Now Reading: Residue-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Auxotrophic Hosts: Quo Vadis?
-
01
Residue-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Auxotrophic Hosts: Quo Vadis?
Residue-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Auxotrophic Hosts: Quo Vadis?
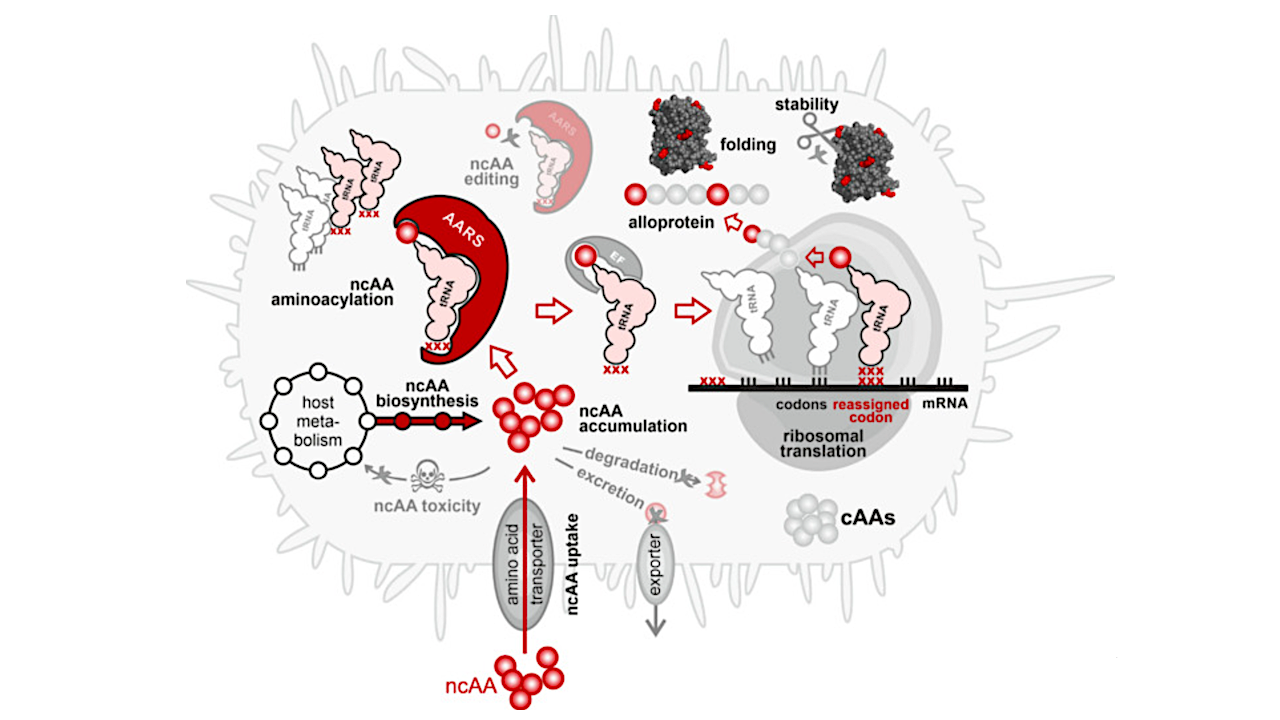

Journey of a noncanonical amino acid into a polypeptide. The cell takes up the ncAA from its environment or biosynthesizes it. The ncAA should not interfere with the host metabolism nor act as a toxin. To accumulate, it must not be degraded nor excreted by the cell. If its intracellular concentration reaches an adequate level, an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (AARS) activates it and charges it onto a tRNA. Discrimination against the ncAA by the editing function of some AARS prevents the downstream steps and should be avoided. An elongation factor delivers the ncAA-charged tRNA to the ribosome, where it participates in ribosomal translation. Peptide bonding stably incorporates the ncAA into the nascent polypeptide. The resulting alloprotein must be able to fold correctly and should not be degraded, e.g., by proteolytic enzymes. Chemical Reviews via PubMed
The residue-specific incorporation of noncanonical amino acids in auxotrophic hosts allows the global exchange of a canonical amino acid with its noncanonical analog.
Noncanonical amino acids are not encoded by the standard genetic code, but they carry unique side chain chemistries, e.g., to perform bioorthogonal conjugation reactions or to manipulate the physicochemical properties of a protein such as folding and stability. The method was introduced nearly 70 years ago and is still in widespread use because of its simplicity and robustness.
In our study, we review the trends in the field during the last two decades. We give an overview of the application of the method for artificial post-translational protein modifications and the selective functionalization and directed immobilization of proteins.
We highlight the trends in the use of noncanonical amino acids for the analysis of nascent proteomes and the engineering of enzymes and biomaterials, and the progress in the biosynthesis of amino acid analogs. We also discuss the challenges for the scale-up of the technique.

Side chain chemistries of canonical and noncanonical amino acids. The canonical amino acids whose analog incorporation is reviewed in this study are highlighted in red together with their coding units in the standard genetic code. The amino acids are shown in the three-letter code. An illustrative selection of noncanonical amino acids for residue-specific incorporation is shown in the pale-red box. — Chemical Reviews via PubMed
Residue-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Auxotrophic Hosts: Quo Vadis?, Chemical Reviews via PubMed
Residue-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Auxotrophic Hosts: Quo Vadis?, Chemical Reviews (open access)
Astrobiology, Genomics,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors