Now Reading: Juno spacecraft finds auroral ‘footprints’ of Jupiter’s moon Callisto for 1st time
-
01
Juno spacecraft finds auroral ‘footprints’ of Jupiter’s moon Callisto for 1st time
Juno spacecraft finds auroral ‘footprints’ of Jupiter’s moon Callisto for 1st time
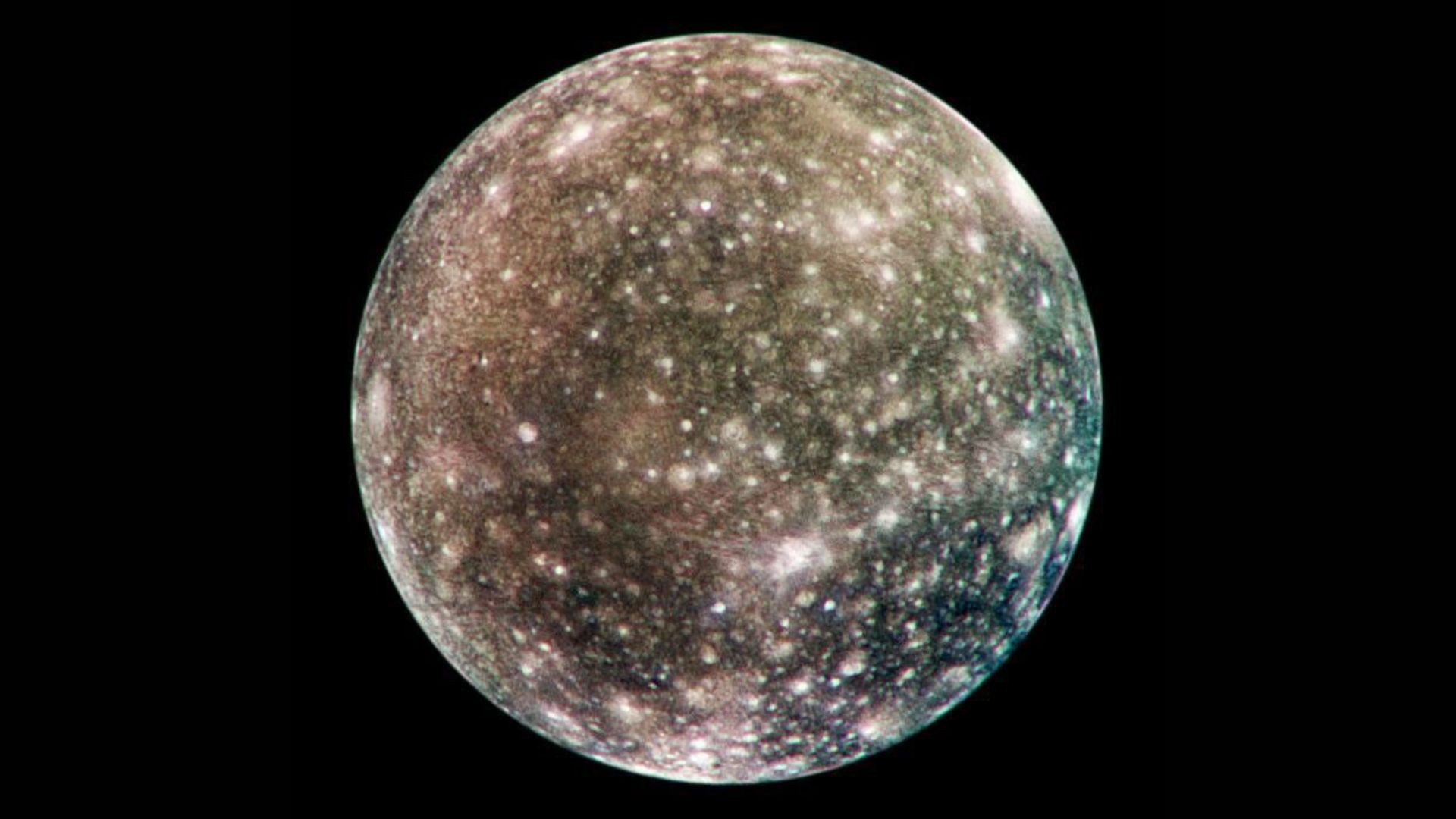


In a landmark observation by a team of international researchers, NASA’s Juno spacecraft has, for the first time, clearly detected the auroras of Jupiter’s moon Callisto. This discovery completes the set of auroral signatures we have from all four Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto.
Like Earth, Jupiter experiences brilliant auroras around its poles — but something funky happens with Jupiter’s Galilean moons that doesn’t happen with our own satellite. “Jupiter exhibits peculiar multiwavelength auroral emissions resulting from the electromagnetic interactions of Io, Europa, and Ganymede with the magnetospheric plasma flow,” write the team in a new paper about the discovery. In other words, the moons interact with Jupiter’s magnetosphere to create distinct auroral footprints.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope had previously observed auroral signatures from Io, Europa and Ganymede, but it only detected trace evidence of a signature from Callisto. “[T]he lack of multiple detections [did] not allow a complete characterization of its properties,” the team wrote in the paper.
The challenge had to do with the faintness of Callisto’s auroral signature, paired with the fact that it frequently overlapped with Jupiter’s much brighter auroral oval. Thus, in order to more clearly observe Callisto’s auroral signature, Jupiter’s auroral oval would have to shift.
Fortunately, that shift happened in September 2019, just as Juno was perfectly positioned to observe not only Callisto, but all four of Jupiter’s Galilean moons simultaneously. An unusually high-density solar stream buffeted Jupiter and pushed its auroral oval toward the equator — the same thing happens on Earth, which is what brings the northern lights down to the mid-latitudes.
“This allowed the auroral footprints of the four Galilean moons to be revealed in a single observation by Juno, enabling the precise characterization in UV, radio, plasma, and waves of the high-latitude signatures of the Callisto-magnetosphere interactions,” wrote the team. Just as expected, Callisto’s auroral signature matches those of its sister moons.
RELATED STORIES
While researchers will continue to study the Galilean moons with Juno, the spacecraft will be joined by others in the coming years, potentially solving even more mysteries in the Jovian system. NASA’s Europa Clipper is due to arrive at Jupiter in 2030, while the European Space Agency’s JUICE (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer) should arrive the following year.
The results were published in the journal Nature Communications on Sept. 1.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly