Now Reading: Tuning a NASA Instrument: Calibrating MASTER
-
01
Tuning a NASA Instrument: Calibrating MASTER
Tuning a NASA Instrument: Calibrating MASTER

2 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
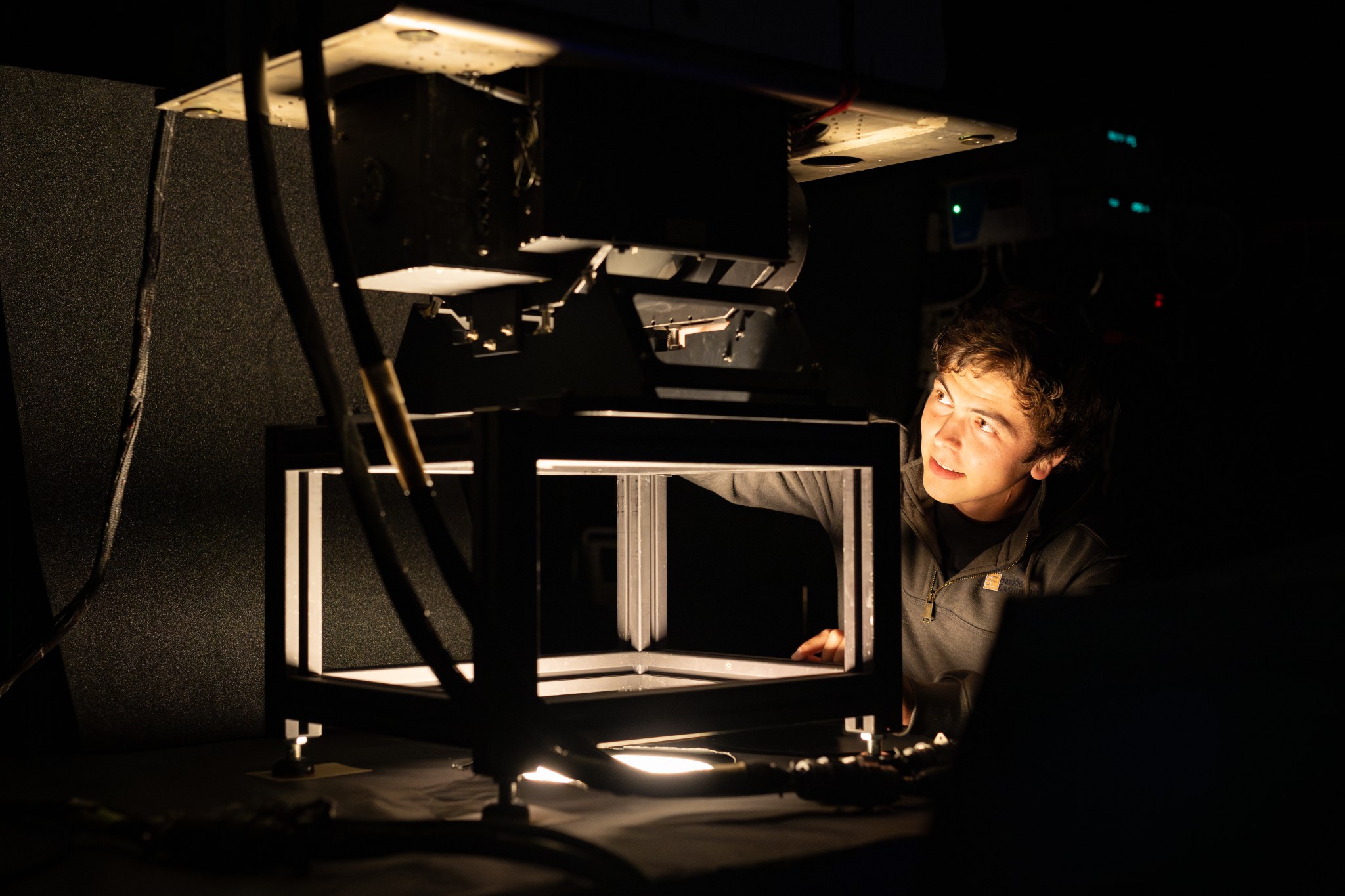

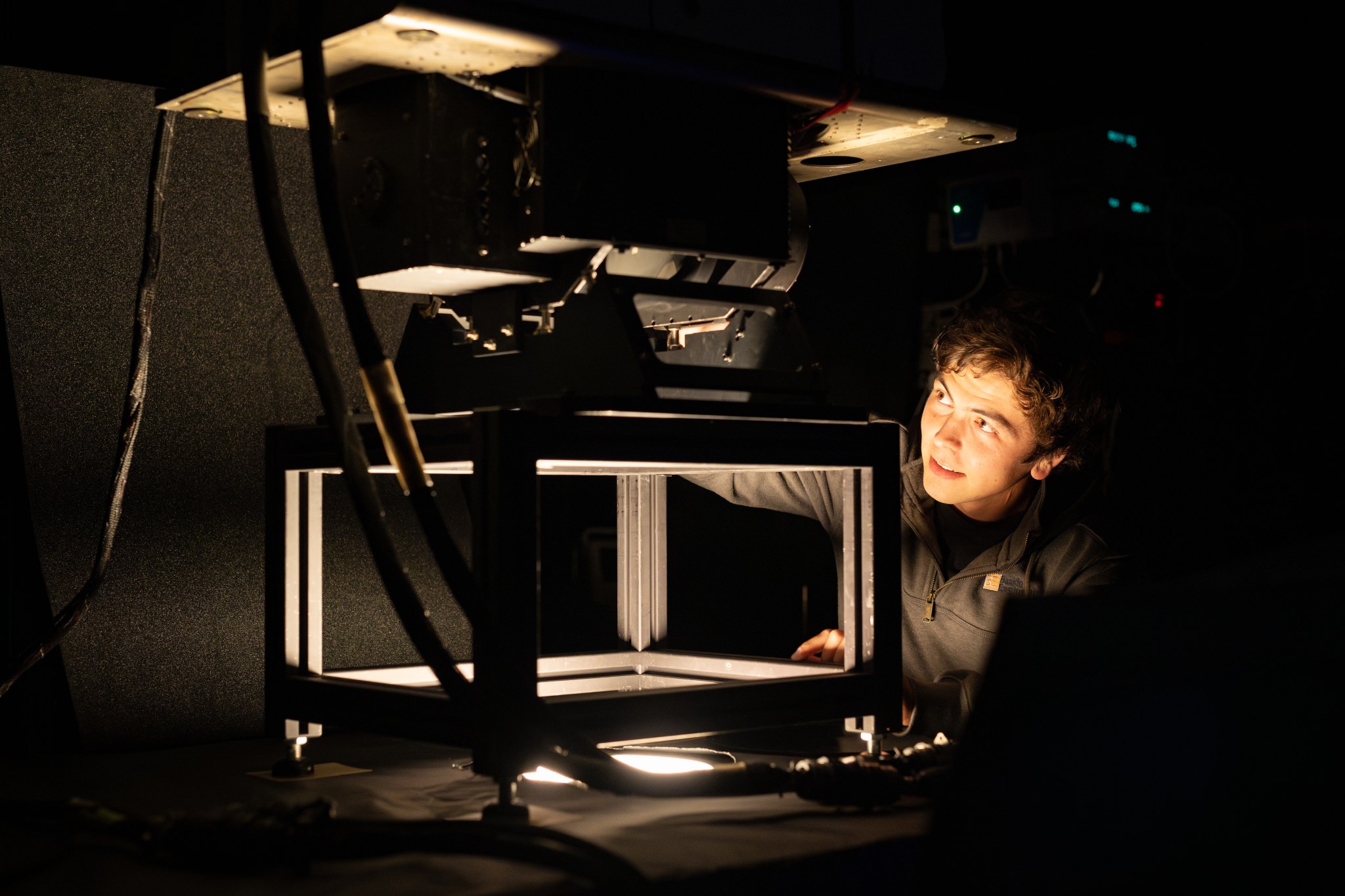
NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley houses a unique laboratory: the Airborne Sensor Facility (ASF). The engineers at the ASF are responsible for building, maintaining, and operating numerous instruments that get deployed on research aircraft, but one of their most important roles is instrument calibration.
Think of calibration like tuning a piano between performances: A musician uses a tuner to set the standard pitch for each string, ensuring that the piano remains on pitch for every concert.
The “tuners” at ASF include lasers, mirrors, and a light source called an integrating sphere – a hollow sphere about 36 inches in diameter that emits a set amount of light from a hole in the top. By checking an instrument against this baseline between each mission, engineers ensure that the instrument sensors provide accurate, reliable data every time.
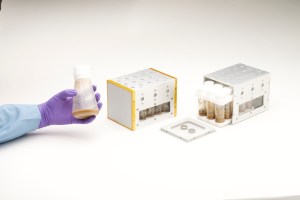
In the photo above, electrical engineer Nikolas Gibson performs calibration tests on the MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER) spectrometer, co-developed by NASA Ames and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
A spectrometer separates light into individual wavelengths, providing researchers with information about the properties of whatever is creating or interacting with that light. The MASTER instrument measures about 50 individual spectral channels, providing data on wavelengths from the visible spectrum through the infrared.
When it comes to calibration, each of these channels functions like a specific key on a piano and needs to be individually checked against the “tuner.” By pointing the instrument’s sensor at a known quantity of light coming from the integrating sphere, the team checks the accuracy of MASTER’s data output and repairs or adjusts the sensor as needed.
In this image, MASTER had returned from an April 2025 scientific campaign observing prescribed fires in Alabama and Georgia with NASA’s FireSense project. It was recalibrated before heading back into the field for the Geological Earth Mapping Experiment, or GEMx, mission in late May 2025, which will use the instrument to help map critical minerals across the southwestern United States.
About the Author
Milan Loiacono
Milan Loiacono is a science communication specialist for the Earth Science Division at NASA Ames Research Center.
Share
Details
Related Terms
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly