Now Reading: Precise Physical Parameters, Habitability, and Orbital Stability of Sun-like SB2 Systems: HD 130669, HD 184467, HD 191854, and HD 214222
-
01
Precise Physical Parameters, Habitability, and Orbital Stability of Sun-like SB2 Systems: HD 130669, HD 184467, HD 191854, and HD 214222
Precise Physical Parameters, Habitability, and Orbital Stability of Sun-like SB2 Systems: HD 130669, HD 184467, HD 191854, and HD 214222
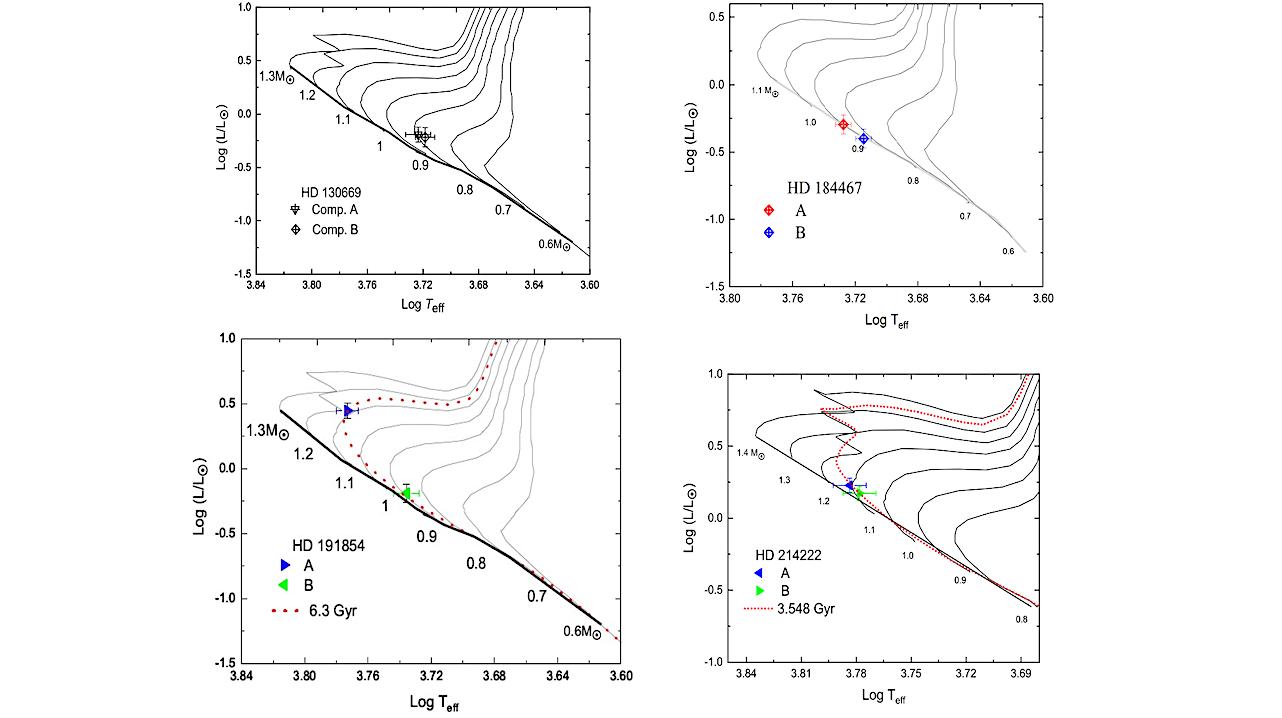

H–R diagrams for the binary systems HD 130669, HD 184467, HD 191854, and HD 214222. The positions of the individual stellar components (A and B) are plotted with their respective uncertainties. Evolutionary tracks corresponding to different stellar masses are shown by black lines, while the system’s best-fitting isochrone (age) is indicated by a red dotted line. The Zero-Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) is depicted as a thick solid black line. These diagrams were constructed using the evolutionary models to determine the masses and ages of the components based on their effective temperatures and luminosities. — astro-ph.EP
This work analyzes four Sun-like double-lined spectroscopic binary (SB2) systems by combining visual and spectroscopic observational data with Al-Wardat’s atmospheric modeling method to accurately determine their fundamental parameters.
For each system, we determine stellar masses, orbital parallaxes, effective temperatures, spectral types, semimajor axes, and eccentricities with high precision, resolving discrepancies between astrometric and spectroscopic measurements.
Moreover, we assess the potential for stable planetary orbits in these systems. We also calculate habitable zones around these binaries based on the orbital evolution of planetary orbits.
These systems may represent promising targets for future extrasolar planet searches around Sun-like stars due to their robust physical and orbital parameters that can be used to determine planetary habitability and stability.
Ahmad Abushattal, Nikolaos Georgakarakos, Mashhoor A. Al-Wardat, Bilal Algnamat, Hassan B. Haboubi, Deshinta Arrova Dewi, Enas M. Abu-Alrob, Abdallah M. Hussein
Comments: Published in AJ
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP); Solar and Stellar Astrophysics (astro-ph.SR)
Cite as: arXiv:2512.23652 [astro-ph.EP] (or arXiv:2512.23652v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.23652
Focus to learn more
Journal reference: The Astronomical Journal, 2025, Volume 170, Issue 5, id.268, 15 pp
Related DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-3881/ae0582
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Nikolaos Georgakarakos Ph.D.
[v1] Mon, 29 Dec 2025 18:04:34 UTC (749 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.23652
astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly