Now Reading: NASA Spaceline Current Awareness List #1,133 24 January 2025 (Space Life Science Research Results)
-
01
NASA Spaceline Current Awareness List #1,133 24 January 2025 (Space Life Science Research Results)
NASA Spaceline Current Awareness List #1,133 24 January 2025 (Space Life Science Research Results)


The abstract in PubMed or at the publisher’s site is linked when available and will open in a new window.
Journal Impact Factor: 5.1
Funding: “This project was funded by both the Flight Opportunity Program and the NASA Biological and Physical Sciences Division as a pathfinder technology demonstration for future Space Biology investigations using the MISSE platform. TAM’s participation was in part supported by a SURA LASSO/NASA visiting scientist award and funding from the Samuel Freeman Charitable Trust. We also thank the KSC’s EDL for conducting the thermal test, and the Cryogenics Test Laboratory (CTL), especially James E. Fesmire and Adam M. Swanger, for recommendations on insulation material selections. We thank especially Matthew W. Romeyn (KSC) for his recommendation on seed selection, Trent M. Smith (KSC) for his technical advice, and Bill Wells (the Bionetics Corporation) and Mark Shumbera (Aegis Aerospace Inc.) for their support. We give special thanks to astronauts (JAXA astronaut Soichi Noguchi, and NASA astronauts Kayla Barron and Mark Vande Hei), the Aegis team, and the whole ISS team for supporting and operating the MISSE-14 payload.”
Journal Impact Factor: 1.5
Funding: “This work was supported by NASA, grant # 80JSC019N001-HHCBPSR; Clinical and Translational Science Awards UL1TR000039 and KL2TR000063; NIGMS, grant P20 GM109005, and the Arkansas Biosciences Institute.”
Journal Impact Factor: 1.3
Funding: “This work was funded by the NASA Human Research Program grant number 80NSSC19K0656, as part of Human Capabilities Assessment for Autonomous Missions Virtual NASA Specialized Center of Research effort. The authors would like to acknowledge Human Exploration Research Analog (HERA) management team for their continuous support in providing access to the Habitat Simulation System, related technical support, and delivery of associated anomaly resolution procedures.”
Journal Impact Factor: Not available for this journal
Funding: “This research was supported by the NASA Human Research Program (HRP), Science Mission Directorate, and Biological and Physical Sciences (BPS) Division. We thank the HRP Radiation Element Translational Radiation Research and Countermeasures team and the GeneLab team for collaboration. Resources supporting this work were provided by the NASA High-End Computing (HEC) Program through the NASA Center for Climate Simulation (NCCS) at Goddard Space Flight Center. We also wish to thank Charlotte Nelson from Mate Bioservices, Inc. for providing us the results from the SPOKE tool.”
Journal Impact Factor: 2.6
Funding: “This work was supported by the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI) Grant CA 00005 through the National Aeronautics and Space Administration cooperative agreement NCC 9-58-49.”
Funding: B. Siegel, E. Seasly, and J.N. Benardini are affiliated with NASA Headquarters.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
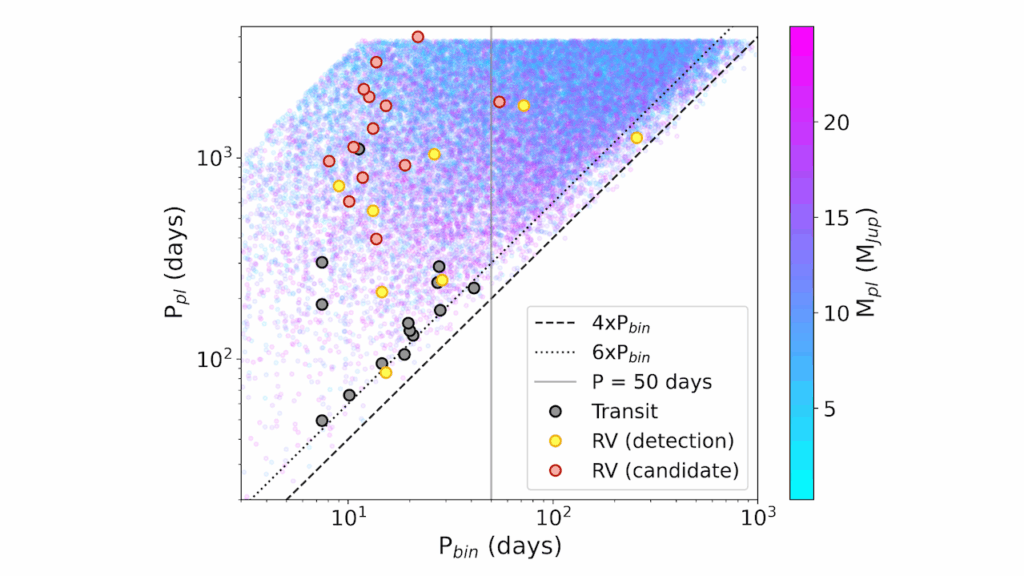
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly