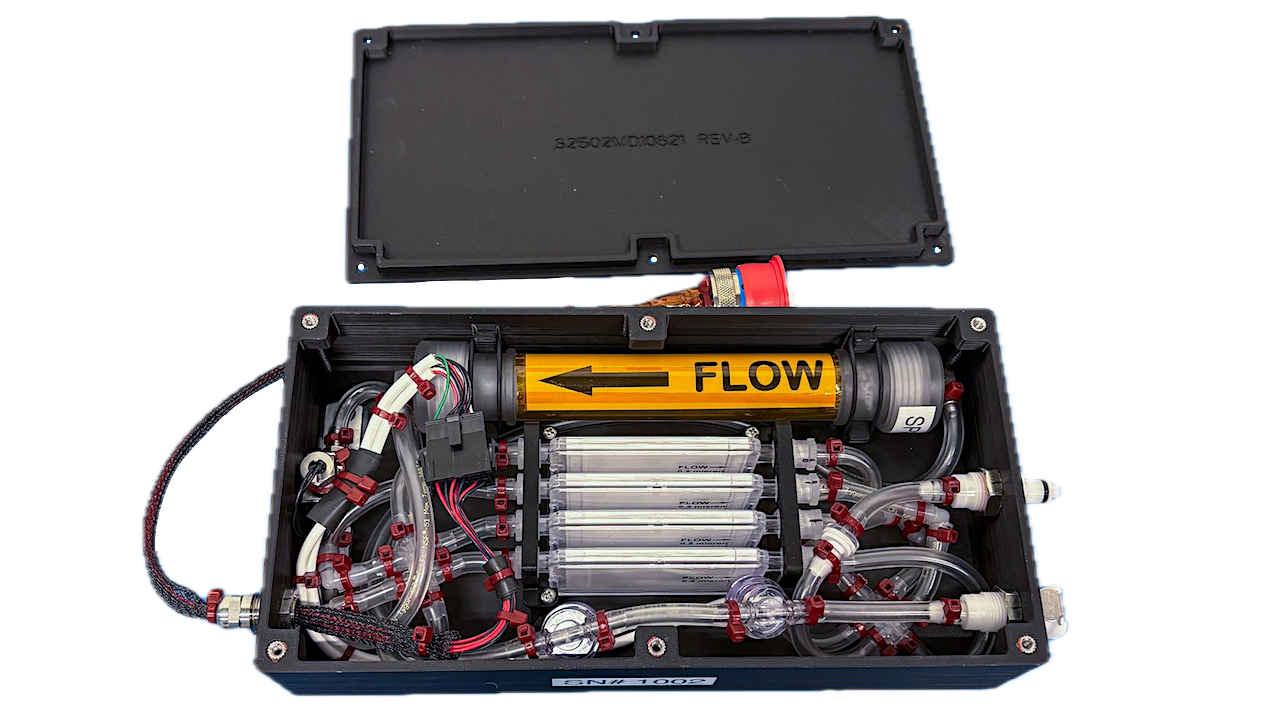
jsc2026e004238 (February 02, 2026) Larger image Credit: NASA. Editor’s note: in addition to biomedical uses for crew health, having the ability to produce sterile solutions – in space – can
Astrobiology11- Page
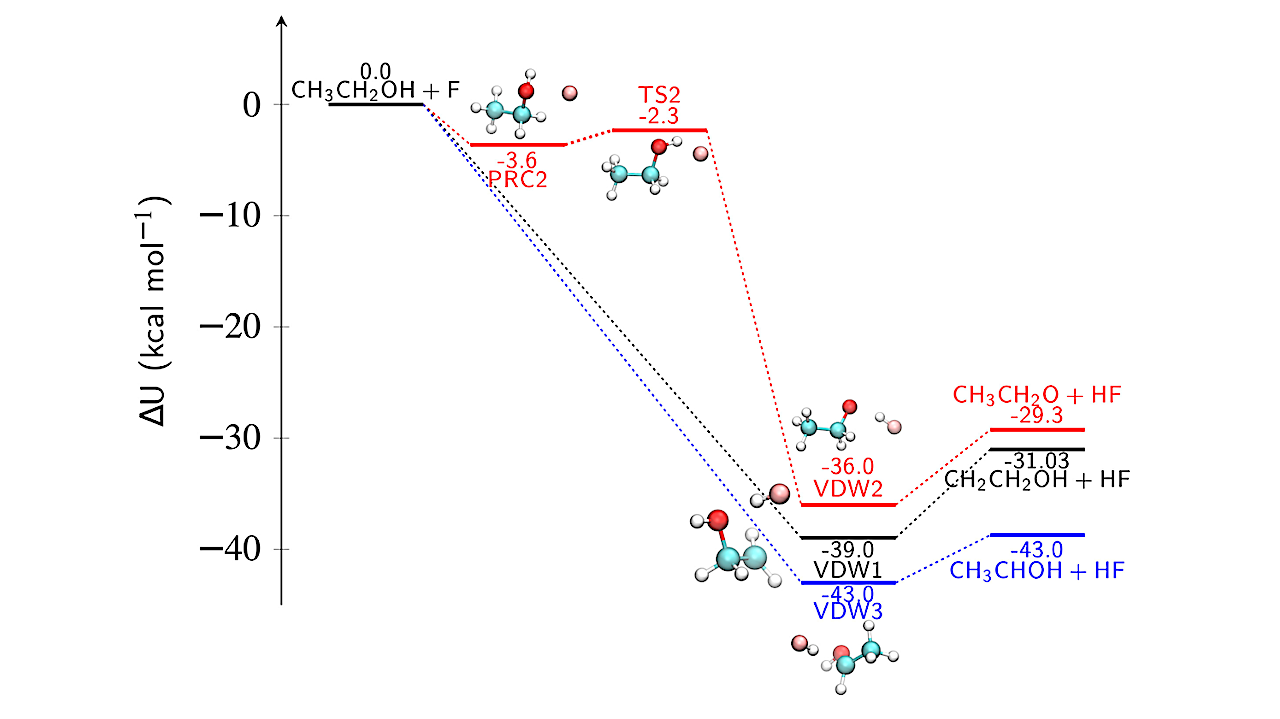
Potential energy profiles for the three abstraction channels in the CH3CH2OH + F reaction. All energies are ZPVE corrected. — astro-ph.GA Alcohols and aldehydes represent two key classes of interstellar
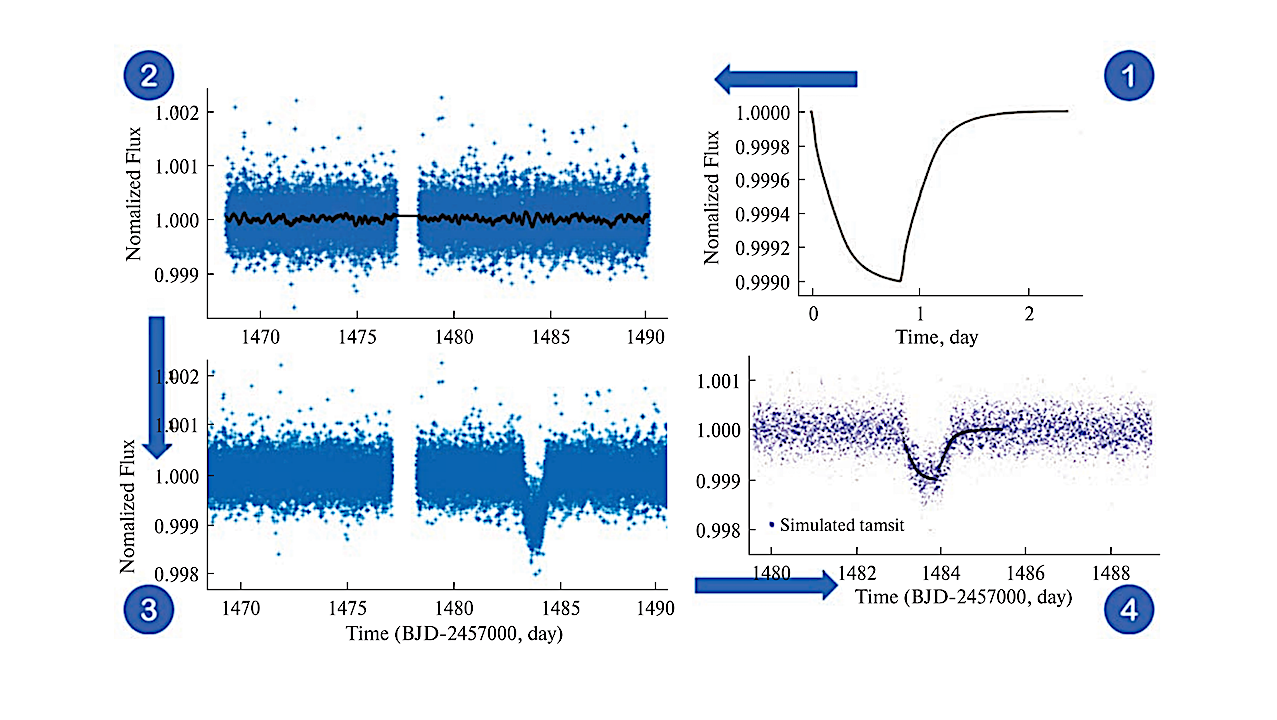
Step-by-step procedure of the transit encapsulation in the TIC 020209388 light curve. The X-axis and Y-axis specify time in days and normalized flux, respectively. Top panel: 1 — simulated transit
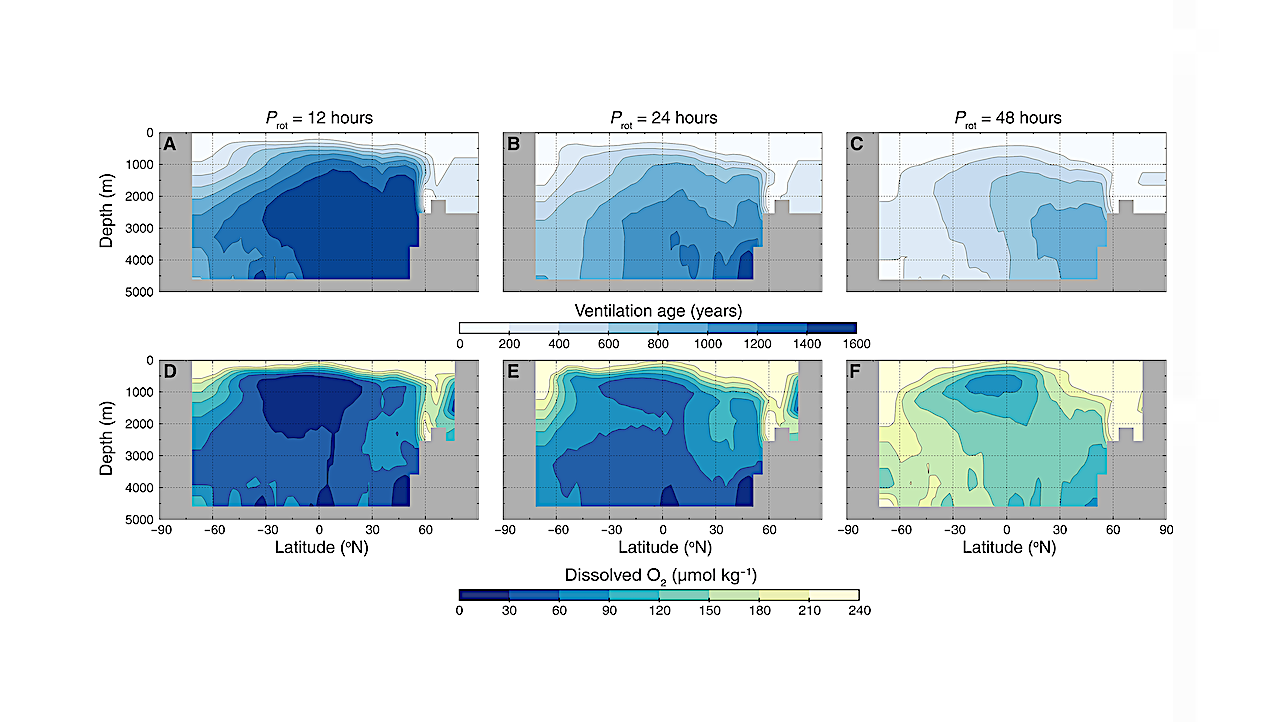
The top row (A to C) shows longitudinally averaged cross sections of ventilation age, where younger ventilation ages represent water parcels that have more recently interacted with the ocean-atmosphere interface.
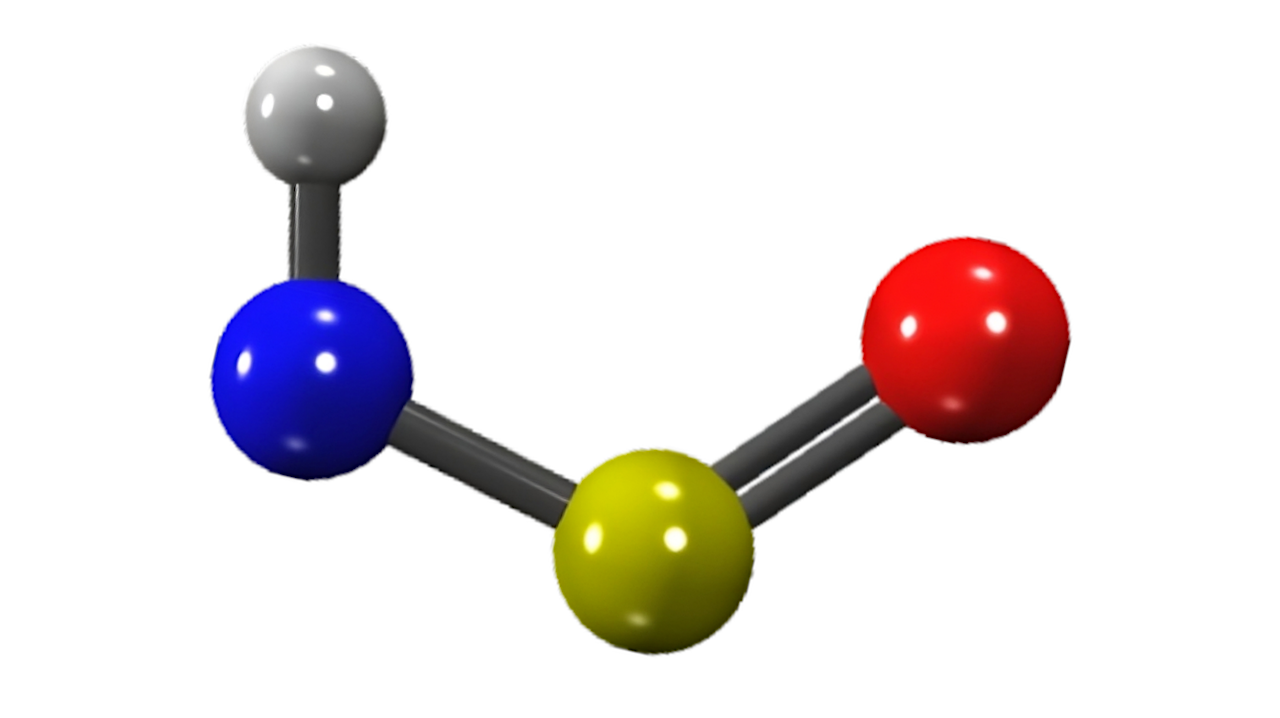
Thionylimide (HNSO) — astro-ph.GA We investigate the formation of the recently detected HNSO molecule using quantum chemical calculations on ices and astrochemical models in tandem. Our results indicate that HNSO
Artist’s impression of Earth around 700 million years ago during Snowball Earth Credit This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. Attribution must be given
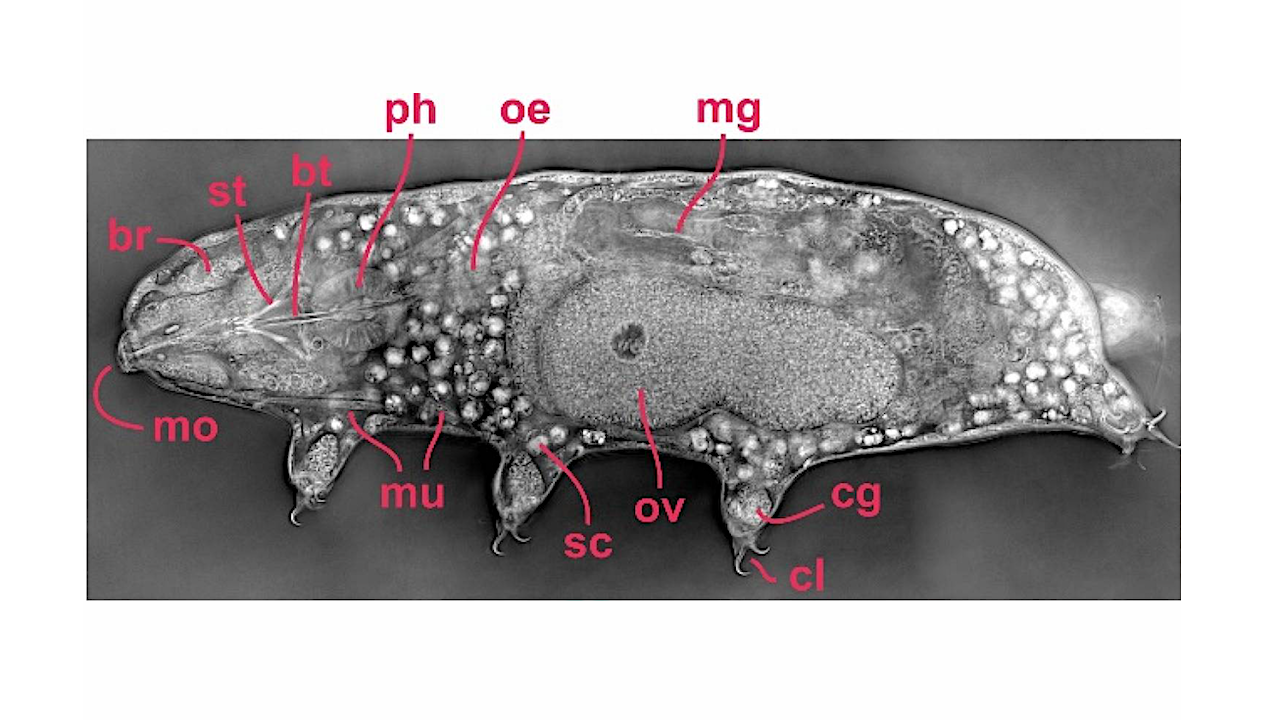
Anatomy of tardigrade visualized using holotomography. — Tomography, via PubMed Background/Objectives: Holotomography is an advanced imaging technique that enables high-resolution, three-dimensional visualization of microscopic specimens without the need for fixation
XTREMOLIFE Advancing Sampling And Screening Of Extremophile Microorganisms For biodiscovery Of Bioactive Compounds from Volcanic, Desert, and Polar Ecosystems Thriving in extreme environments, such as high pressure, temperature, or acidity,
Tidally Heated H2-Dominated Exomoon – Grok via Astrobiology.com Exomoons around free-floating planets (FFPs) can survive their host planet’s ejection. Such ejections can increase their orbital eccentricity, providing significant tidal heating
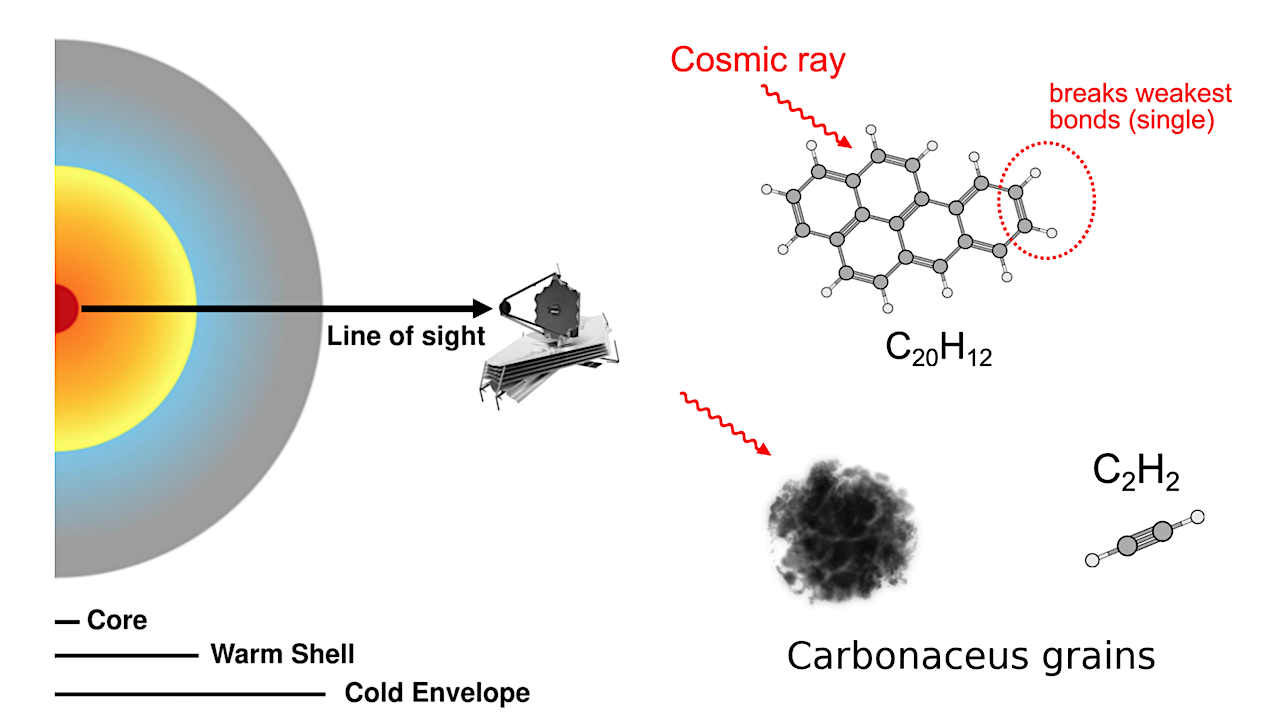
Nuclear dust and molecular structure, with a sketch summarizing grain and PAH processing in IRAS 07251−0248. Left panel: A schematic view of the central region of IRAS 07251−0248. The color
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly