Now Reading: Towards the Habitable Worlds Observatory: 1D CNN Retrieval of Reflection Spectra from Evolving Earth Analogs
-
01
Towards the Habitable Worlds Observatory: 1D CNN Retrieval of Reflection Spectra from Evolving Earth Analogs
Towards the Habitable Worlds Observatory: 1D CNN Retrieval of Reflection Spectra from Evolving Earth Analogs
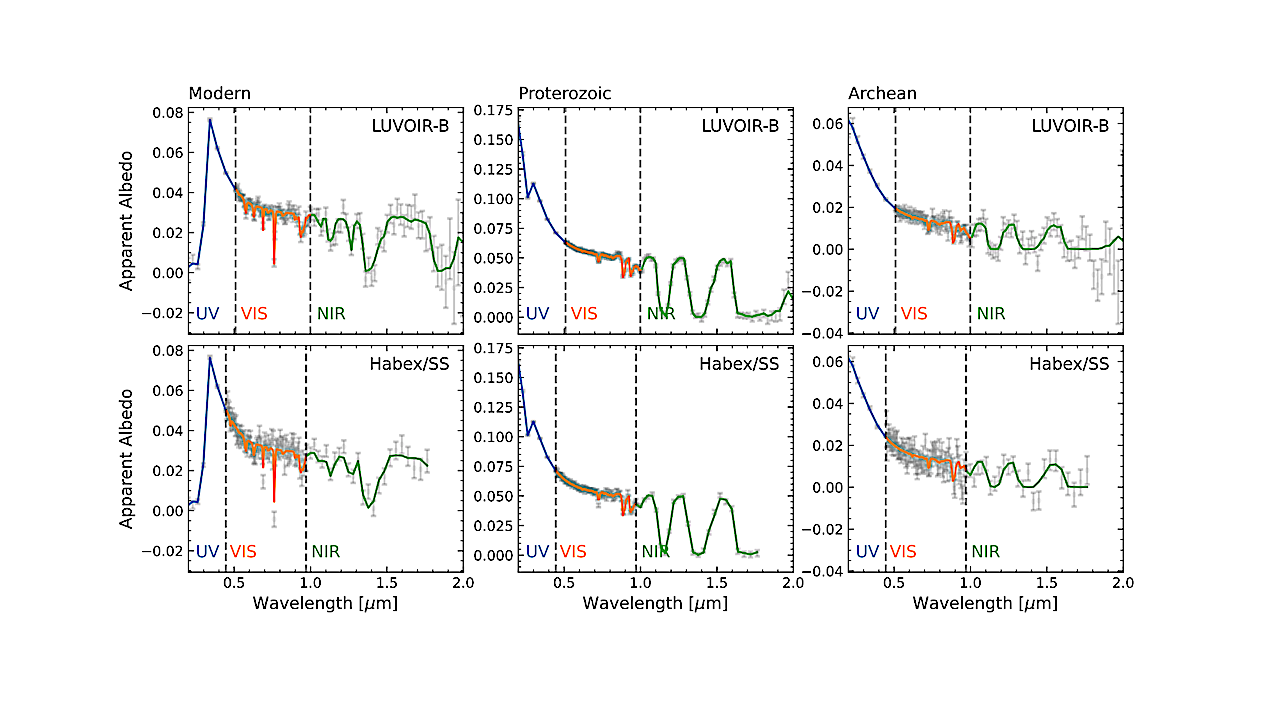

Examples of training reflection spectra for Earth-like exoplanets in the Archean (left), Proterozoic (center), and Modern (right) eras, observed with LUVOIR-B (top row) and Habex/SS (bottom row). Colored lines represent the total radiance 𝐴(𝜆), while points with error bars correspond to 𝐴noisy (𝜆) as defined by Equation 13. — astro-ph.EP
However, traditional atmospheric retrieval frameworks are too computationally intensive to explore the high-dimensional parameter spaces such missions will generate.
Here, we present a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D CNN), trained on over one million synthetic, noise-injected spectra simulating Archean, Proterozoic, and Modern Earth analogs, as observed by LUVOIR-B (0.2-2.0 μm) and HabEx/SS (0.2-1.8 μm).
Our model simultaneously infers six molecular abundances (including biosignatures O2 and O3 ) along with radius, gravity, surface pressure, and temperature. Inference on unseen test data is performed via Monte Carlo Dropout, enabling uncertainty estimation across thousands of realizations within seconds.
The network performs best where spectral features are prominent, accurately recovering CH4 and CO2 in Archean atmospheres and O2 and O3 in Modern cases, while avoiding false positives and outputting near-zero abundances in scenarios of true absence such as Archean O2 and O3 . Interpretation via Integrated Gradients confirms that the model bases its predictions on physically meaningful features, including the Fraunhofer A band for O2, and the Hartley-Huggins band for O3 .
Credibility curve analysis indicates that O3 remains retrievable across a wide range of stellar types and distances, while O2 is detectable out to 12 pc around FG stars. These results elevate the CNN from proof of concept to a mission-ready retrieval engine, capable of processing direct-imaging spectra with HWO on an operational cadence.
Sarah G. A. Barbosa, Raissa Estrela, Paulo C. F. da Silva Filho, Daniel B. de Freitas
Comments: 19 pages, 9 figures, submitted to MNRAS
Subjects: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP)
Cite as: arXiv:2508.00076 [astro-ph.EP](or arXiv:2508.00076v1 [astro-ph.EP] for this version)
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2508.00076
Focus to learn more
Submission history
From: Sarah Barbosa
[v1] Thu, 31 Jul 2025 18:10:12 UTC (4,445 KB)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.00076
Astrobiology, exoplanet,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly