Now Reading: Plasmidome, Resistome, and Virulence-associated Genes Characterization of Acinetobacter Johnsonii in NASA Cleanrooms and a Clinical Setting
-
01
Plasmidome, Resistome, and Virulence-associated Genes Characterization of Acinetobacter Johnsonii in NASA Cleanrooms and a Clinical Setting
Plasmidome, Resistome, and Virulence-associated Genes Characterization of Acinetobacter Johnsonii in NASA Cleanrooms and a Clinical Setting

Evidence shows persistence of non-spore-forming Acinetobacter johnsonii in high-stakes controlled and nutrient-limited environments.
This study aims to explore the mechanisms underpinning such adaptability through a comprehensive genomic analysis of 22 isolates of A. johnsonii from NASA Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) and one carbapenem-resistant strain (E154408A) from patient colonization in Ireland.
Core-genome phylogeny revealed clustering of PHSF-originating isolates in a monophyletic clade divergent from the main species lineage. Species-wide virulence-associated genes and metabolic profiling indicated the unique presence in PHSF-originating isolates of two complete efflux pumps and of a conserved allantoin racemase, suggesting adaptability for multiple environmental stresses.
Observed ubiquity of blaOXA in investigated genomes (n=112) and phenotypically-validated multidrug-resistant profile of E154408A strain highlight the potential of A. johnsonii as antimicrobial resistance (AMR) reservoir.
Plasmidome analysis suggested gain/loss events across the monophyletic population and potential AMR acquisition pathways. Genome-to-metagenome mapping identified genomic signatures of A. johnsonii in PHSF >10 years post initial isolation.

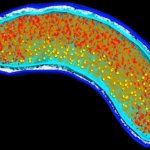
Phylogenomic analysis. Phylogeny of PHSF-originating isolates (highlighted in 431 yellow) and E154408A strain (orange) inferred through Maximum Likelihood. Pie Charts 432 associated with the terminal branches represent identified ARGs in correspondent genomes. A. johnsonii reference genome ANC 3681 and CIP 64.6T 433 type strain are highlighted in respectively 434 red and purple. The reference genome of A. haemolyticus HW-2A served as an outgroup. — biorxiv.org
Plasmidome, resistome, and virulence-associated genes characterization of Acinetobacter johnsonii in NASA cleanrooms and a clinical setting., biorxiv.org
Astrobiology, Genomics,
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
03Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
06Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly -
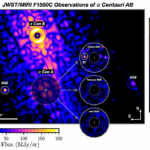 07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
07Worlds Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of α Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits