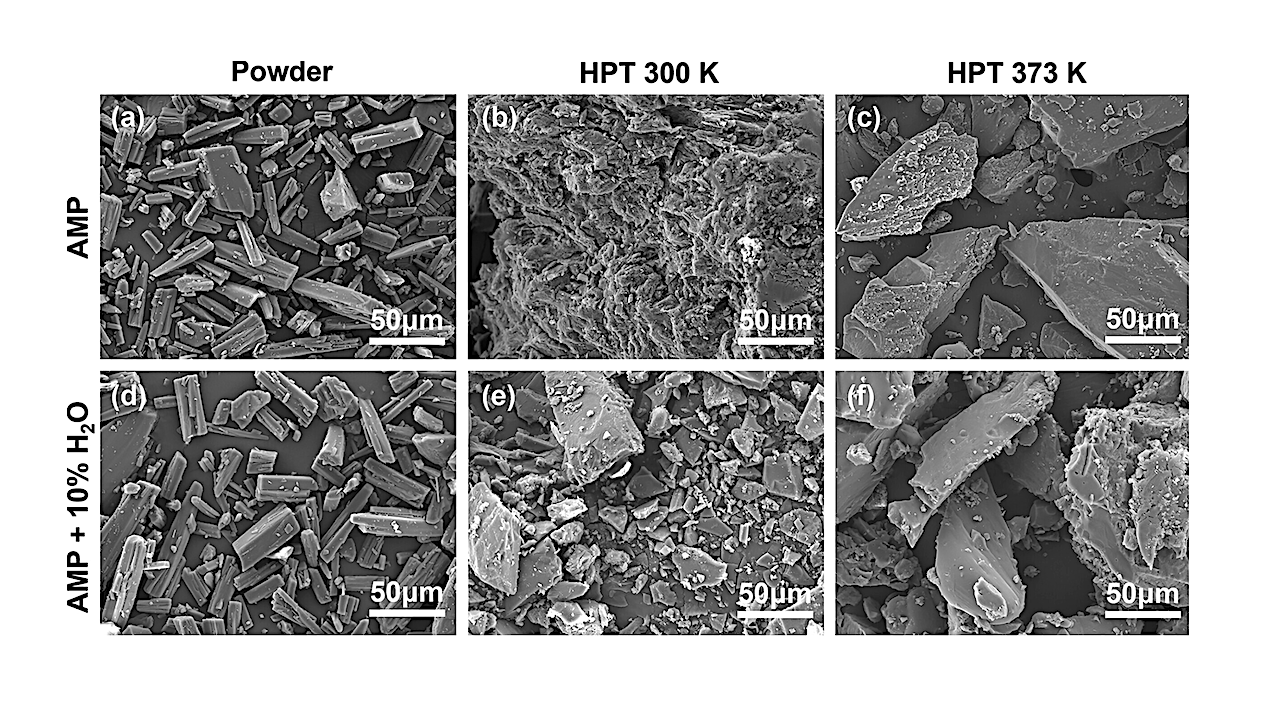
Scanning electron microscopy images of AMP in (a–c) dry condition and (d–f) hydrated condition prior to and following treatment through HPT at ambient and boiling water temperatures. — Astrobiology via
Astrobiology15- Page
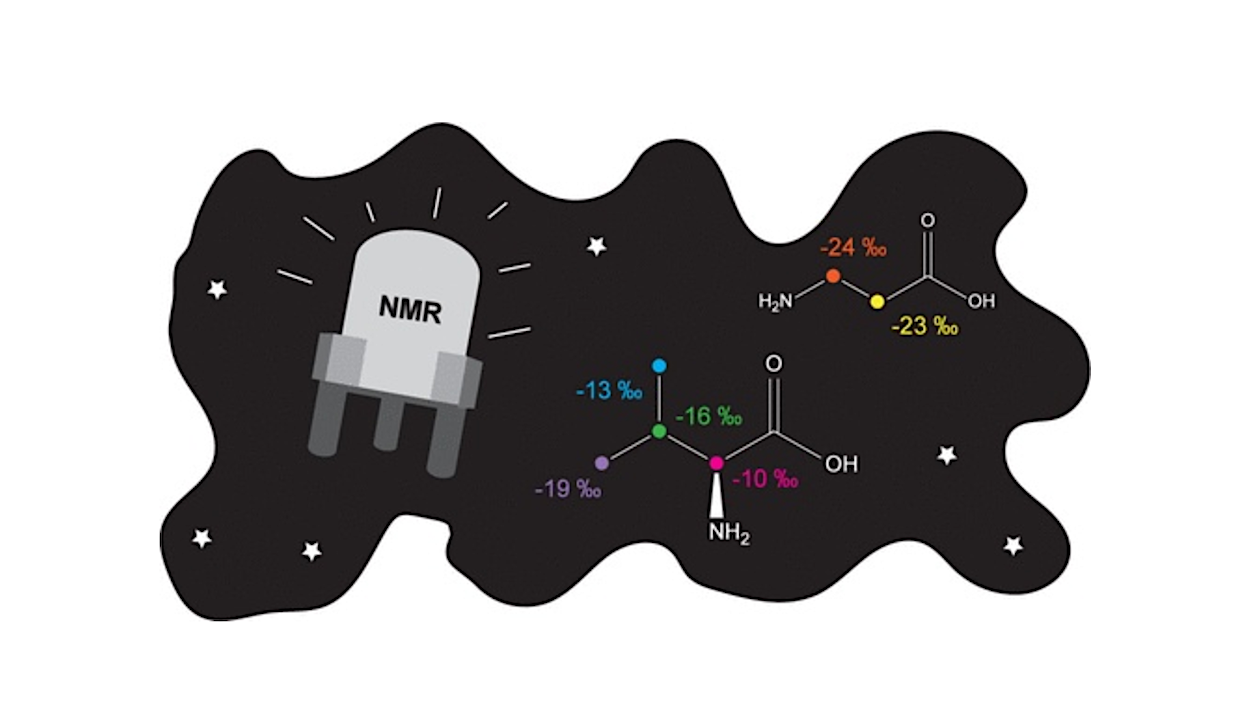
Graphical Abstract – ACS Earth and Space Chemistry via Xmol For decades, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has been utilized as a powerful tool in various scientific disciplines, most prominently
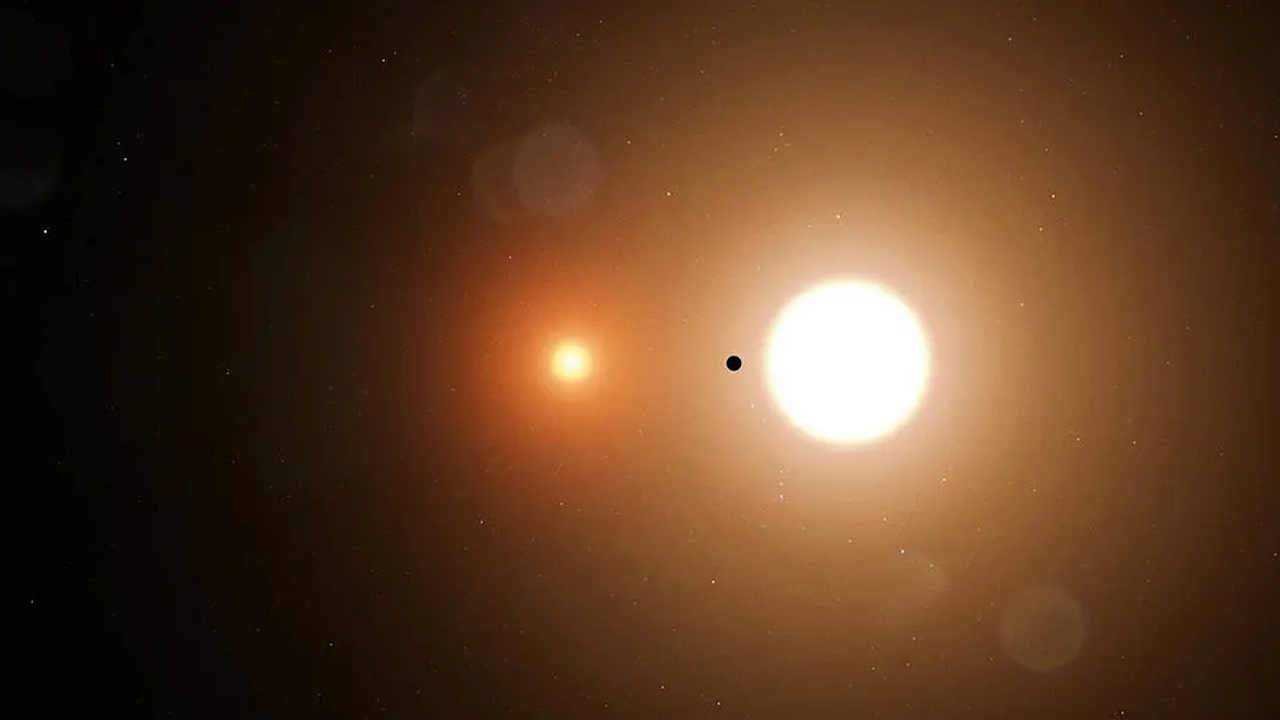
An artist’s depiction of a planet, represented by the black circle, orbiting a pair of stars — a so-called binary star system. (Image Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center) Of the
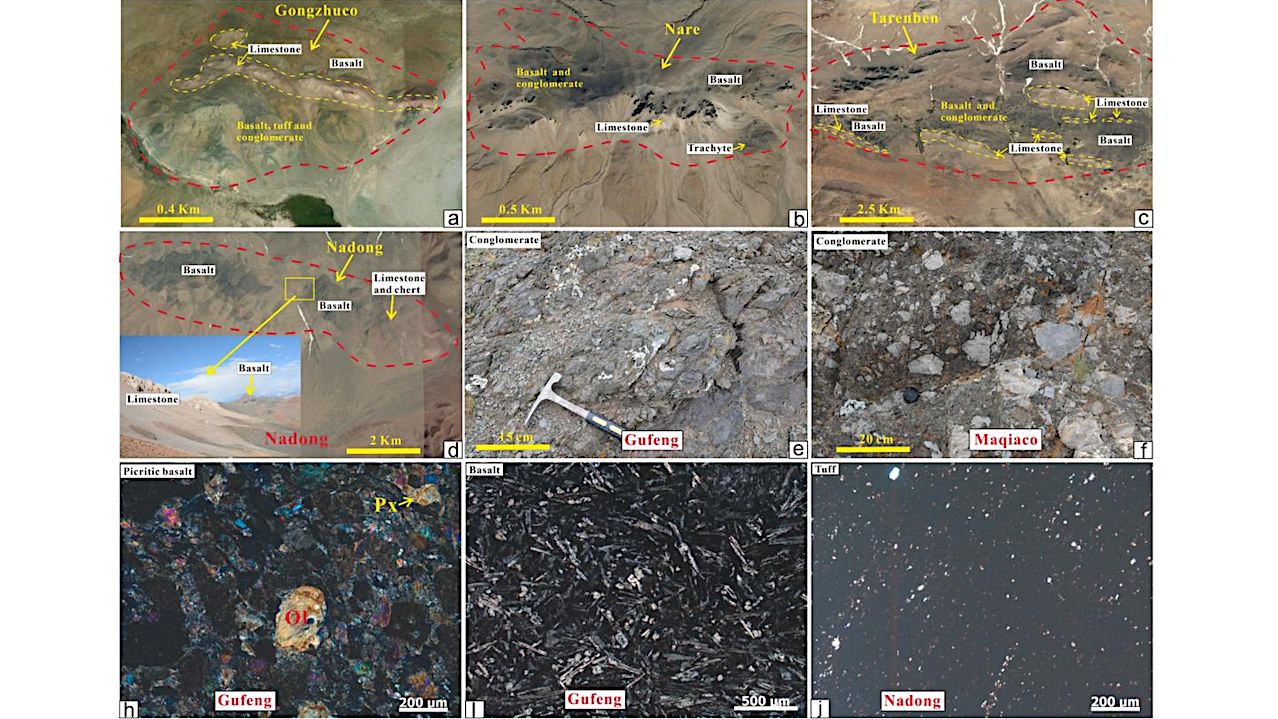
(a) Remote sensing satellite image of Gongzhuco; (b) Remote sensing satellite image of Nare; (c) Remote sensing satellite image of Tarenben; (d) Remote sensing satellite and field photograph (inset) of
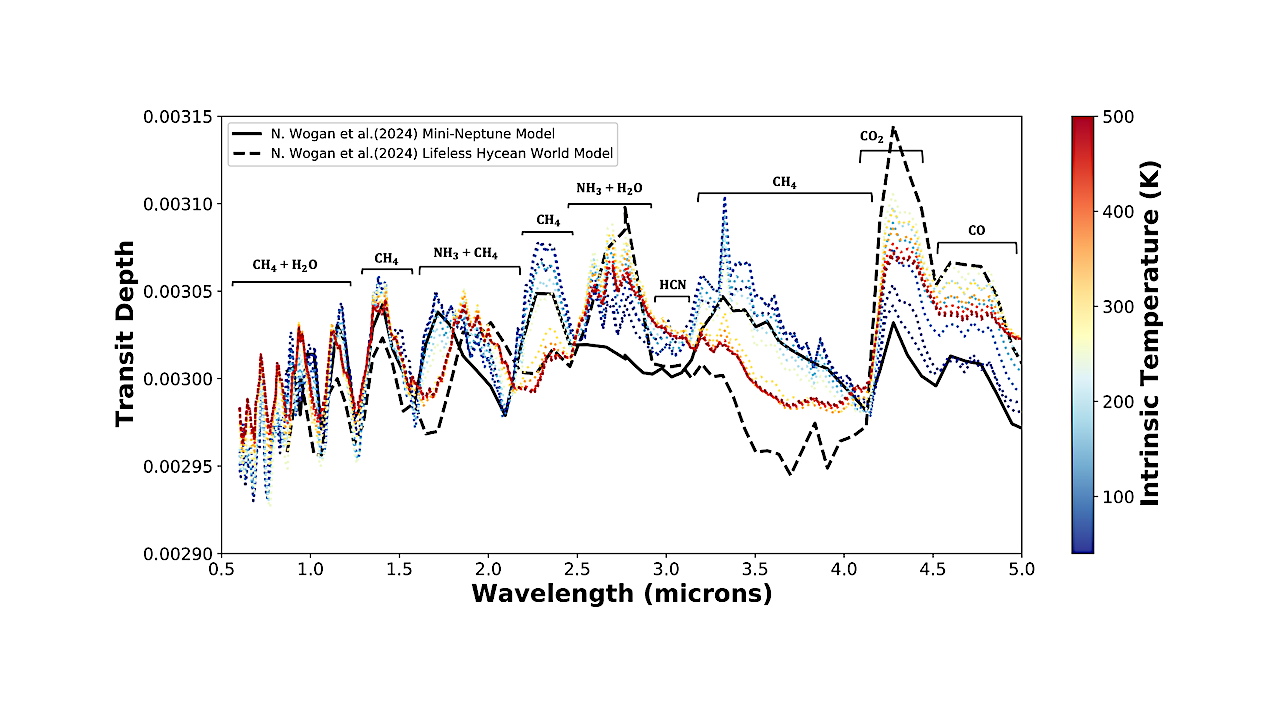
Spectrum grid with varying intrinsic temperature and Kzz profile. The Kzz profile follows the parameterization from N. F. Wogan et al. (2024) for mini-Neptune atmospheres. The grid showcases atmospheric temperature
An international team including Cornell researcher Jake Turner has developed a novel analysis method capable of uncovering previously undetectable stellar and exoplanetary signals hidden within archival radio-astronomical data. Thanks to
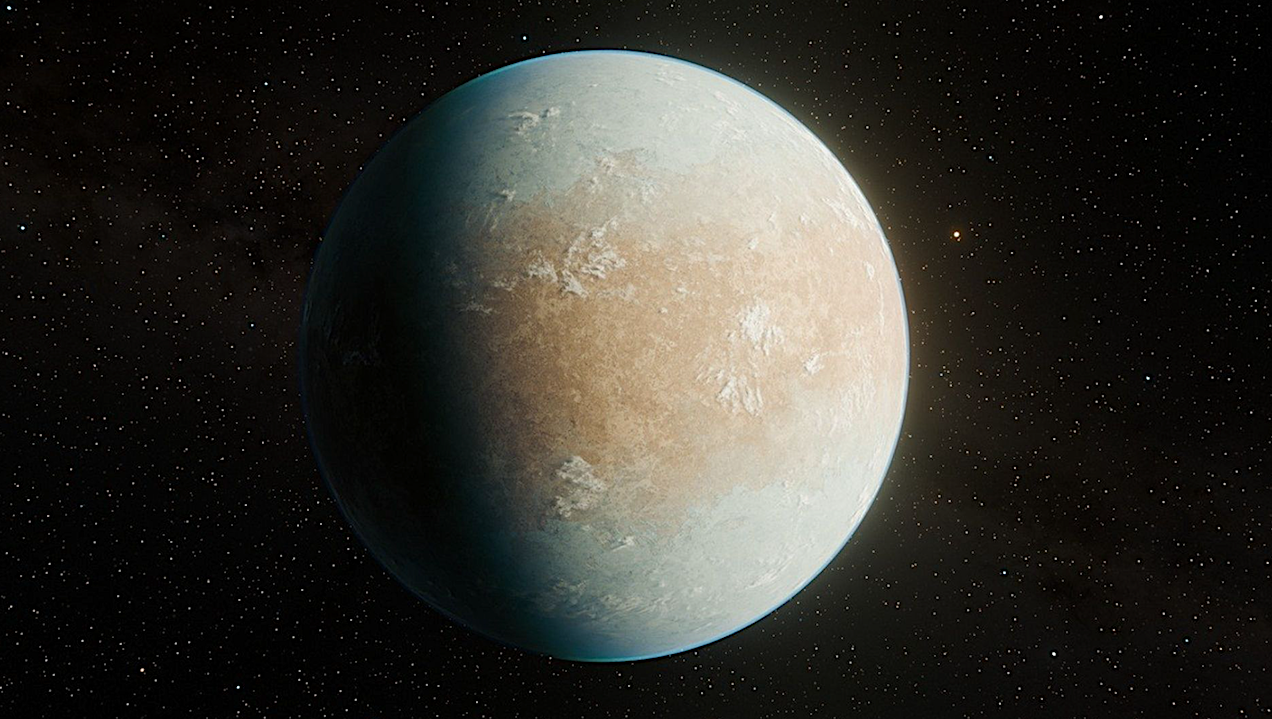
Artist’s concept of exoplanet candidate HD 137010 b, dubbed a “cold Earth” because it’s a possible rocky planet slightly larger than Earth, orbiting a Sun-like star about 146 light-years away.
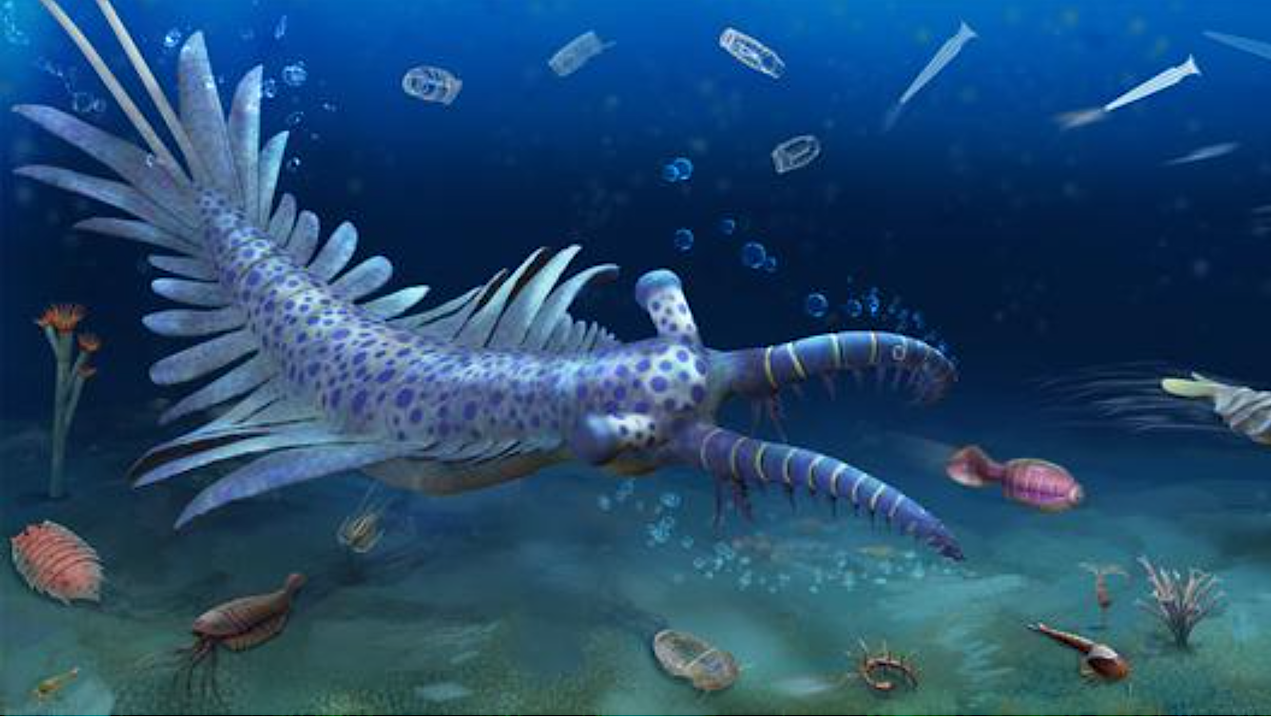
Artistic reconstruction of the Huayuan biota. Credit Image by YANG Dinghua. Around 540 million years ago, Earth’s biosphere underwent a pivotal transformation, shifting from a microbe-dominated world to one teeming
Artist’s impression of the HD 206893 system: a substellar companion orbits the star, and could itself host a massive exomoon. Credit: DR A study led by a researcher from the
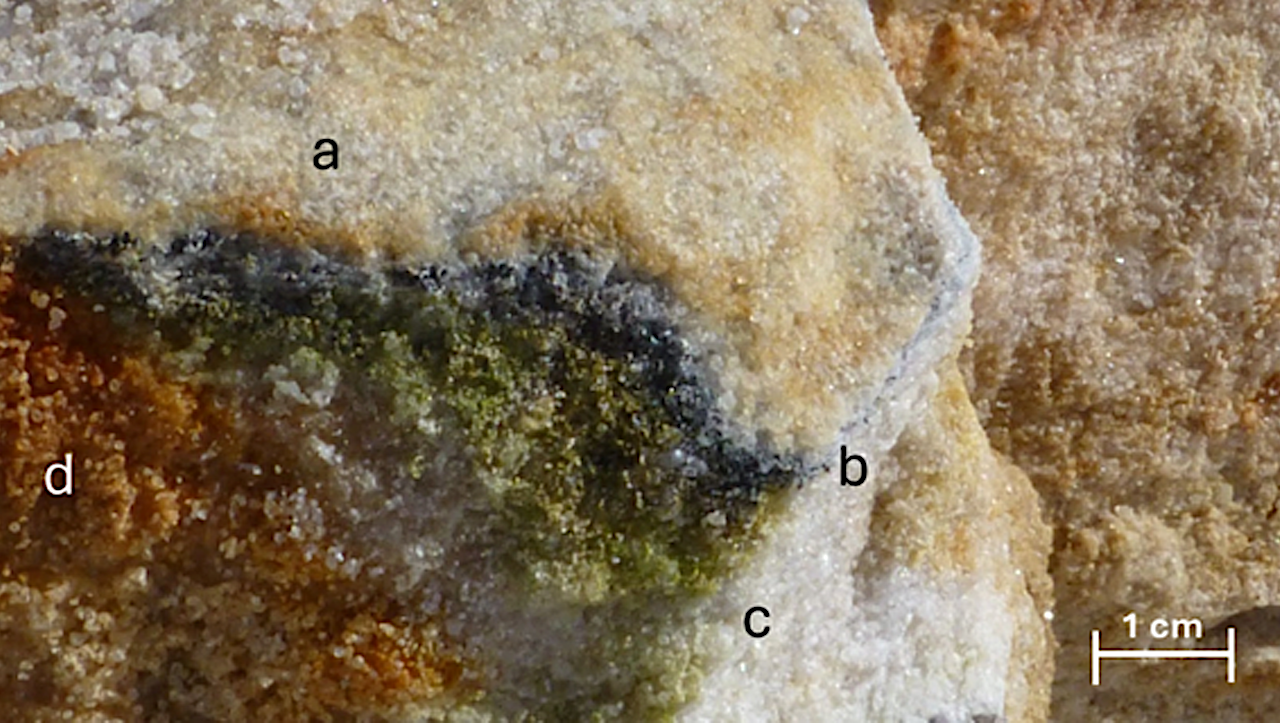
Antarctic cryptoendolithic community colonising sandstones collected in Linnaeus Terrace by Laura Selbmann during the XXXI Italian Antarctic expedition (PNRA, 2015–2016) showing the typical stratification: (a) crust, (b) black fungi layer,
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly