Now Reading: Meet the new Comet SWAN! See it in binoculars now
-
01
Meet the new Comet SWAN! See it in binoculars now
Meet the new Comet SWAN! See it in binoculars now


Looking up has never felt more important.
Help EarthSky keep bringing the sky to your screen.
Meet the new comet
There’s a new comet speeding toward the sun, and you can see it with binoculars in the morning sky. SWAN, an instrument aboard the European Space Agency’s SOHO spacecraft that studies the sun, first detected the comet. On April 8, 2025, comet SWAN25F was officially designated as C/2025 F2 (SWAN) by the Minor Planet Center. The new comet was independently co-discovered by Vladimir Bezugly from Ukraine and Michael Mattiazzo from Australia. Both comet hunters detected the moving object on March 29 by examining the latest images taken by the spacecraft.
To see the comet, look toward the east-northeastern horizon just before sunrise. Although the comet is gradually brightening, at the moment you’ll still need binoculars or a small telescope to see it.
The good news is that if the comet survives its perihelion – or closest approach to the sun – in a few weeks, it might be visible during sunset. Just how bright it will be remains to be seen, as comets have shown us they are erratic and unpredictable. But if the comet survives its closest approach to the sun, it would make its transition from the dawn sky to the dusk sky during the first days of May.
By then, the comet’s very high speed will be noticeable when comparing its position during each sunset.
Preliminary observations suggest that closest approach to Earth and to the sun will occur on the same day, on May 1, 2025. The comet will be passing at around 31 million miles from the sun, or just inside of planet Mercury’s average orbit.
At closest approach, the comet’s brightness or magnitude might be between 4.5 to 5. But it will probably be quite close to the horizon.

Recent outburst and brightness variations
Did you try to spot the comet in the last couple days but have trouble?
Astronomer Mike Olason, who has been monitoring the celestial visitor from Tucson, Arizona, said:
For those who have wondered why the comet has been so hard to observe the past few mornings, it is because the comet has faded a magnitude since reaching its brightest point several days ago.
Since comets are so erratic, this behavior does not necessarily mean bad news for observers. Comet hunter Nick James reports he has detected activity or recent brightness peaks on the mornings of April 6 and 8.
These recent changes on the brightness of the comet might be due to sudden eruptions caused by pockets of ice, but as the comet continues to approach both the sun and Earth, it should continue to gradually brighten.


Look for the comet in Pegasus
During the first days of April, the comet has been inside the Great Square of Pegasus the Flying Horse. And it’s moving toward Andromeda the Chained Lady.
In fact, one of the stars of the Great Square can help you locate the comet. Look toward the star Alpha Andromedae, or Alpheratz, the brightest of the four corner stars. Comet SWAN passed not far from Alpheratz around April 13, 2025.


A once-in-a-lifetime event
While refining the orbit of comet C/2025 F2 (SWAN) as observations show the different positions in the sky, astronomers can determine where the celestial visitor should have been before. And they were successful in finding the comet as an extremely faint object in “pre-discovery” images as far back as September 2024. That’s even though it was just discovered a few days ago.
By comparing the location of the comet during both previous and recent observations, calculations indicate the newly found comet completes an orbit around the sun every 2.1 million years!
This means the visibility of comet C/2025 F2 (SWAN) is a once-in-a-lifetime event.
More on Comet SWAN
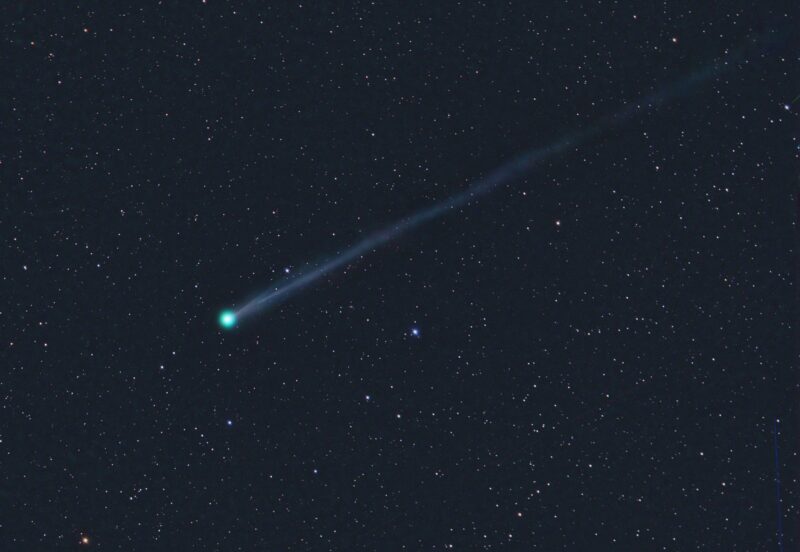
The new comet appears as a small green sphere, which means its coma – or cometary atmosphere – has reactive molecules called diatomic carbon (C2). These appear green when sunlight illuminates the celestial visitor.
Long-exposure images are also showing a faint tail that extends for more than two moon diameters.
Latest reported brightness or magnitude is around 8 to 7.5 and improving (the lower the number, the brighter). Keep checking back, because we’ll keep you updated on its progress!
Images of the new comet

Did you capture an image of Comet SWAN? Submit it to us.
Bottom line: The new Comet SWAN is approaching the sun and you can currently see it with binoculars in the morning sky. Keep track of its progress here.
The post Meet the new Comet SWAN! See it in binoculars now first appeared on EarthSky.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly