Now Reading: Sunrise over NASA’s ‘quiet’ supersonic X-59 jet | Space photo of the day for Sept. 12, 2025
-
01
Sunrise over NASA’s ‘quiet’ supersonic X-59 jet | Space photo of the day for Sept. 12, 2025
Sunrise over NASA’s ‘quiet’ supersonic X-59 jet | Space photo of the day for Sept. 12, 2025
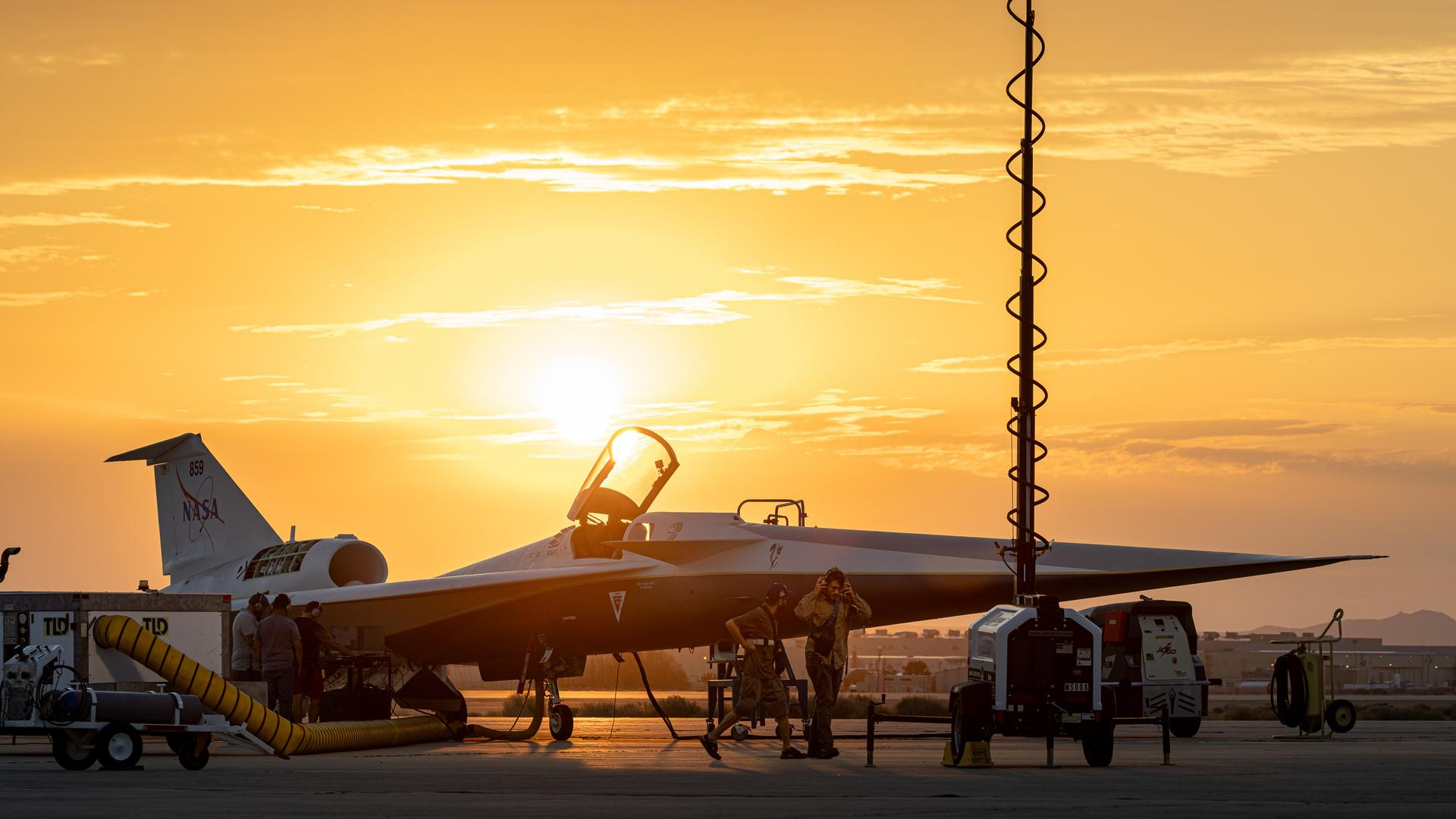

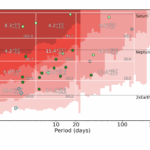
On July 18, 2025, NASA’s experimental X-59 supersonic research aircraft basked in golden light on the ramp at Lockheed Martin‘s Skunk Works facility before being put through a series of ground tests.
What is it?
The X-59 Quesst (Quiet SuperSonic Technology) is an experimental aircraft developed by Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works for NASA, designed to achieve supersonic speeds with dramatically reduced noise, transforming the traditional sonic “boom” into a softer “thump.”
Despite schedule delays in the early 2020s, the X-59 was delivered to NASA for flight testing in January 2025. Ground tests, including low-speed taxiing, began in mid-July, with a maiden flight expected later this year.
Where is it?
This photo was taken at the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California.
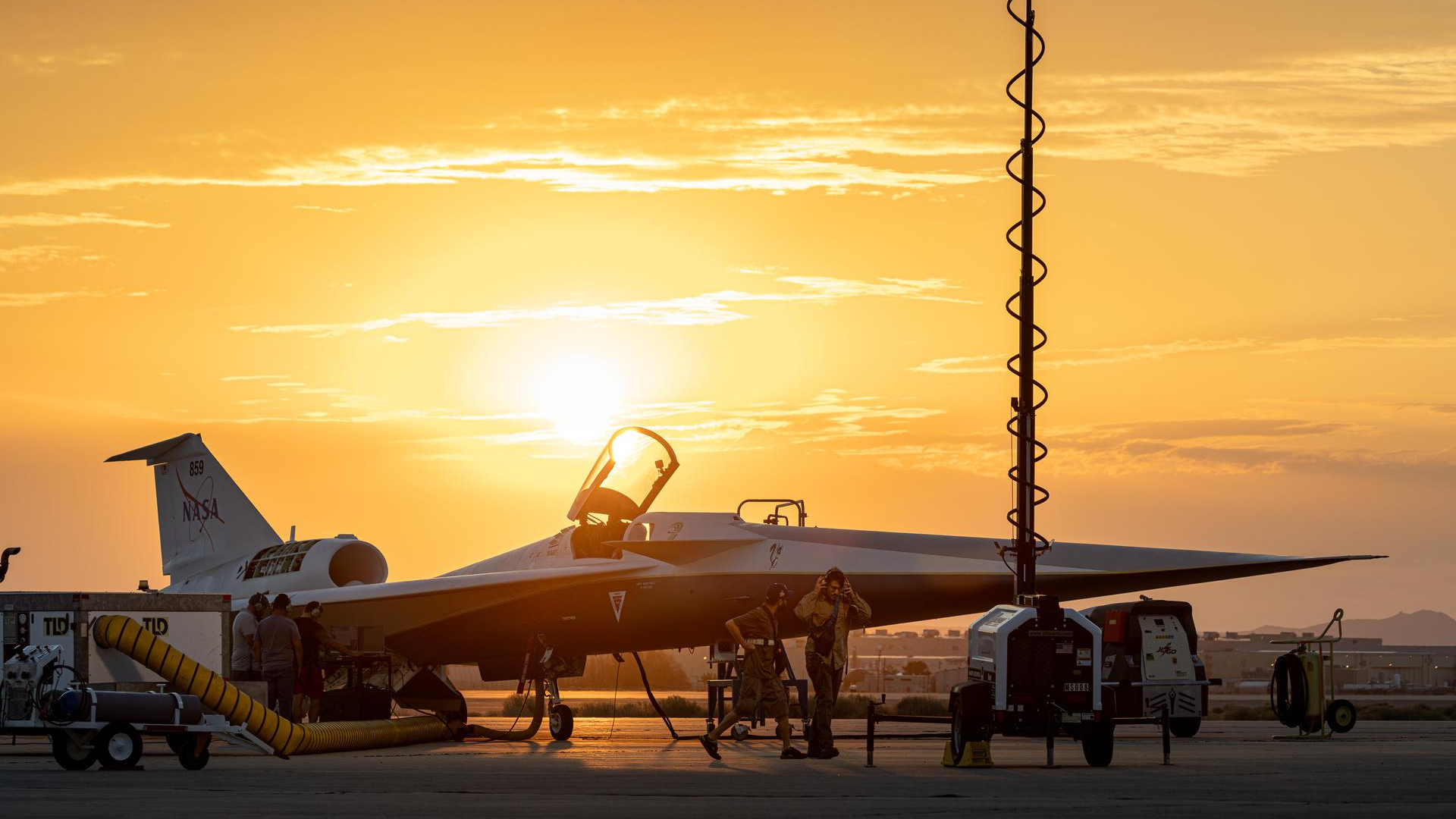

Why is it amazing?
Supersonic travel has long been restricted over land due to the disruptive noise of sonic booms. The X-59’s design works to avoid this issue by dampening the sound, potentially allowing for future commercial supersonic travel over populated areas.
NASA plans to conduct community overflights and gather public perception data on these quieter sonic thumps. The feedback will then be shared with the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration and international regulators to inform updates to noise regulations.
Want to learn more?
You can read more about the X-59 supersonic jet and NASA’s airplanes.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
06True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
07Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors