Now Reading: Radioprotection Redefined: Drug Discovery At The Intersection Of Tardigrade Biology And Translational Pharmacology
-
01
Radioprotection Redefined: Drug Discovery At The Intersection Of Tardigrade Biology And Translational Pharmacology
Radioprotection Redefined: Drug Discovery At The Intersection Of Tardigrade Biology And Translational Pharmacology
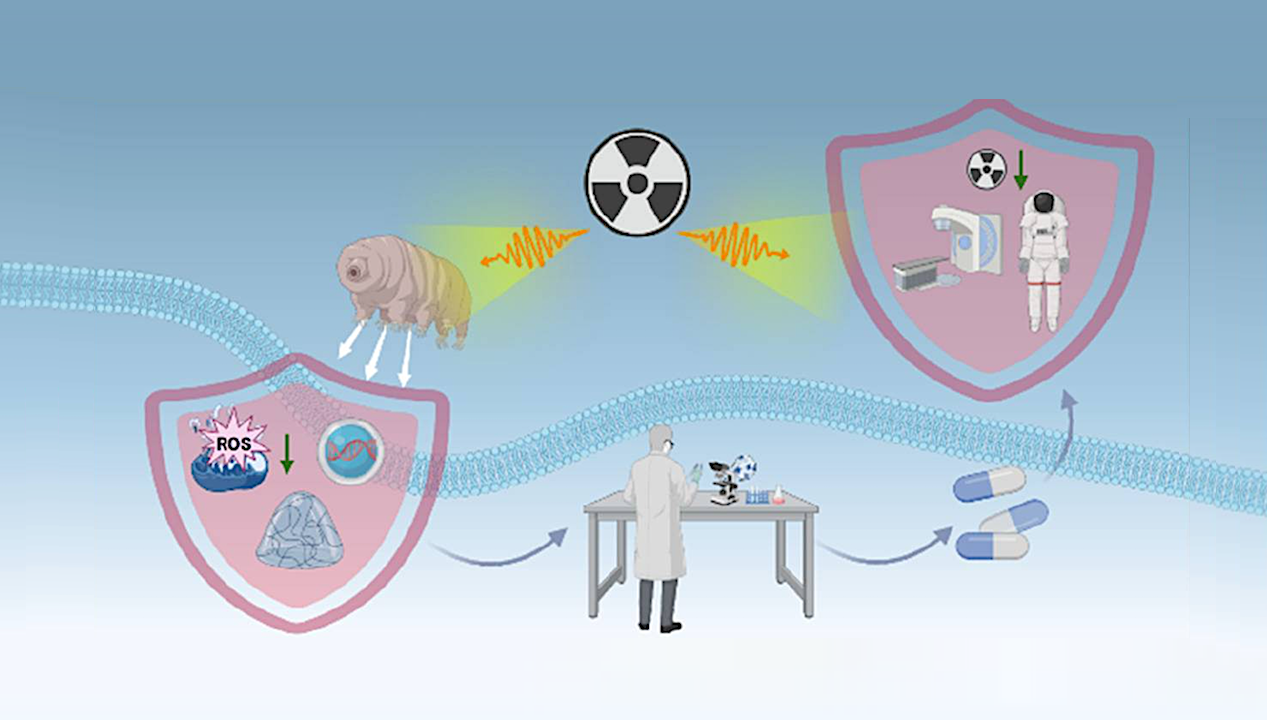

Graphical abstract — Frontiers
Harnessing tardigrade-inspired radioprotective strategies to revolutionize defense against ionizing radiation in medicine and space exploration.
Ionizing radiation inflicts lethal double-strand DNA breaks and oxidative stress that underlie acute radiation syndrome, secondary malignancies, and dose-limiting toxicity in radiotherapy; yet the conventional armamentarium of radioprotectants—aminothiols, broad-spectrum antioxidants, cytokines, and superoxide-dismutase mimetics—yields only modest benefit because of narrow therapeutic windows, systemic toxicity, and inadequate protection of radiosensitive tissues.
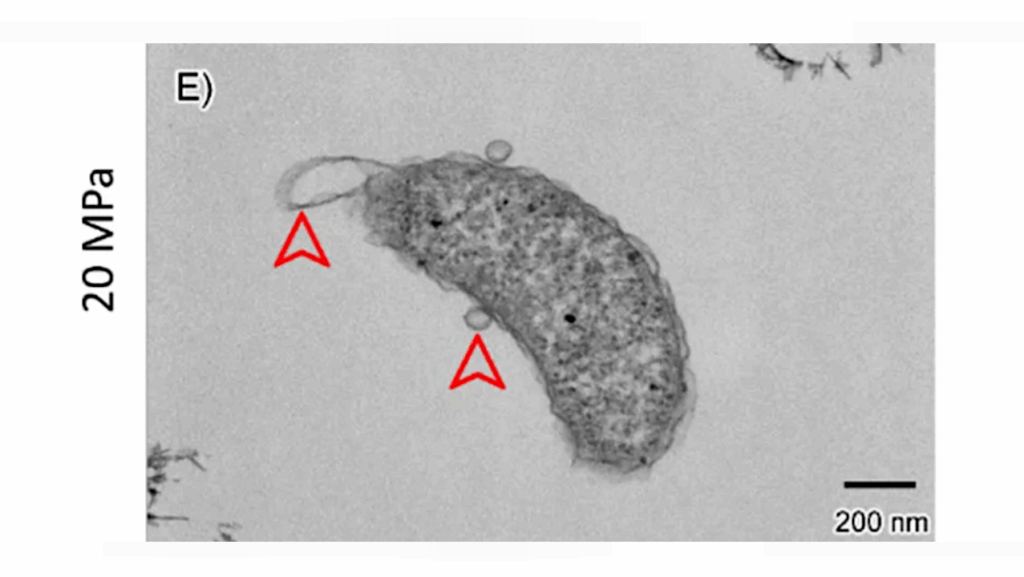
In striking contrast, tardigrades (phylum Tardigrada) routinely endure exposures beyond 5 kGy by deploying a multifaceted defense repertoire that includes genome-shielding proteins such as damage suppressor (Dsup) and Tardigrade DNA-Repair protein 1 (TDR1), families of intrinsically disordered proteins that vitrify cytoplasm and scavenge radicals, antioxidant pigments acquired via horizontal gene transfer, and exceptionally efficient DNA-repair and redox networks.
Viewing radioprotection through a translational pharmacology lens reveals a pipeline of emerging modalities—including recombinant or cell-penetrating proteins, mRNA therapeutics, peptidomimetics, and biomimetic nanomaterials—while also spotlighting critical hurdles of scalable bioprocessing, macromolecule stability, immunogenicity, and targeted delivery.
By integrating insights from extremophile biology with cutting-edge drug-discovery platforms, tardigrade-inspired interventions promise to safeguard healthy tissue during cancer treatment, reduce casualties in nuclear accidents, and shield astronauts on deep-space missions, thereby redefining the future landscape of radioprotection and transforming an evolutionary curiosity into a potent arsenal of medical countermeasures.

Molecular mechanisms underlying radiation resistance in tardigrades. Key adaptations include: (1) anhydrobiosis, a desiccation-induced ametabolic state; (2) intrinsically disordered proteins that vitrify cellular components and limit radical diffusion; (3) genome-shielding proteins that coat chromatin and reduce DNA damage; (4) distinctive antioxidant pigments that neutralize reactive oxygen species; and (5) hyper-efficient DNA repair and redox systems that rapidly restore genomic integrity post-irradiation. — Frontiers
Astrobiology, extremophile,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly