Now Reading: TOI-283 b: A Transiting Mini-Neptune In A 17.6-day Orbit Discovered With TESS And ESPRESSO
-
01
TOI-283 b: A Transiting Mini-Neptune In A 17.6-day Orbit Discovered With TESS And ESPRESSO
TOI-283 b: A Transiting Mini-Neptune In A 17.6-day Orbit Discovered With TESS And ESPRESSO
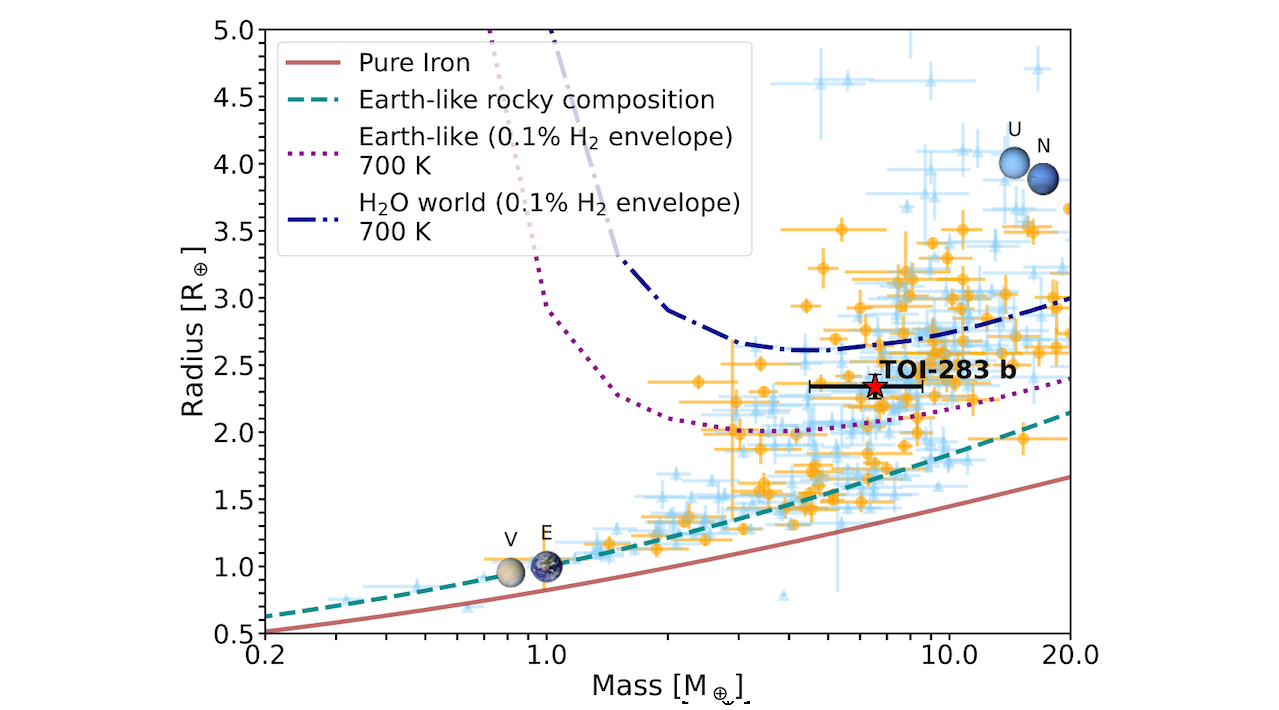

Mass-radius diagram for TOI-283 b (red star) and known transiting planets with mass determinations with a precision better than 30 % (parameters taken from the TEPCat database; Southworth 2011). Planets orbiting K-type stars (4000 ≤ Teff ≤ 5300 K) are marked with orange circles. The lines in the mass-radius diagram represent the composition models of Zeng et al. (2016, 2019) for planets with pure iron cores (100 % Fe, brown line), Earth-like rocky compositions (32.5 % Fe plus 67.5 % MgSiO3, dashed green line), Earth-like compositions with a 0.1% H2 envelope (dotted purple line), and a water world with a 0.1 % H2 gas envelope (dash-dotted blue line). We show some Solar System planets for reference (Venus, Earth, Uranus, and Neptune). — astro-ph.EP
Super-Earths and mini-Neptunes are missing from our Solar System, yet they appear to be the most abundant planetary types in our Galaxy.
A detailed characterization of key planets within this population is important for understanding the formation mechanisms of rocky and gas giant planets and the diversity of planetary interior structures. In 2019, NASA’s TESS satellite found a transiting planet candidate in a 17.6-day orbit around the star TOI-283.
We started radial velocity (RV) follow-up observations with ESPRESSO to obtain a mass measurement. Mass and radius are measurements critical for planetary classification and internal composition modeling. We used ESPRESSO spectra to derive the stellar parameters of the planet candidate host star TOI-283. We then performed a joint analysis of the photometric and RV data of this star, using Gaussian processes to model the systematic noise present in both datasets.
We find that the host is a bright K-type star (d=82.4 pc, Teff=5213±70 K, V=10.4 mag) with a mass and radius of M⋆=0.80±0.01M⊙ and R⋆=0.85±0.03R⊙. The planet has an orbital period of P=17.617 days, a size of Rp=2.34±0.09R⊕, and a mass of Mp=6.54±2.04M⊕. With an equilibrium temperature of ∼600 K and a bulk density of ρp=2.81±0.93 g cm−3, this planet is positioned in the mass-radius diagram where planetary models predict H2O- and H/He-rich envelopes.
The ESPRESSO RV data also reveal a long-term trend that is probably related to the star’s activity cycle. Further RV observations are required to confirm whether this signal originates from stellar activity or another planetary body in the system.
F. Murgas, E. Pallé, A. Suárez Mascareño, J. Korth, F. J. Pozuelos, M. J. Hobson, B. Lavie, C. Lovis, S. G. Sousa, D. Bossini, H. Parviainen, A. Castro-González, V. Adibekyan, C. Allende Prieto, Y. Alibert, F. Bouchy, C. Briceño, D. A. Caldwell, D. Ciardi, C. Clark, K. A. Collins, K. I. Collins, S. Cristiani, X. Dumusque, D. Ehrenreich, P. Figueira, E. Furlan, R. Génova Santos, C. Gnilka, J. I. González Hernández, Z. Hartman, S. B. Howell, J. M. Jenkins, N. Law, C. Littlefield, G. Lo Curto, A. W. Mann, C. J. A. P. Martins, A. Mehner, G. Micela, P. Molaro, N. J. Nunes, F. Pepe, R. Rebolo, H. M. Relles, N. C. Santos, N. J. Scott, S. Seager, A. Sozzetti, S. Udry, C. N. Watkins, J. N. Winn, M. R. Zapatero Osorio, C. Ziegler
Comments: Accepted for publication in A&A, 25 pages, 20 figures
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP); Solar and Stellar Astrophysics (astro-ph.SR)
Cite as: arXiv:2510.15084 [astro-ph.EP] (or arXiv:2510.15084v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2510.15084
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Felipe Murgas
[v1] Thu, 16 Oct 2025 18:59:42 UTC (7,872 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.15084
Astrobiology, Exoplanet,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly