Now Reading: Performance Calibration of the Wavefront Sensor’s EMCCD Detector for the Cool Planets Imaging Coronagraph Aboard CSST
-
01
Performance Calibration of the Wavefront Sensor’s EMCCD Detector for the Cool Planets Imaging Coronagraph Aboard CSST
Performance Calibration of the Wavefront Sensor’s EMCCD Detector for the Cool Planets Imaging Coronagraph Aboard CSST
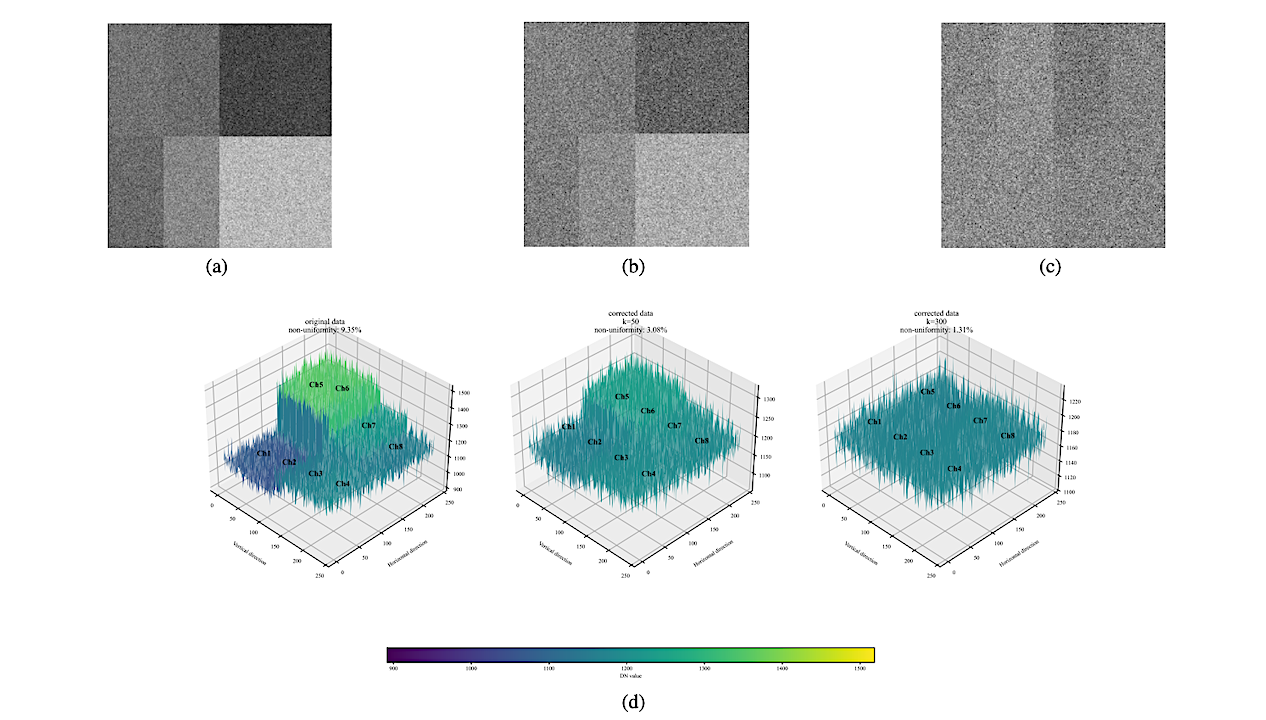

The systematic evaluation of algorithm effectiveness. (a) displays the original flat-field response distributions following background correction. Panels (b,c) illustrate the corrected results after algorithm processing, while (d) presents the distribution profiles of channel DN values. Notably, as evidenced in the comparative diagrams (a–c), Channel 1 (Ch1) maintains consistent spatial positioning in the upper-right quadrant of each schematic layout. — astro-ph.IM
The wavefront sensor (WFS), equipped with an electron-multiplying charge-coupled device (EMCCD) detector, is a critical component of the Cool Planets Imaging Coronagraph (CPI-C) on the Chinese Space Station Telescope (CSST).
Precise calibration of the WFS’s EMCCD detector is essential to meet the stringent requirements for high-contrast exoplanet imaging. This study comprehensively characterizes key performance parameters of the detector to ensure its suitability for astronomical observations.
Through a multi-stage screening protocol, we identified an EMCCD chip exhibiting high resolution and low noise. The electron-multiplying gain (EM Gain) of the EMCCD was analyzed to determine its impact on signal amplification and noise characteristics, identifying the optimal operational range. Additionally, noise properties such as readout noise were investigated.
Experimental results demonstrate that the optimized detector meets CPI-C’s initial application requirements, achieving high resolution and low noise. This study provides theoretical and experimental foundations for the use of EMCCD-based WFS in adaptive optics and astronomical observations, ensuring their reliability for advanced space-based imaging applications
Jiangpei Dou, Bingli Niu, Gang Zhao, Xi Zhang, Gang Wang, Baoning Yuan, Di Wang, Xingguang Qian
Comments: 12pages, 11figures, 1table
Subjects: Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM)
Cite as: arXiv:2511.20386 [astro-ph.IM] (or arXiv:2511.20386v1 [astro-ph.IM] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2511.20386
Focus to learn more
Journal reference: Journal of Imaging 2025
Related DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060203
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: BingLi Niu
[v1] Tue, 25 Nov 2025 15:07:28 UTC (7,249 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.20386
astrobiology, astronomy, ISS, exoplanet,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly