Now Reading: Sagittarius B2 Molecular Cloud
-
01
Sagittarius B2 Molecular Cloud
Sagittarius B2 Molecular Cloud
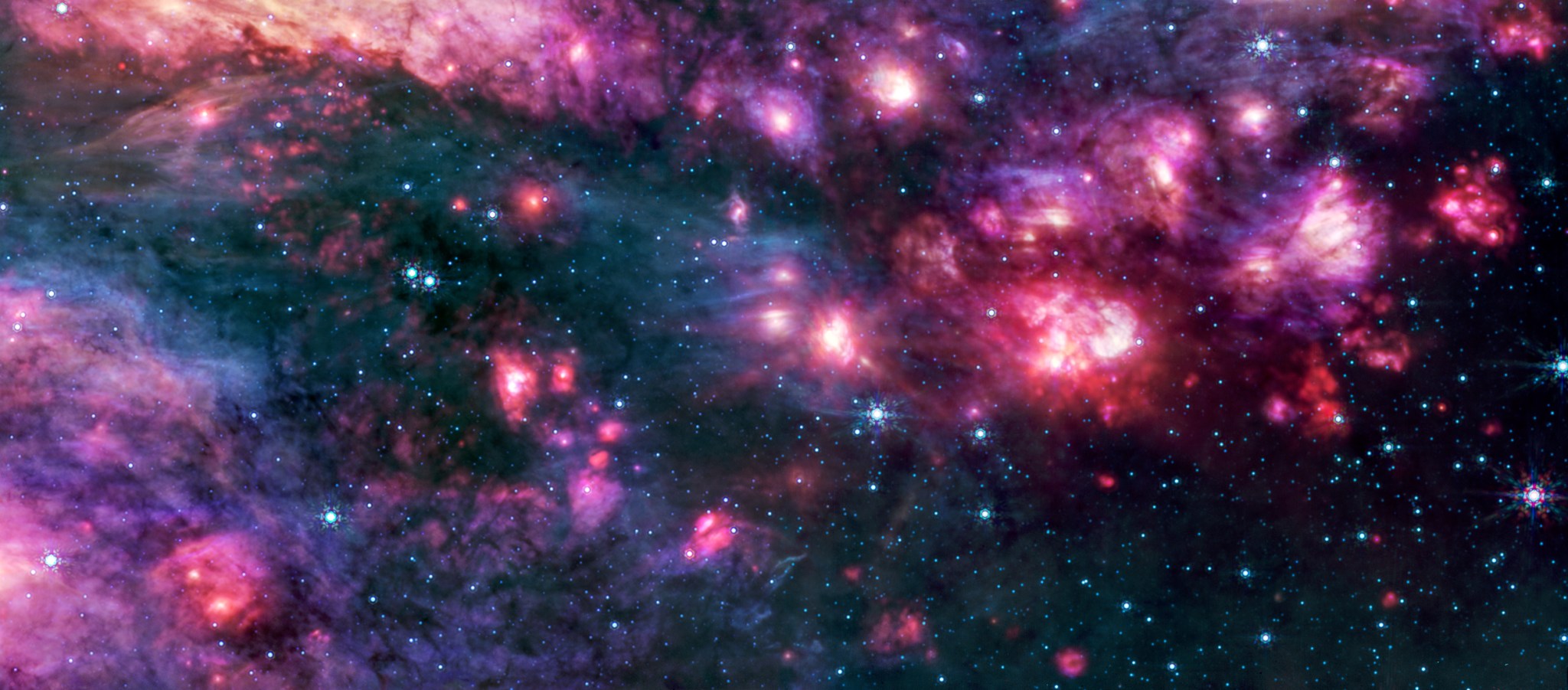

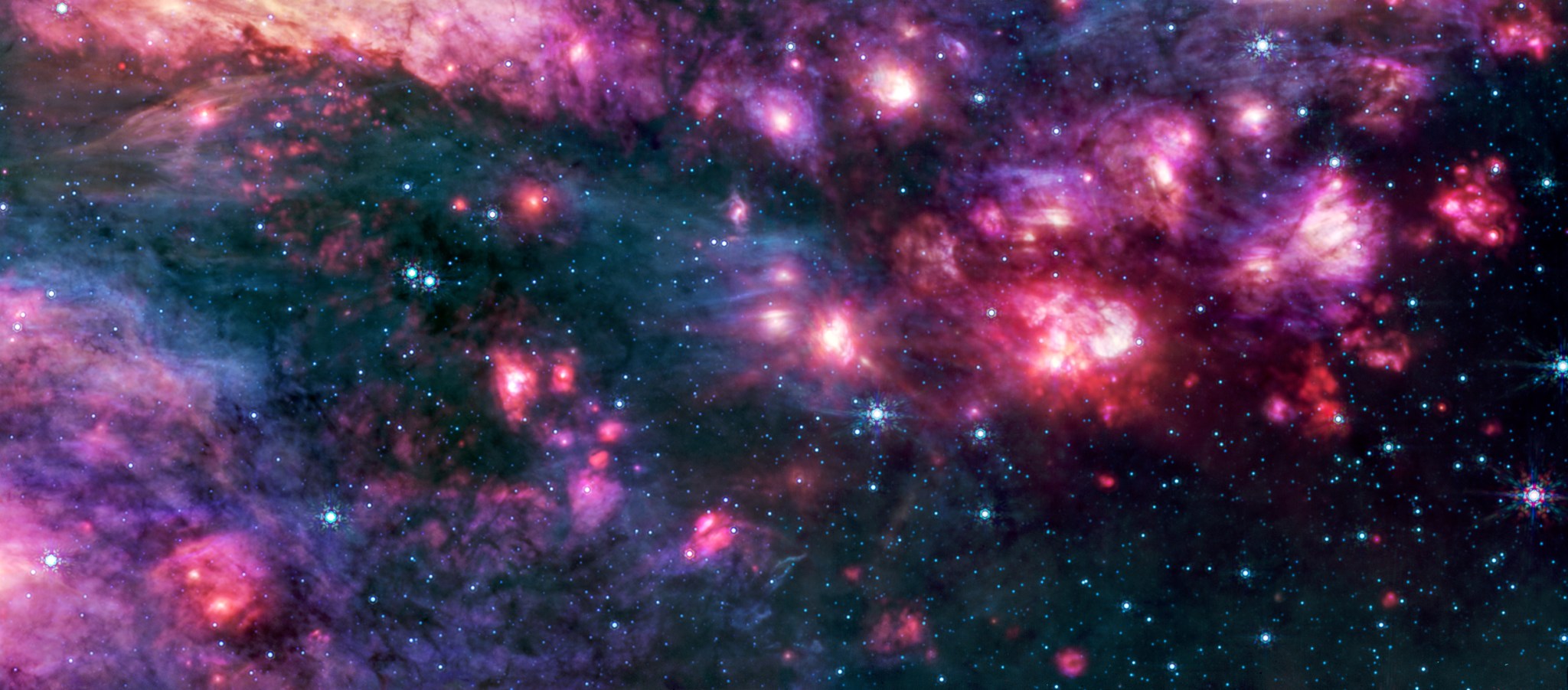
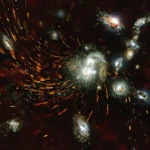
The Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope captured glowing cosmic dust heated by very young massive stars in unprecedented detail in this image of the Sagittarius B2 (Sgr B2) molecular cloud released on Sept. 24, 2025.
Sgr B2 is the most massive, and active star-forming region in our galaxy, located only a few hundred light years from our central supermassive black hole. While Sgr B2 has only 10% of the galactic center’s gas, it produces 50% of its stars. Astronomers want to figure out why it is so much more active than the rest of the galactic center.
MIRI has both a camera and a spectrograph that sees light in the mid-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. MIRI’s view reveals colorful stars punctuated occasionally by bright clouds of gas and dust. Further research into these stars will reveal details of their masses and ages, which will help astronomers better understand the process of star formation in this dense, active galactic center region.
Image credit: Image: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Adam Ginsburg (University of Florida), Nazar Budaiev (University of Florida), Taehwa Yoo (University of Florida); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly