One of the most vivid portraits of “reborn” black hole activity—likened to the eruption of a “cosmic volcano” spreading almost 1 million light-years across space—has been captured in a gigantic
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astronomers has discovered a new Type II supernova. The newly detected supernova, named SN Eos, exploded when the universe
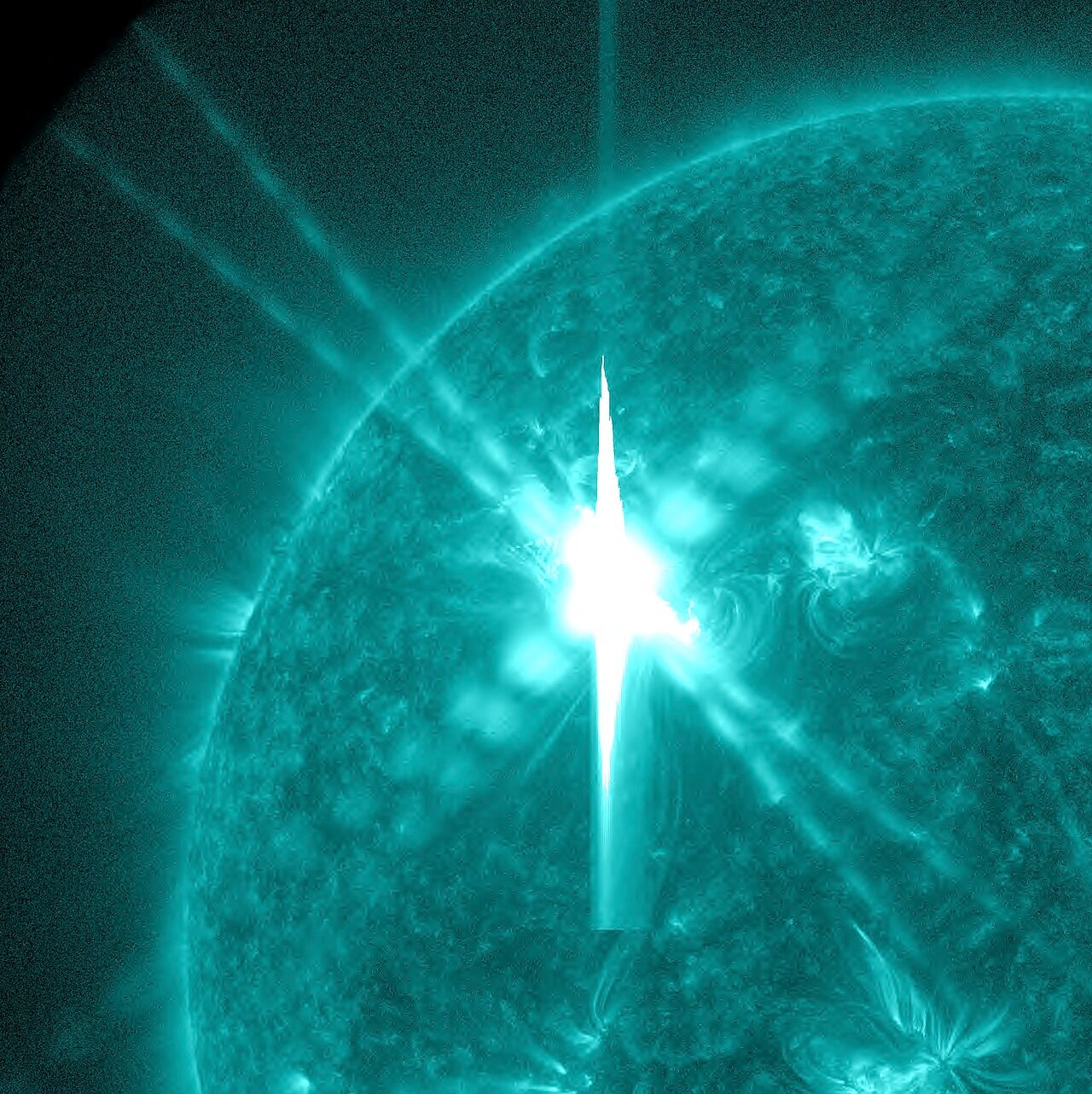
Scientists have finally identified where some of the most powerful radiation bursts from solar flares originate, solving a mystery that has puzzled solar physicists for decades. Researchers at the New
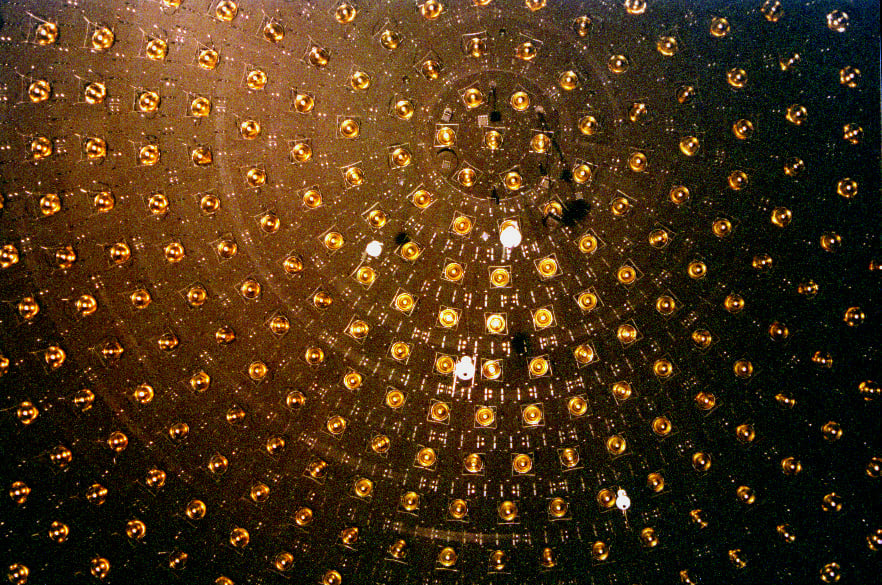
Every second, a trillion ghost particles stream through your body unnoticed, invisible messengers carrying secrets from the hearts of distant stars. Astrophysicists at the University of Copenhagen have now mapped
There is a fundamental tension in space exploration that has created ongoing debates for decades. By creating the infrastructure we need to explore other worlds, we damage them in some
When fire breaks out in the low-gravity, high-stakes conditions inside spacecraft or space stations, it behaves very differently than back here on Earth.
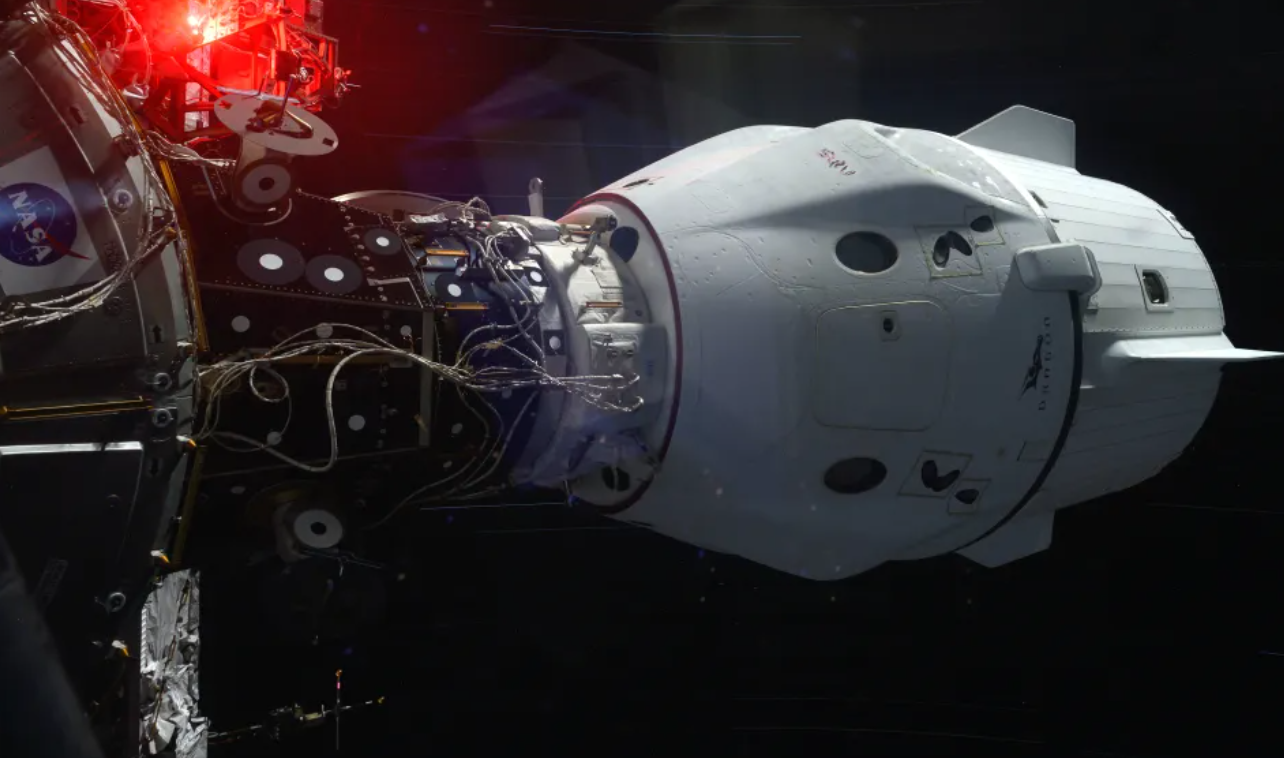
NASA gave the go for the SpaceX Crew-11 mission to depart the International Space Station on Wednesday headed for an overnight splashdown back on Earth in the Pacific Ocean.
What exists beneath the surface of Jupiter’s icy moon, Callisto? This is what a recent study accepted by The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers
A research team from the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with domestic and international partners, has carried out observational studies on SN 2024gy—a high-velocity
In a historic first, an unspecified medical issue is prompting an early return from the International Space Station on Wednesday night, January 14th. And while the return will be featured
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly