Now Reading: Probing Habitable Regions With SRG/eROSITA
-
01
Probing Habitable Regions With SRG/eROSITA
Probing Habitable Regions With SRG/eROSITA
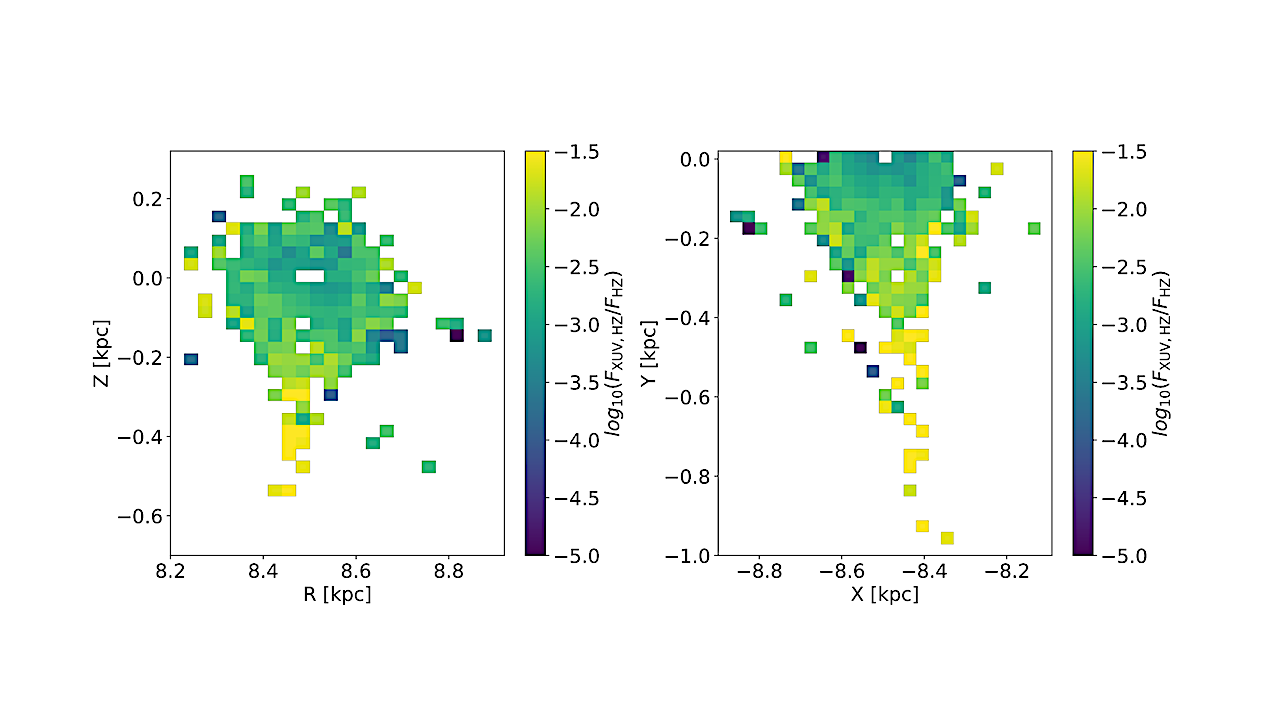

Left panel: Map of the normalized XUV flux in the habitable zone, FXUV,HZ/FHZ, in the Galactic R-Z plane. Right panel: Map of the normalized XUV flux in the habitable zone, FXUV,HZ/FHZ, in the Galactic X-Y plane. — astro-ph.SR
Stellar high-energy radiation is a key driver of atmospheric erosion and evolution in exoplanets, directly affecting their long-term habitability.
We present a comprehensive study on stellar high-energy radiation and its impact on exoplanetary atmospheres, leveraging data from the SRG/eROSITA all-sky survey. Our sample consists of 3750 main-sequence stars identified by cross-matching with Gaia DR3.
Utilizing X-ray spectral fits from the eROSITA catalog, we computed X-ray (LX) and combined extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) luminosities (LEUV), which we used to derive XUV fluxes at the habitable zone (FXUV,HZ). We find that the majority of stars in our sample are significantly more XUV-active than the Sun, with habitable zone fluxes ranging from 100 to 105 erg~cm−2~s−1.
The ratio of LXUV/Lbol is found to be higher for cooler, magnetically active stars, highlighting their potentially hazardous nature for planetary atmospheres. Applying the energy-limited escape model, we computed atmospheric mass-loss rates for hypothetical earth-like planets located at the habitable zone of each star. We also present local maps for distances up to 500~pc of the average XUV flux, revealing “hazard zones” where stellar radiation could significantly influence planetary atmospheric evolution.
This work demonstrates the power of X-ray surveys in constraining the high-energy environments of exoplanets and underscores the critical role of stellar activity in planetary habitability.
E. Gatuzz, S. Rukdee, S. Freund, T. Kallman
Comments: 8 pages, 11 figures
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP); High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena (astro-ph.HE); Solar and Stellar Astrophysics (astro-ph.SR)
Cite as: arXiv:2602.06124 [astro-ph.EP] (or arXiv:2602.06124v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2602.06124
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Efrain Gatuzz
[v1] Thu, 5 Feb 2026 19:00:58 UTC (854 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.06124
Astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly