Now Reading: The Fraction Of Distilled White Dwarfs With Long-Lived Habitable Zones
-
01
The Fraction Of Distilled White Dwarfs With Long-Lived Habitable Zones
The Fraction Of Distilled White Dwarfs With Long-Lived Habitable Zones
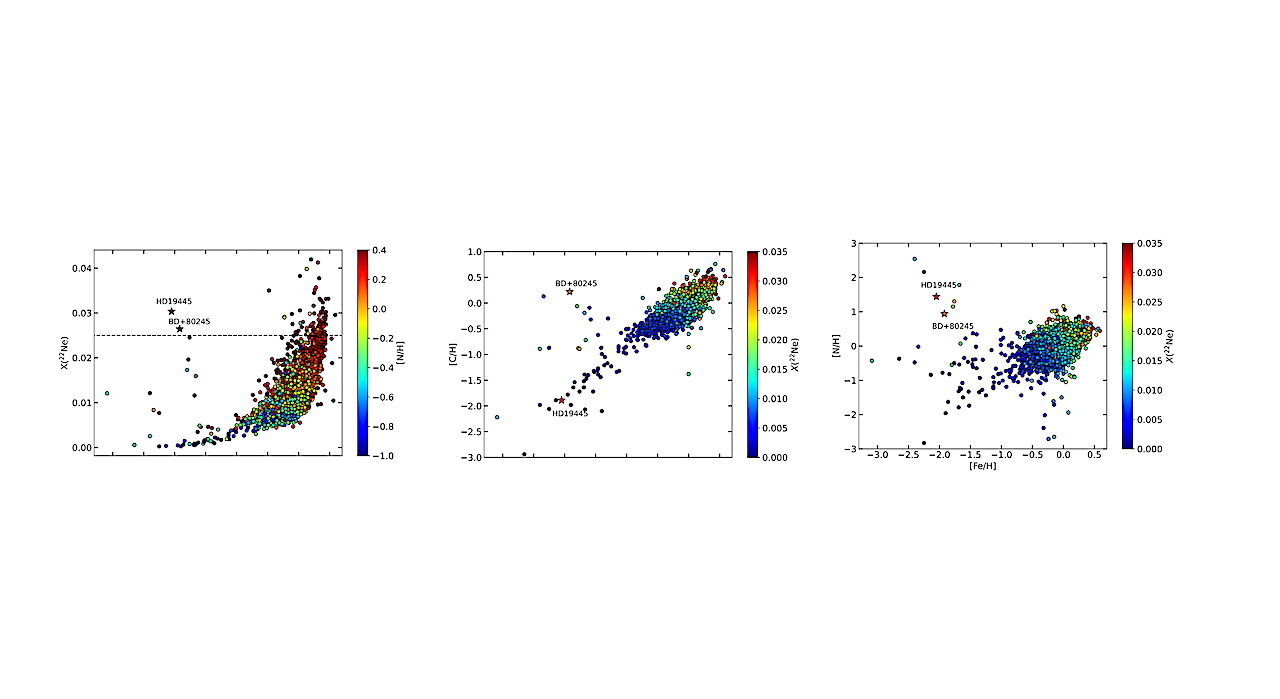

LEFT: Predicted 22Ne mass fraction as a function of metallicity for the WD remnants of stars in the Hypatia Catalog (Hinkel et al. 2014). The colors represent [N/H] for the same stars. MIDDLE and RIGHT: C and N abundances of the same stars from the Hypatia Catalog. The color bars represent the predicted neon mass fraction, X(22Ne), in their remnants. Two chemically peculiar low-metallicity objects, BD+80 245 and HD 19445, are labeled and marked as stars. — astro-ph.SR
After carbon and oxygen, 22Ne is the most abundant element in white dwarf interiors. As C/O white dwarfs (WDs) crystallize, they are predicted to go through a distillation process in the central layers if they have a sufficiently high 22Ne mass fraction of ≳2.5%.
Observational evidence for distillation comes from an over-density of WDs on the Q-branch in Gaia color-magnitude diagrams, which indicates that ∼6% of massive WDs are delayed in their cooling by as much as ∼10 Gyr.
However, it is unclear how these stars end up with such a high concentration of 22Ne and if a significant fraction of the more common average-mass WDs go through distillation. We argue that a significant metal-rich stellar population in the solar neighborhood should lead to distilled WDs, without requiring a binary merger.
We use MESA along with the CNO abundances derived from high-resolution spectroscopy of stars included in the Hypatia catalog to predict the 22Ne mass fraction in their descendant WDs. We find that 0.6-2.5% of the WDs in the solar neighborhood have sufficient 22Ne in their interiors to go through multi-Gyr cooling delays, which could significantly inflate their numbers in the observed samples.
Hence, 22Ne distillation and long-lived habitable zones around WDs should be relatively common in the solar neighborhood. We also use a Galactic model to predict the fraction of WDs that go through distillation as a function of Galactocentric distance. The fraction of distilled WDs is ∼2-8% near the Galactic center, and declines steadily toward the outer disk.
Manuel Barrientos, Mukremin Kilic, Simon Blouin, Michael R. Hayden, Sanjib Sharma, Matthew J. Green
Comments: Accepted for Publication in ApJL. 7 pages, 4 figures
Subjects: Solar and Stellar Astrophysics (astro-ph.SR); Astrophysics of Galaxies (astro-ph.GA)
Cite as: arXiv:2508.12600 [astro-ph.SR] (or arXiv:2508.12600v1 [astro-ph.SR] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2508.12600
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Manuel Barrientos
[v1] Mon, 18 Aug 2025 03:26:32 UTC (305 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.12600
Astrobiology,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly