Now Reading: Winter Grips the Michigan Mitten
-
01
Winter Grips the Michigan Mitten
Winter Grips the Michigan Mitten
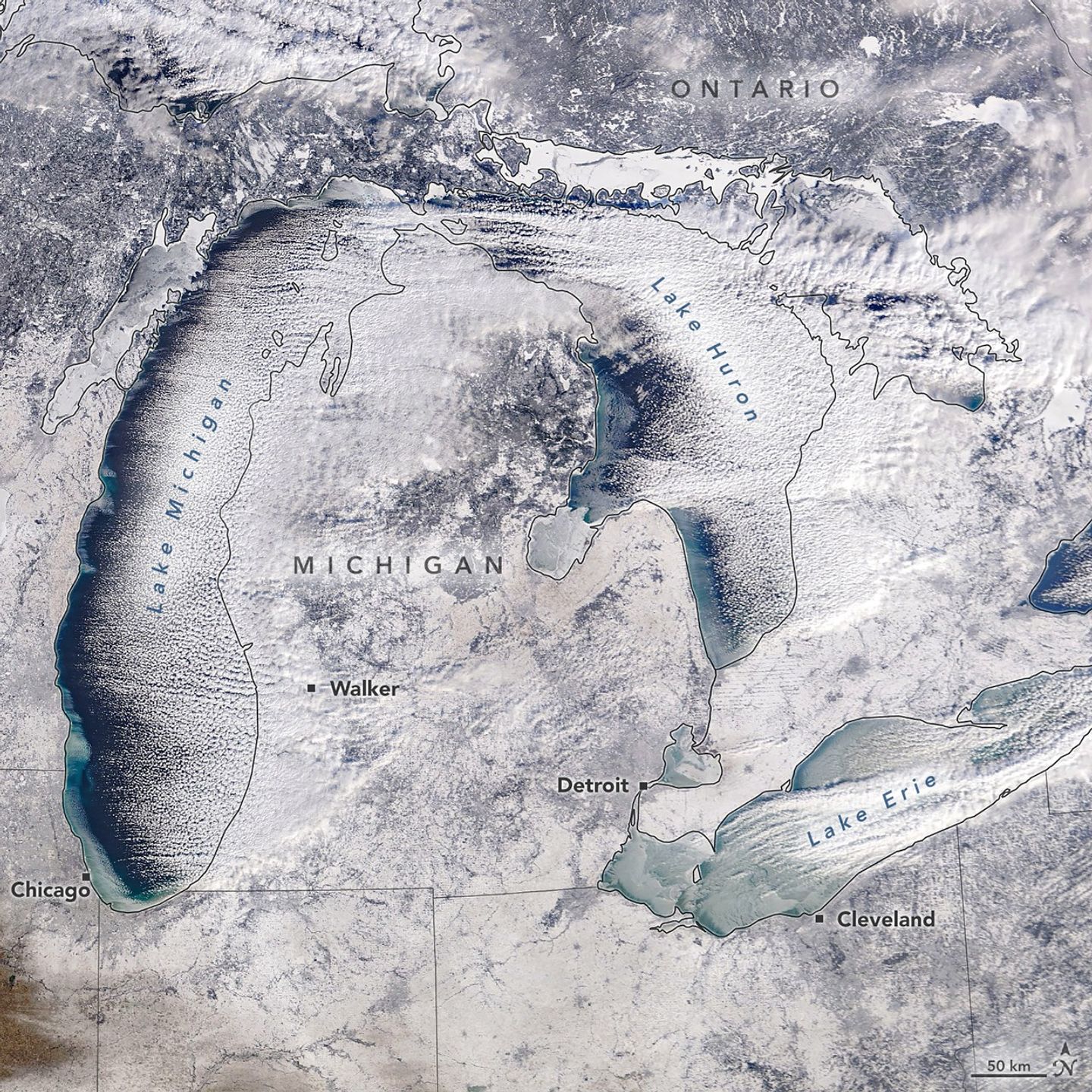
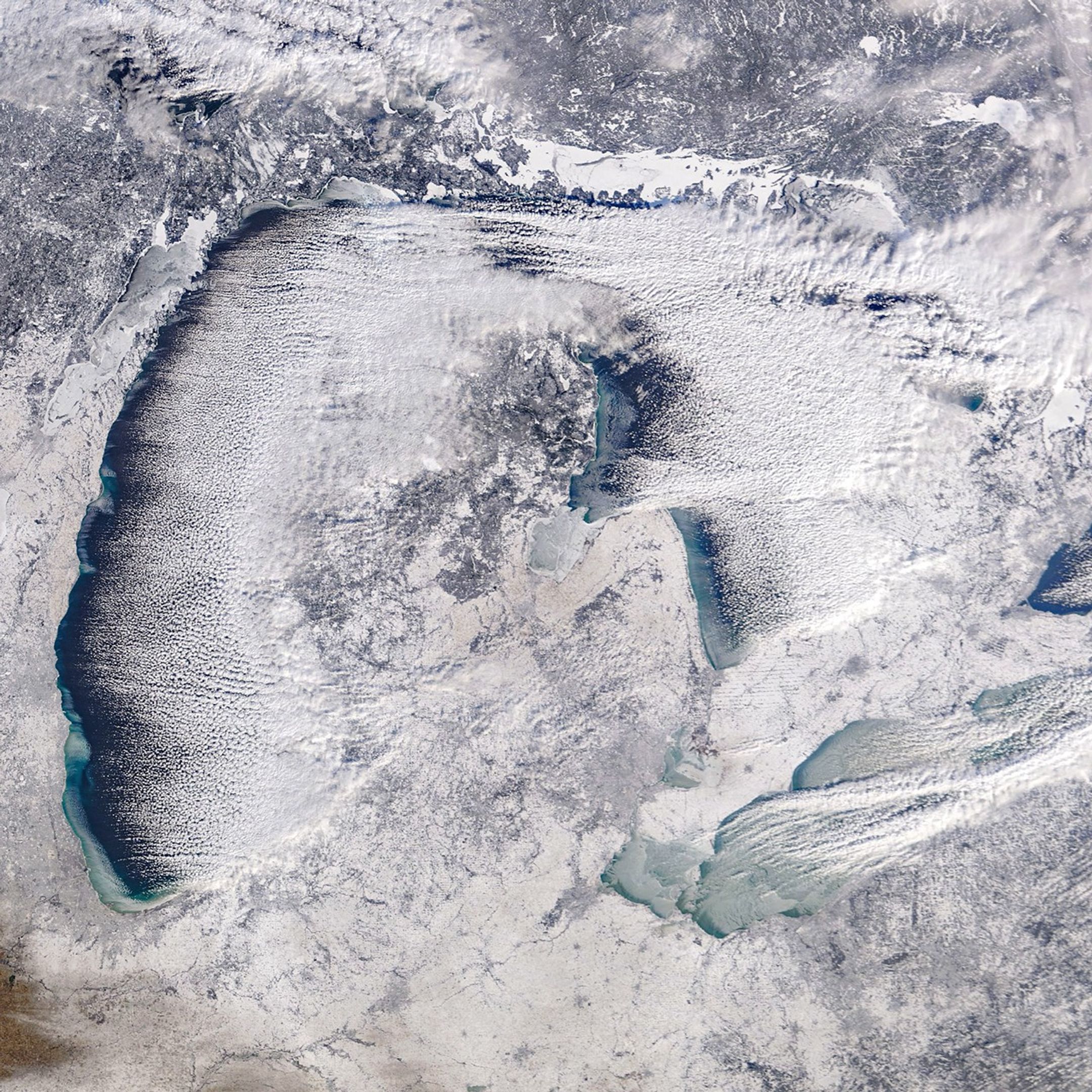
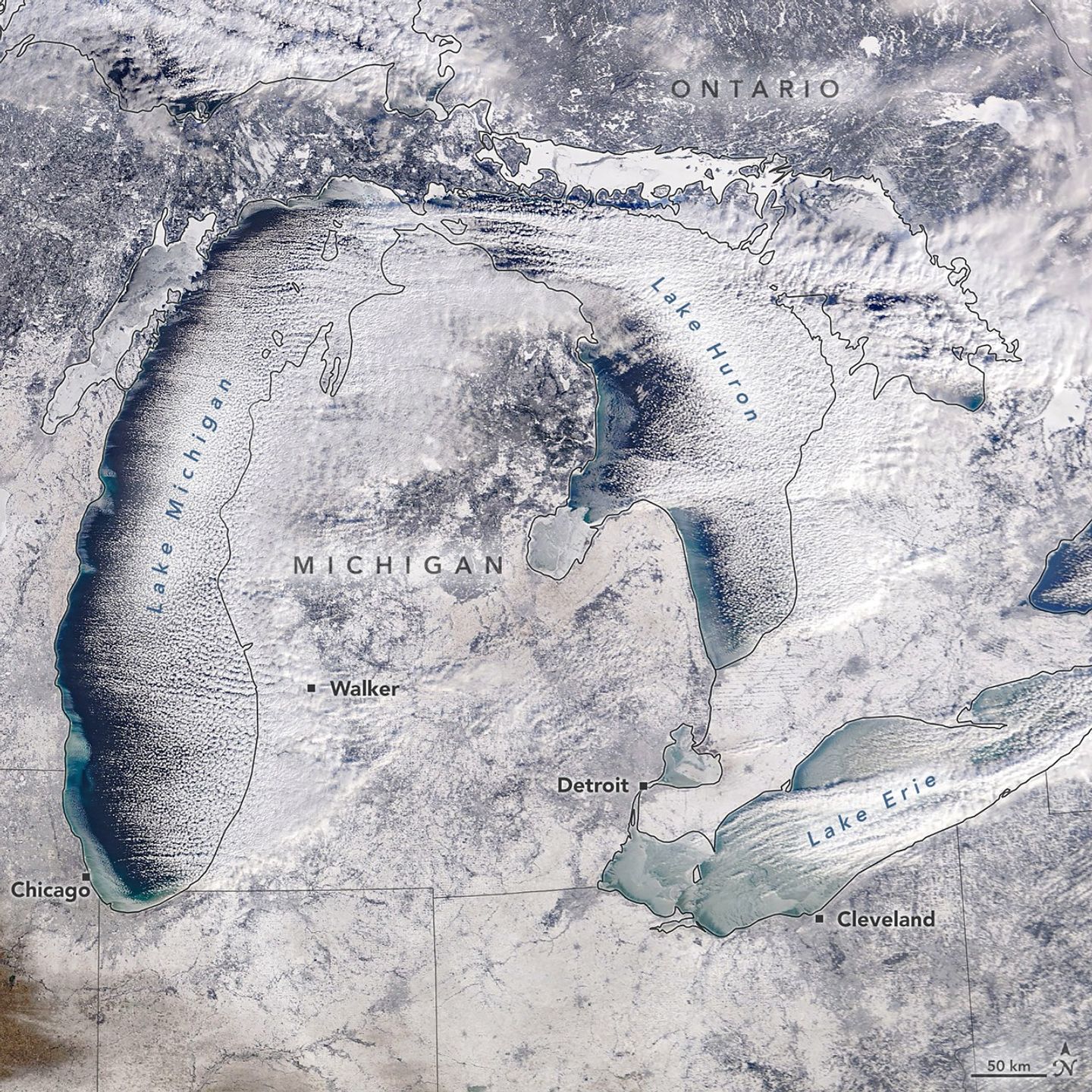
A winter chill descended on the Great Lakes region of North America in January 2026. Some of the effects were apparent in this satellite image as newly formed lake ice and a fresh layer of snow. The image, acquired by the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) instrument on NASA’s Terra satellite, shows the region on the morning of January 20, 2026.
In the days prior, a winter storm blanketed many parts of western Michigan near the lake with nearly a foot of snow, according to the National Weather Service. West of Walker, snowfall totals surpassed that amount, reaching nearly 14 inches (36 centimeters). The storm’s effects extended beyond Michigan as well, including blizzard conditions in parts of Ontario east of Lake Huron.
Lake effect snow is common in the Great Lakes area during late fall and winter, occurring when cold air moves over relatively warm, unfrozen water. As the air picks up heat and moisture, it rises to form narrow cloud bands that can produce heavy snowfall.
The air over Lake Erie was still moist enough for clouds to form, though the amount of open water on this lake has decreased sharply in recent days. Around mid-month, during a period of unseasonably warm air temperatures, ice coverage dropped to cover about 2 percent of the lake, according to the NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory. It then spiked to nearly 85 percent on January 21 after temperatures plummeted.
The frigid temperatures were brought about by an Arctic cold front that moved across the region. In Cleveland, for instance, the weather service issued a cold weather advisory on January 19 for wind chills as low as minus 15 to 20 degrees Fahrenheit. On that day, even colder wind chills were reported in the area around Chicago. Forecasts called for another round of cold Arctic air to spill over the Great Plains and Eastern U.S. over the coming weekend, accompanied by heavy snow.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Michala Garrison, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. Story by Kathryn Hansen.
References & Resources
- CBC Lite (2026, January 20) Several rural roads closed as heavy snow, intense winds batter Huron, Perth. Accessed January 22, 2026.
- Cleveland.com (2026, January 20) Lake Erie freezing rapidly: See how fast. Accessed January 22, 2026.
- Cleveland.com (2026, January 19) Northeast Ohio school closings and delays for Tuesday, Jan. 20, 2026. Accessed January 22, 2026.
- National Weather Service What is Lake Effect Snow? Accessed January 22, 2026.
- National Weather Service (2026, January 22) Short Range Public Discussion. Accessed January 22, 2026.
- NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory (2026, January 21) Lake Erie Average Ice Cover. Accessed January 22, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

Rounding out a remarkable year, the outback lake displayed distinct green and reddish water in its two main bays.
Another major tributary reached the Australian outback lake in 2025, extending the months-long flood of the vast, ephemeral inland sea.

An asteroid that struck the rainforest in Africa around 1 million years ago created Ghana’s only natural lake.Â
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer
04True Anomaly hires former York Space executive as chief operating officer -
 05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
05Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
06Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly