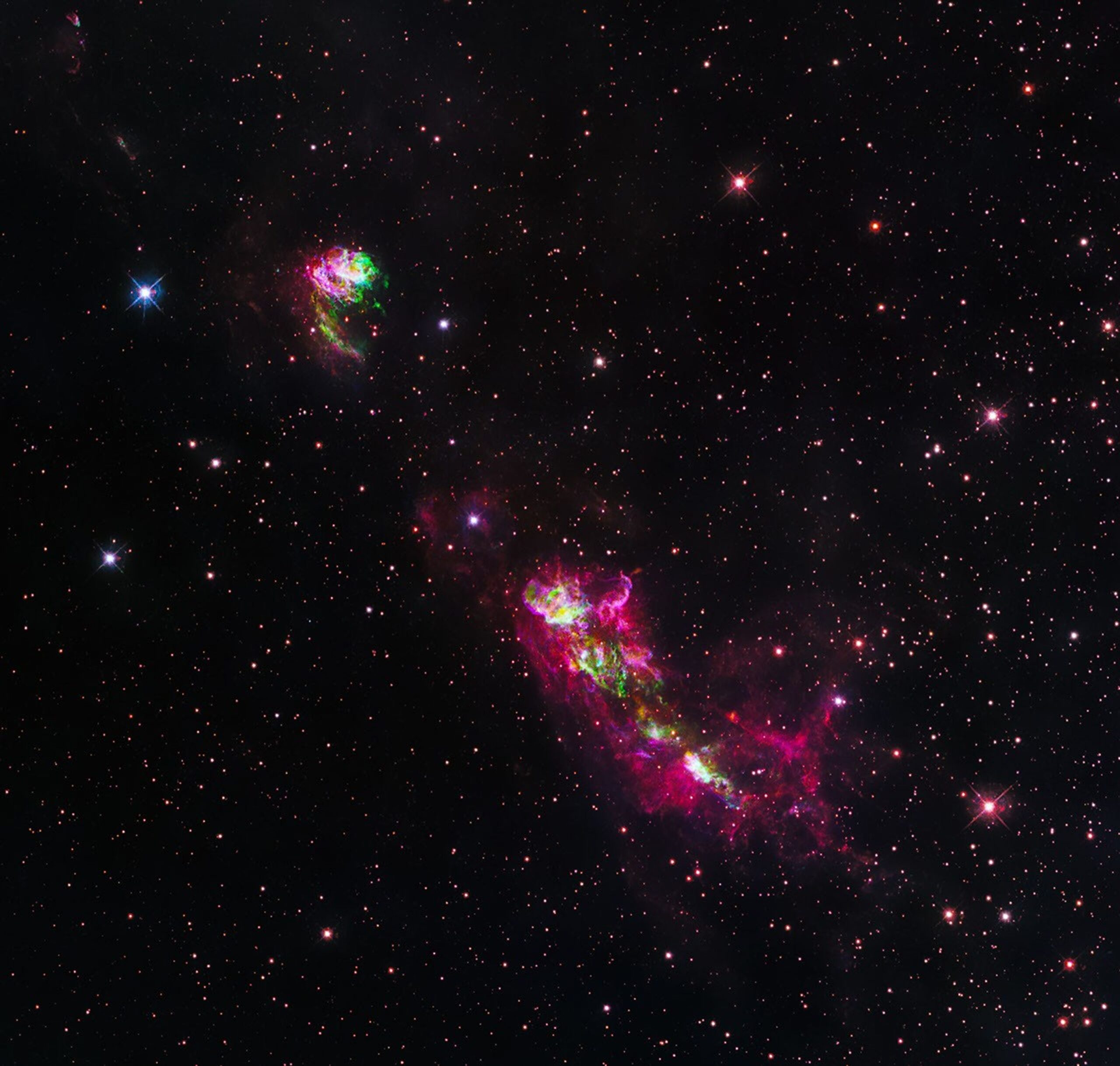
This new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image captures a jet of gas from a forming star shooting across the dark expanse. The bright pink and green patches running diagonally through the image are HH 80/81, a pair of Herbig-Haro (HH) objects previously observed by Hubble in 1995. The patch to the upper left is part of HH 81, and the bottom streak is part of HH 80.
Herbig-Haro objects are bright, glowing regions that occur when jets of ionized gas ejected by a newly forming star collide with slower, previously ejected outflows of gas from that star. HH 80/81’s outflow stretches over 32 light-years, making it the largest protostellar outflow known.
Protostars are fed by infalling gas from the surrounding environment, some of which can be seen in residual “accretion disks” orbiting the forming star. Ionized material within these disks can interact with the protostars’ strong magnetic fields, which channel some of the particles toward the pole and outward in the form of jets.
As the jets eject material at high speeds, they can produce strong shock waves when the particles collide with previously ejected gas. These shocks heat the clouds of gas and excite the atoms, causing them to glow in what we see as HH objects.
HH 80/81 are the brightest HH objects known to exist. The source powering these luminous objects is the protostar IRAS 18162-2048. It’s roughly 20 times the mass of the Sun, and it’s the most massive protostar in the entire L291 molecular cloud. From Hubble data, astronomers measured the speed of parts of HH 80/81 to be over 1,000 km/s, the fastest recorded outflow in both radio and visual wavelengths from a young stellar object. Unusually, this is the only HH jet found that is driven by a young, very massive star, rather than a type of young, low-mass star.
The sensitivity and resolution of Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 was critical to astronomers, allowing them to study fine details, movements, and structural changes of these objects. The HH 80/81 pair lies 5,500 light-years away within the Sagittarius constellation.
New images added every day between January 12-17, 2026! Follow @NASAHubble on social media for the latest images and news and see Hubble’s Stellar Construction Zones for more images of young stellar objects.
Explore More
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Leave a reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly