Now Reading: NASA’s Lucy Spacecraft Images Asteroid Donaldjohanson
-
01
NASA’s Lucy Spacecraft Images Asteroid Donaldjohanson
NASA’s Lucy Spacecraft Images Asteroid Donaldjohanson
4 min read
NASA’s Lucy Spacecraft Images Asteroid Donaldjohanson
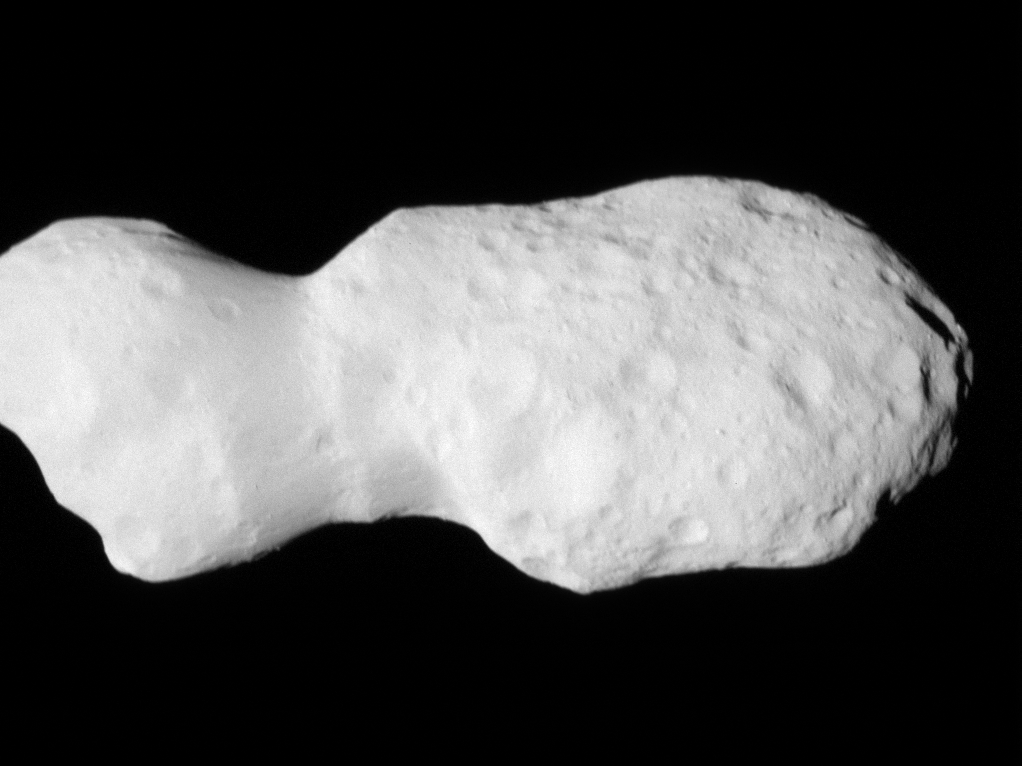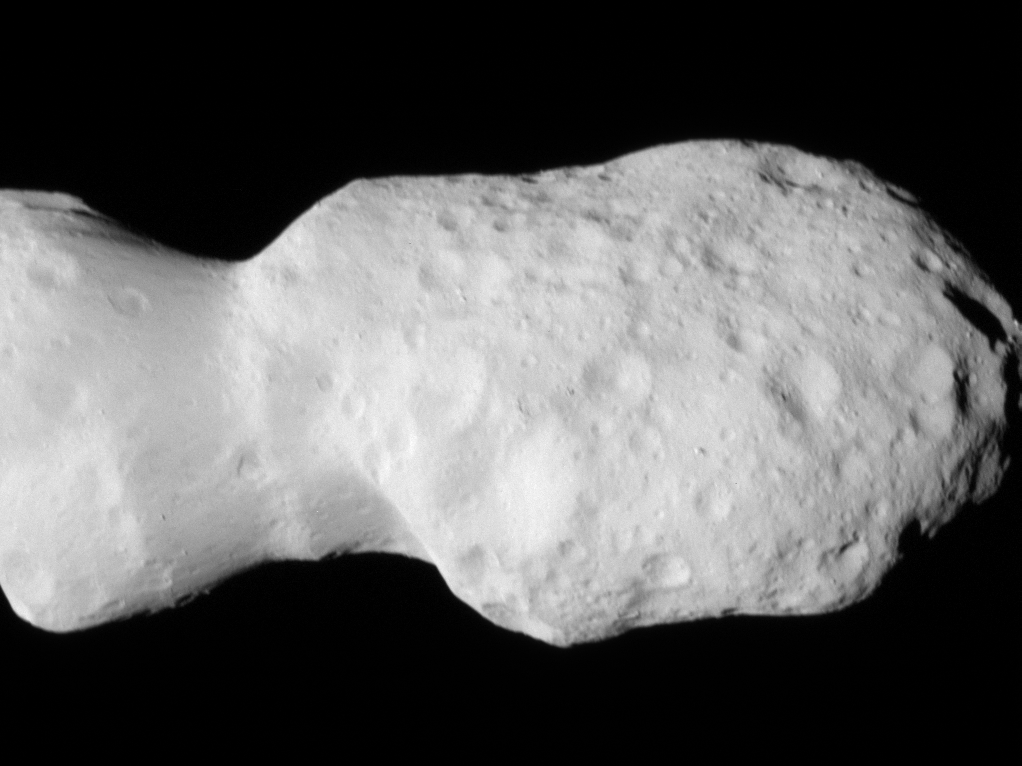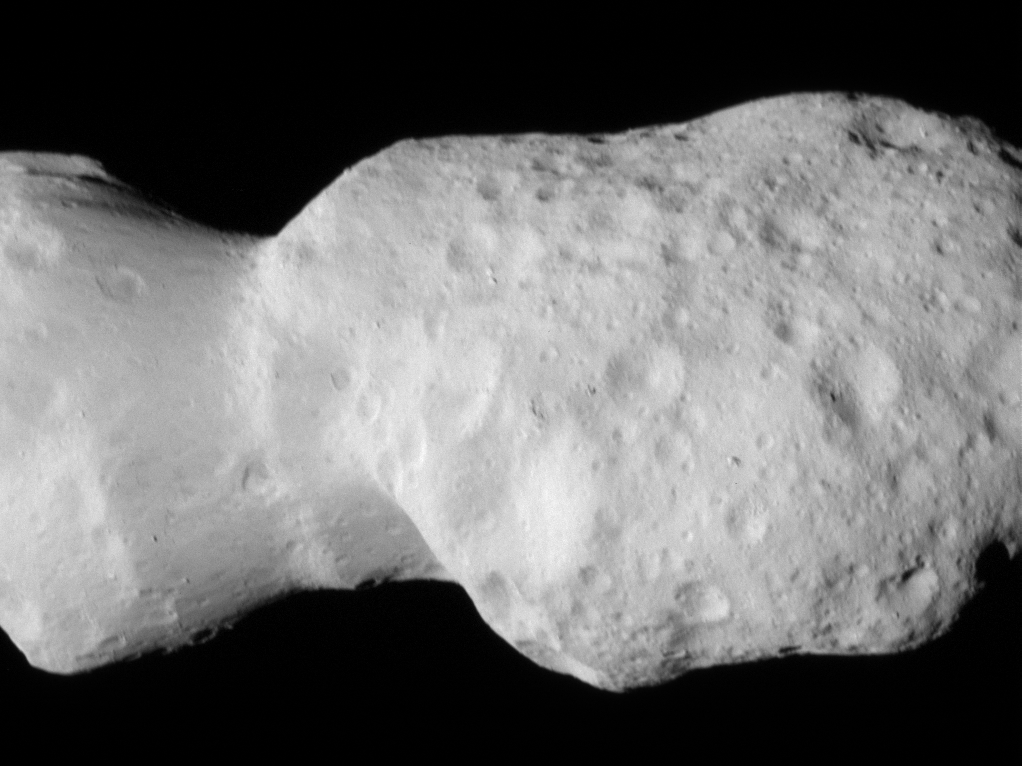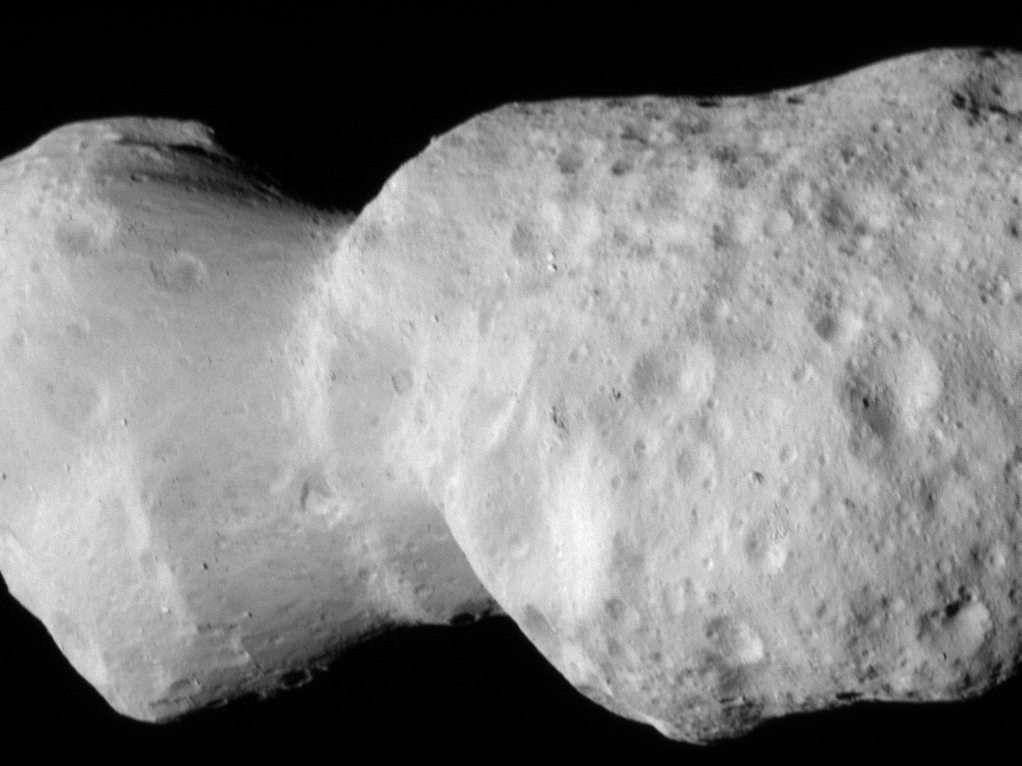
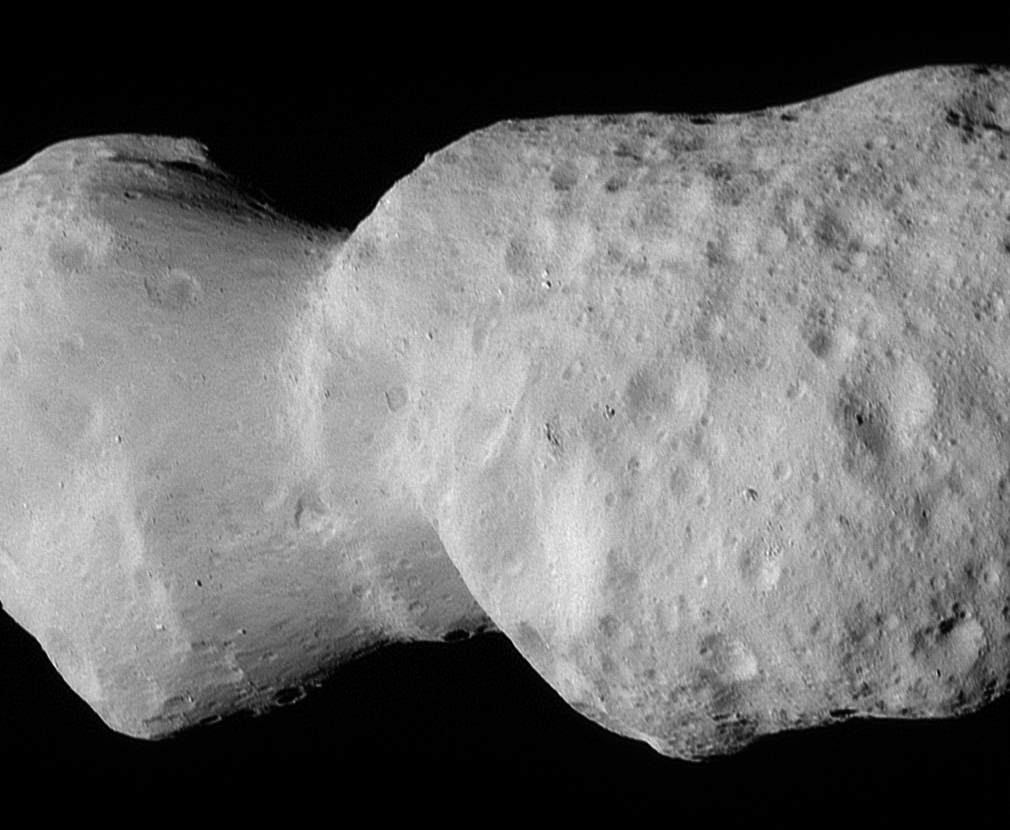
In its second asteroid encounter, NASA’s Lucy spacecraft obtained a close look at a uniquely shaped fragment of an asteroid that formed about 150 million years ago. The spacecraft has begun returning images that were collected as it flew approximately 600 miles (960 km) from the asteroid Donaldjohanson on April 20, 2025.
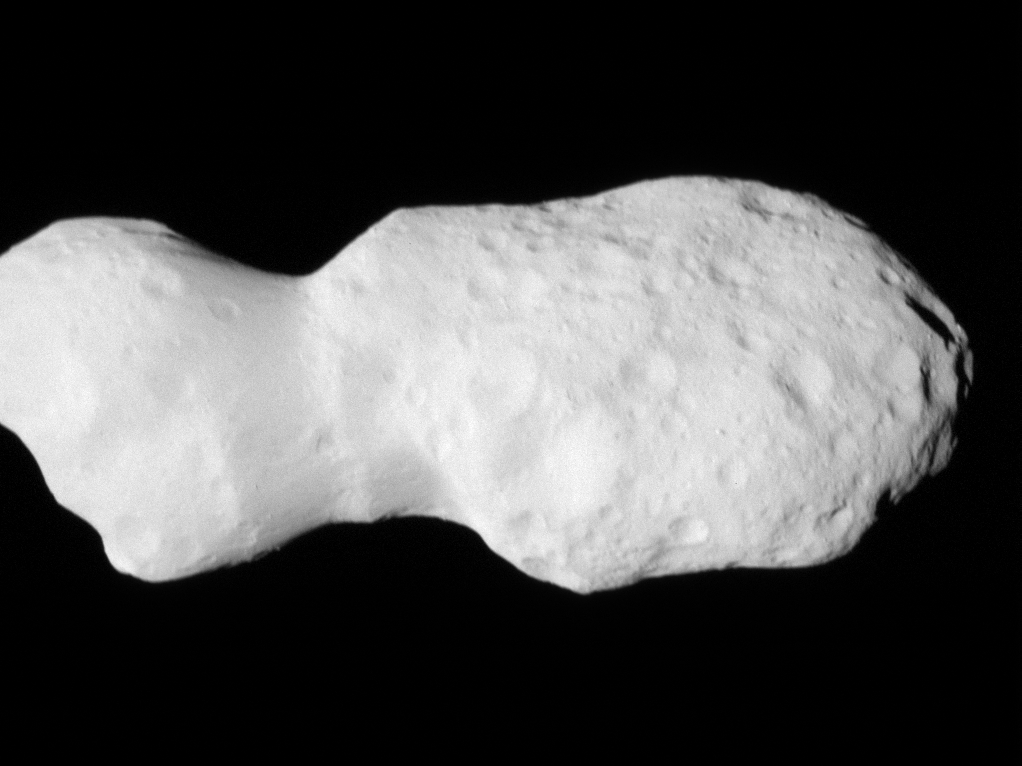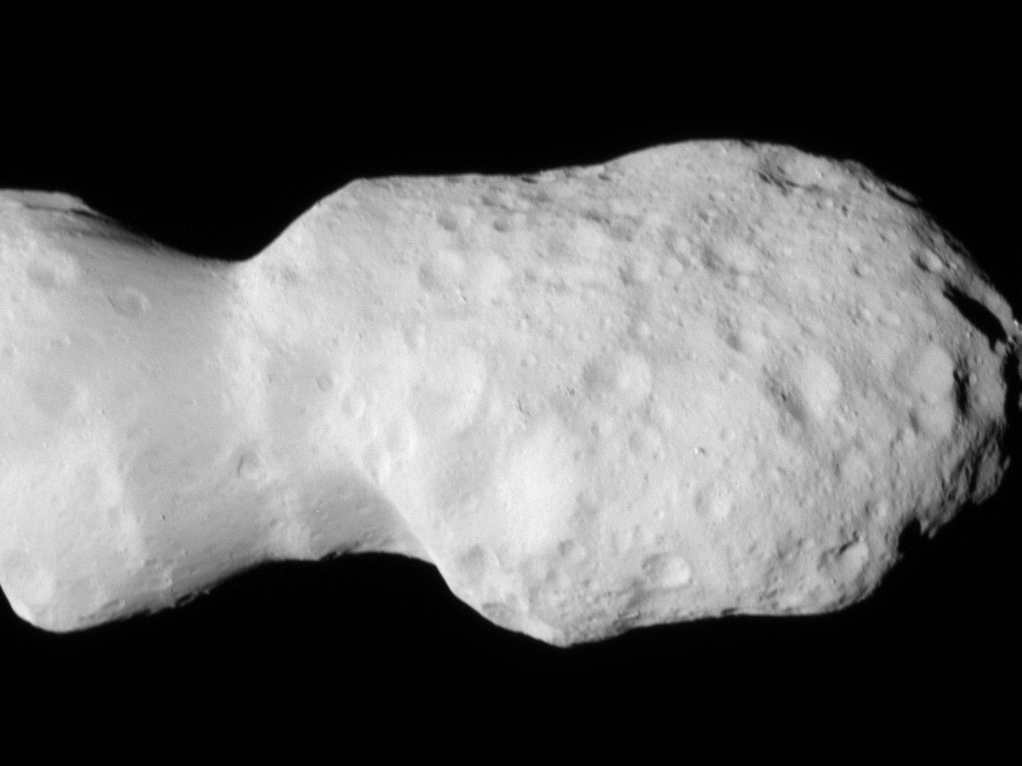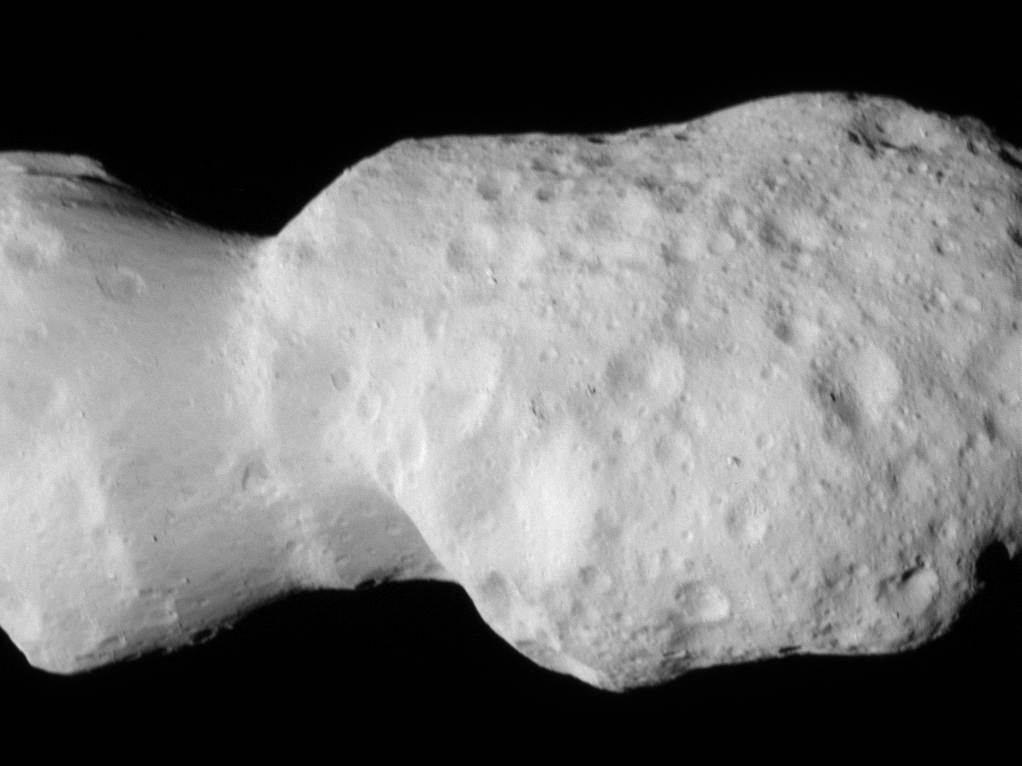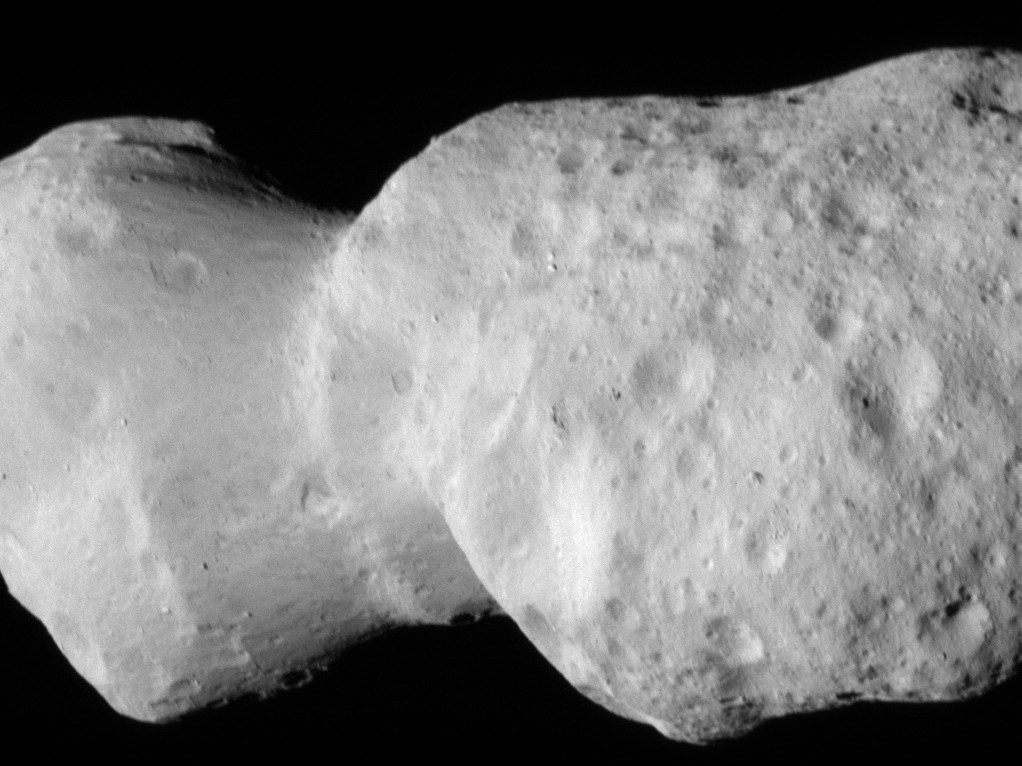
The asteroid was previously observed to have large brightness variations over a 10-day period, so some of Lucy team members’ expectations were confirmed when the first images showed what appeared to be an elongated contact binary (an object formed when two smaller bodies collide). However, the team was surprised by the odd shape of the narrow neck connecting the two lobes, which looks like two nested ice cream cones.
“Asteroid Donaldjohanson has strikingly complicated geology,” says Hal Levison, principal investigator for Lucy at Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, Colorado. “As we study the complex structures in detail, they will reveal important information about the building blocks and collisional processes that formed the planets in our Solar System.”
From a preliminary analysis of the first available images collected by the spacecraft’s L’LORRI imager, the asteroid appears to be larger than originally estimated, about 5 miles (8 km) long and 2 miles (3.5 km) wide at the widest point. In this first set of high-resolution images returned from the spacecraft, the full asteroid is not visible as the asteroid is larger than the imager’s field of view. It will take up to a week for the team to downlink the remainder of the encounter data from the spacecraft; this dataset will give a more complete picture of the asteroid’s overall shape.
Like Lucy’s first asteroid flyby target, Dinkinesh, Donaldjohanson is not a primary science target of the Lucy mission. As planned, the Dinkinesh flyby was a system’s test for the mission, while this encounter was a full dress rehearsal, in which the team conducted a series of dense observations to maximize data collection. Data collected by Lucy’s other scientific instruments, the L’Ralph color imager and infrared spectrometer and the L’TES thermal infrared spectrometer, will be retrieved and analyzed over the next few weeks.
The Lucy spacecraft will spend most of the remainder of 2025 travelling through the main asteroid belt. Lucy will encounter the mission’s first main target, the Jupiter Trojan asteroid Eurybates, in August 2027.
“These early images of Donaldjohanson are again showing the tremendous capabilities of the Lucy spacecraft as an engine of discovery,” said Tom Statler, program scientist for the Lucy mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “The potential to really open a new window into the history of our solar system when Lucy gets to the Trojan asteroids is immense.”

NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provides overall mission management, systems engineering and the safety and mission assurance for Lucy, as well as the designing and building the L’Ralph instrument. Hal Levison of the Boulder, Colorado, office of SwRI is the principal investigator. SwRI is headquartered in San Antonio and also leads the mission’s science team, science observation planning, and data processing. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provides overall mission management, systems engineering, and the safety and mission assurance for Lucy, as well as the L’Ralph instrument. Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, built the spacecraft, designed the orbital trajectory, and provides flight operations. Goddard and KinetX Aerospace are responsible for navigating the Lucy spacecraft. The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, designed and built the L’LORRI (Lucy Long Range Reconnaissance Imager) instrument. Arizona State University designed and built the L’TES (Lucy Thermal Emission Spectrometer). Lucy is the thirteenth mission in NASA’s Discovery Program, which is managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
By Katherine Kretke
Southwest Research Institute
Media Contact:
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov
Nancy N. Jones
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Share
Related Terms
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly