Galaxy clusters are formed by a dense packing of many galaxies, making them the most massive structures in the universe. Their progenitors, protoclusters, show these galaxies in their infancy, offering
Using the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT), Indian astronomers have performed multi-frequency observations of a repeating fast radio burst designated FRB 20201124A. Results of these observations shed more light
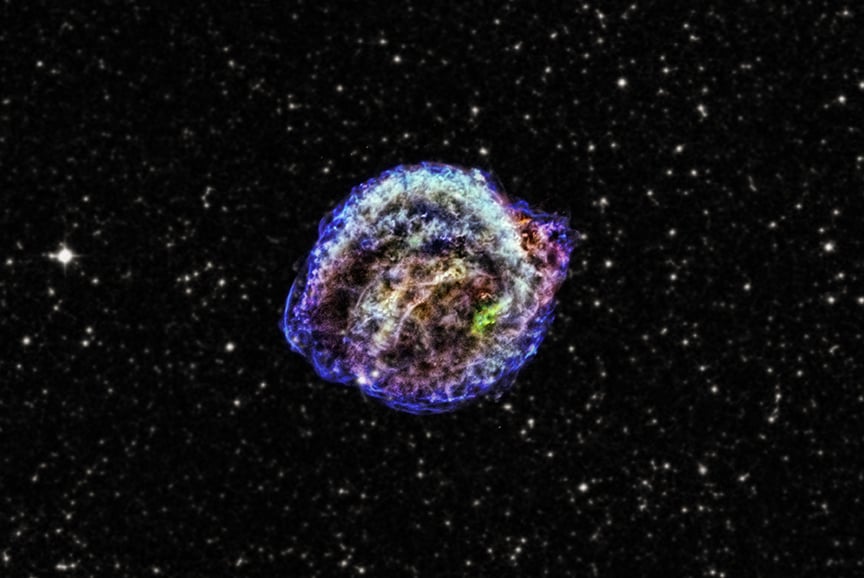
A new video shows the evolution of Kepler’s Supernova Remnant using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory captured over more than two and a half decades.
So let’s say you set up an experiment to measure a quantum property of subatomic particles. Like, I don’t know, spin.
All of physics rests on causal determinism. It’s like…how we do physics. It IS physics.
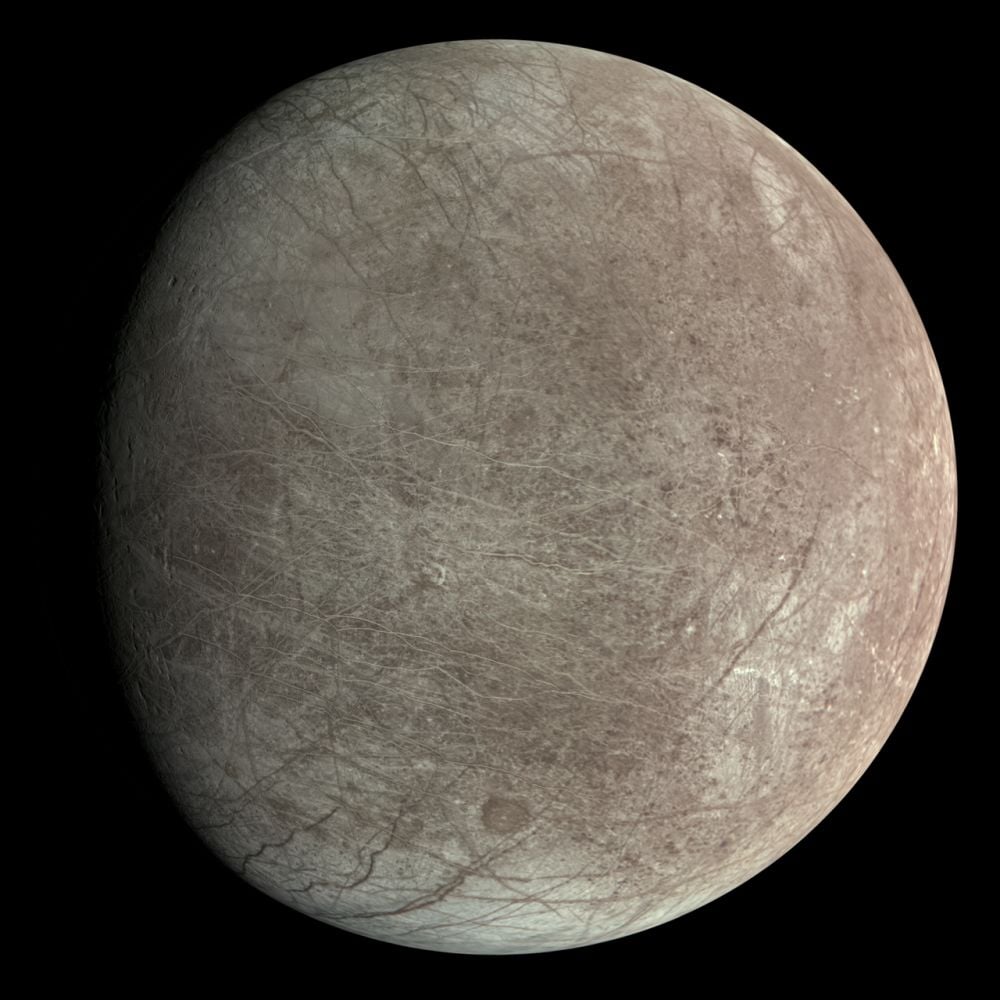
New research shows that Jupiter’s moon Europa, one of the prime targets in the search for life, may not have the conditions required after all. The research shows that the
What will we see in the southern sky in 2026? A total eclipse of the moon (at a convenient time), a blue moon and a supermoon, the two brightest planets
Scientists are a step closer to solving one of the universe’s biggest mysteries as new research finds evidence that two of its least understood components may be interacting, offering a
Google, SpaceX and Blue Origin are reportedly racing to develop technology for AI data centers in space, but it will likely be years before we see them rocketing into the
Check this out. There are some experiments that just make you…stop. That make you reconsider everything you’ve ever known.
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly