Now Reading: Prebiosignatures With The Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO)
-
01
Prebiosignatures With The Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO)
Prebiosignatures With The Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO)
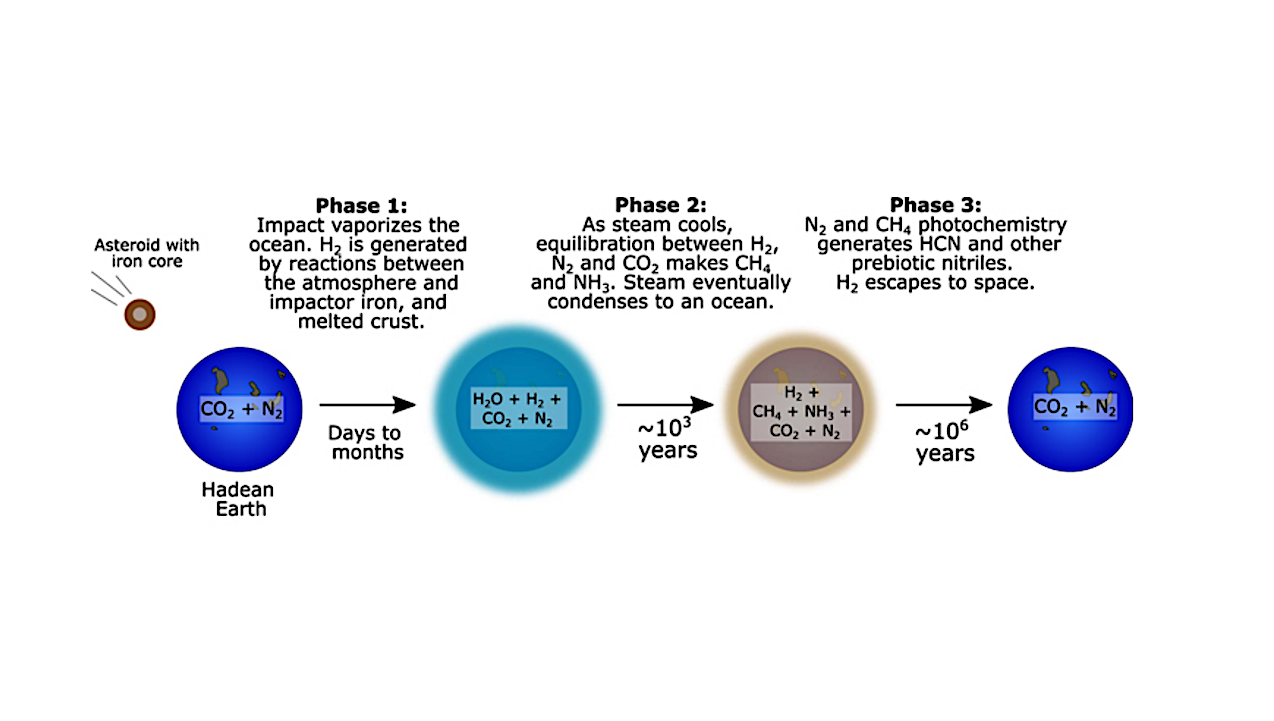

Schematic of the post-impact scenario for prebiotic atmospheres (Genda et al. 2017; Zahnle et al. 2020; Wogan et al. 2023). In this scenario, reducing power is delivered to the surface-atmosphere system by reaction of an iron-rich meteor with the planetary ocean, generating a transient Miller-Urey type atmosphere. We anticipate such atmospheres to be strongly distinguishable by HWO observations through their copious concentrations of reducing species (Goodis Gordon et al. 2025). However, we also anticipate such atmospheres to be rare due to their transient nature, and a sample of 25 planets is unlikely to capture them. Figure taken from Wogan et al. (2023). — astro-ph.IM
The Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO) aims to characterize habitable exoplanets in search of signs of life. However, detectable life may be rare, either because abiogenesis is intrinsically contingent and unlikely, or because biospheres may efficiently recycle their products.
Here, we explore the potential of HWO to test theories of life in the universe even if detectable life is rare by searching for “prebiosignature gases”. Prebiosignatures gases are gases whose detection constrains theories of the evolution of prebiotic (habitable but uninhabited) planets, thereby testing theories of abiogenesis and guiding laboratory investigations of the origin of life.
We catalog 5 theories of prebiotic environments that are potentially testable by HWO, identify their observational tests, and rank them by perceived detection plausibility. The prebiosignature paradigm is novel and potentially compelling, but considerable work is required to mature it and assess its practical relevance for HWO, especially simulated spectral observation and retrieval studies.
However, consideration of the absorption properties of prebiosignature observables alone reveals that coverage at NUV wavelengths (200-400 nm) will be required to effectively realize a prebiosignature science case for HWO, supporting the argument for UV capabilities for HWO.

Prebiosignature atmospheric species and the wavelengths where they absorb or scatter (extinct) light. Wavelengths where species extinction exceeds 10−24 cm−2 molecule−1 and 10−18 cm−2 molecule−1 are indicated by dashed lines and solid lines, respectively. Species are grouped by the origin-of-life scenario they correspond to. The UV bandpass will be key to detecting prebiosignature gas species. Underlying extinction data are from Arney et al. (2016); Hu et al. (2013); Ranjan & Sasselov (2017); Keller-Rudek et al. (2013). Underlying extinction data are limited to what is available in the literature; it is possible that these species absorb at other wavelengths as well, but such absorption is not yet known. Figure motivated by Figure 2 of Rimmer et al. (2021). — astro-ph.IM
Sukrit Ranjan, Danica Adams, Michael Wong, Martin Schlecker, Nicholas Wogan, Jessica M. Weber
Comments: Science Case Development Document for the Habitable Worlds Observatory (https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/HWOCOMMUNITYSCI/HWO+Community+Science+Case+Portal). Comments and endorsements welcomed via the link provided or at [email protected]. Comments/Endorsements received by August 15 will be incorporated into the published version (PASP conference proceedings)
Subjects: Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM); Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP)
Cite as: arXiv:2507.00165 [astro-ph.IM] (or arXiv:2507.00165v1 [astro-ph.IM] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2507.00165
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Sukrit Ranjan
[v1] Mon, 30 Jun 2025 18:14:44 UTC (629 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.00165
Astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly