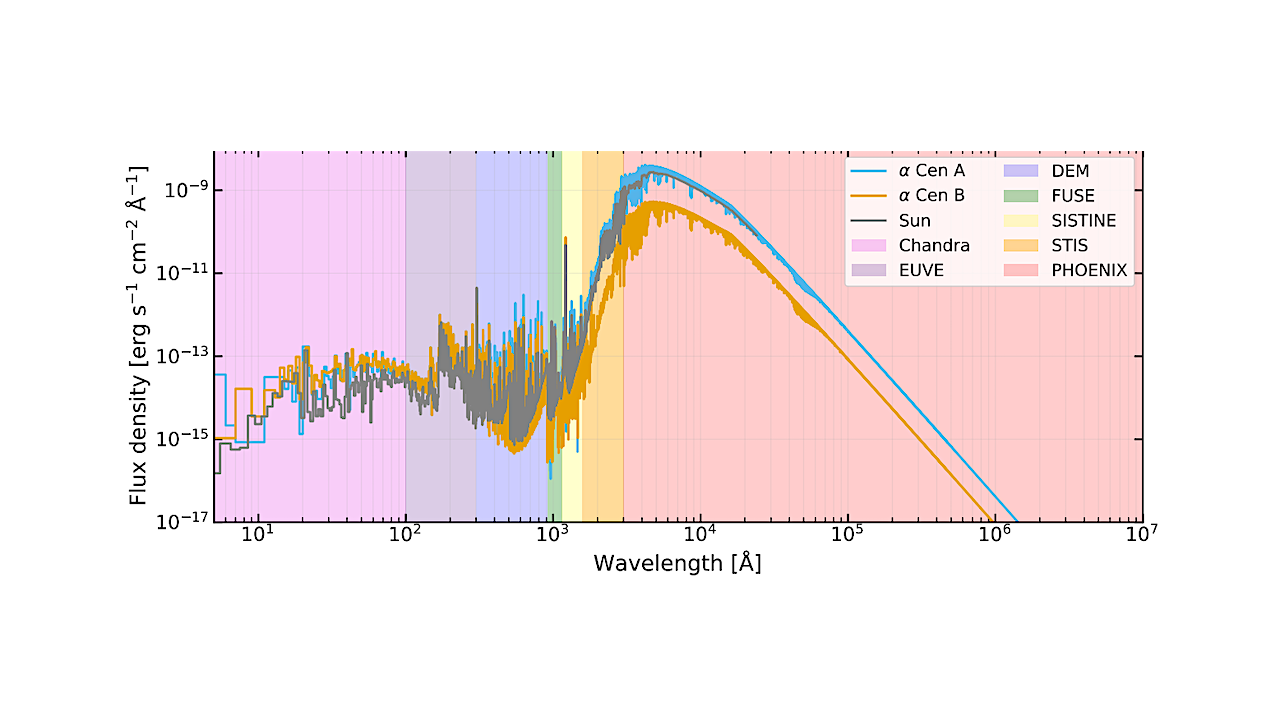
Stellar SEDs for α Cen A (blue) and B (orange) binned to 1 ˚A. The SED of the Sun, scaled to a distance of 1.33 pc, from Woods et al.
Astrobiology31- Page
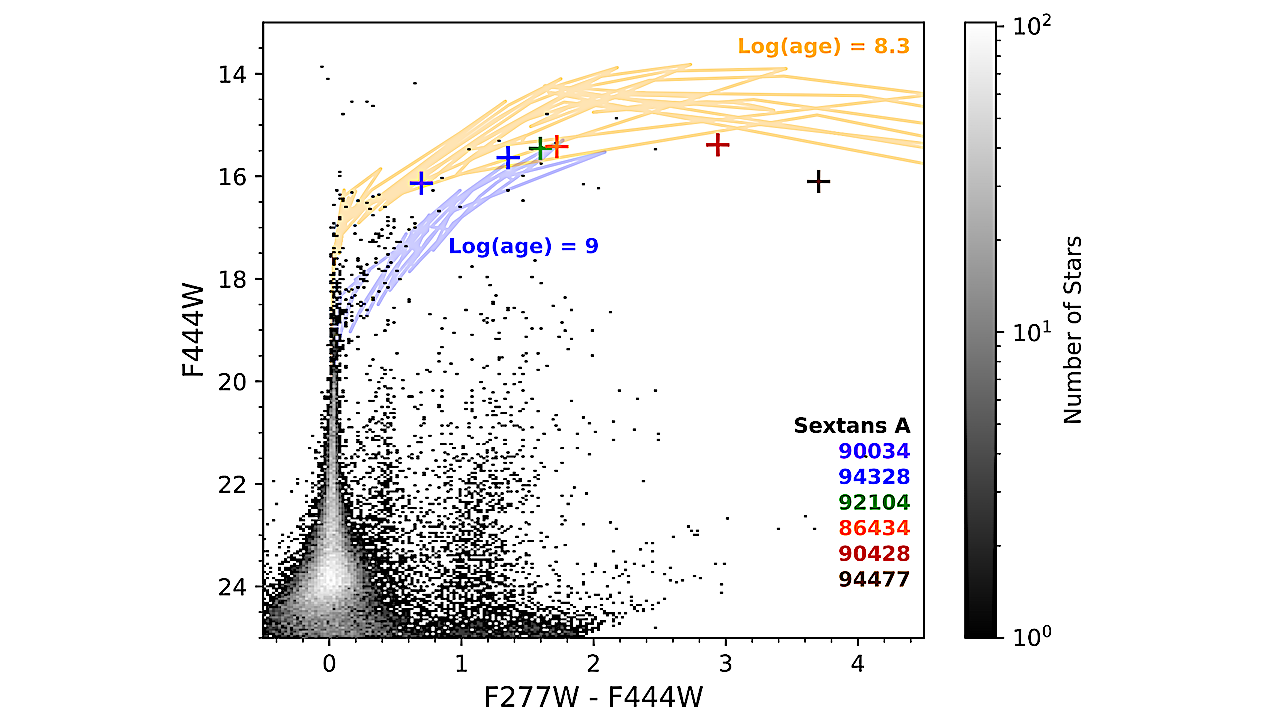
A color–magnitude Hess diagram of Sextans A with JWST/ NIRCam photometry at 2.7 and 4.4 μm with the positions of the JWST/LRS targets overplotted. COLIBRI isochrones with = −1.7
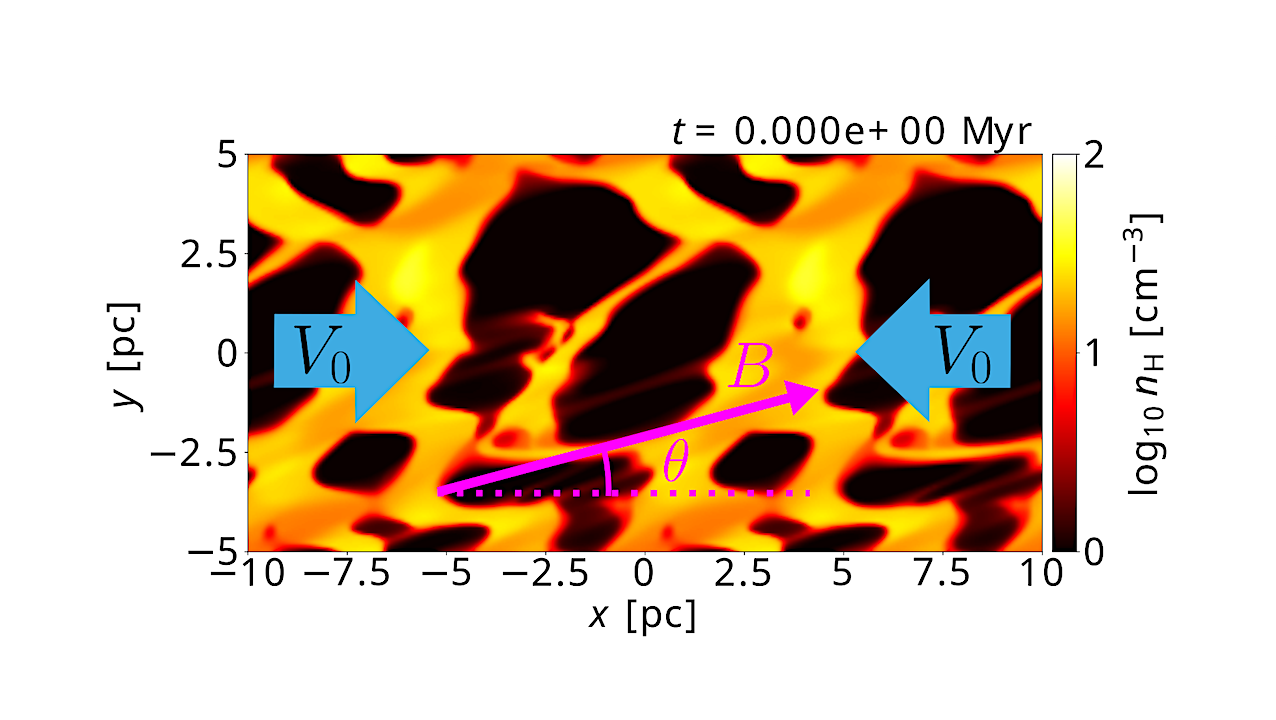
The initial condition of the converging flow simulation. The color shows the number density of hydrogen nuclei on the 𝑧 = 0 plane. — astro-ph.GA We investigate the chemical evolution
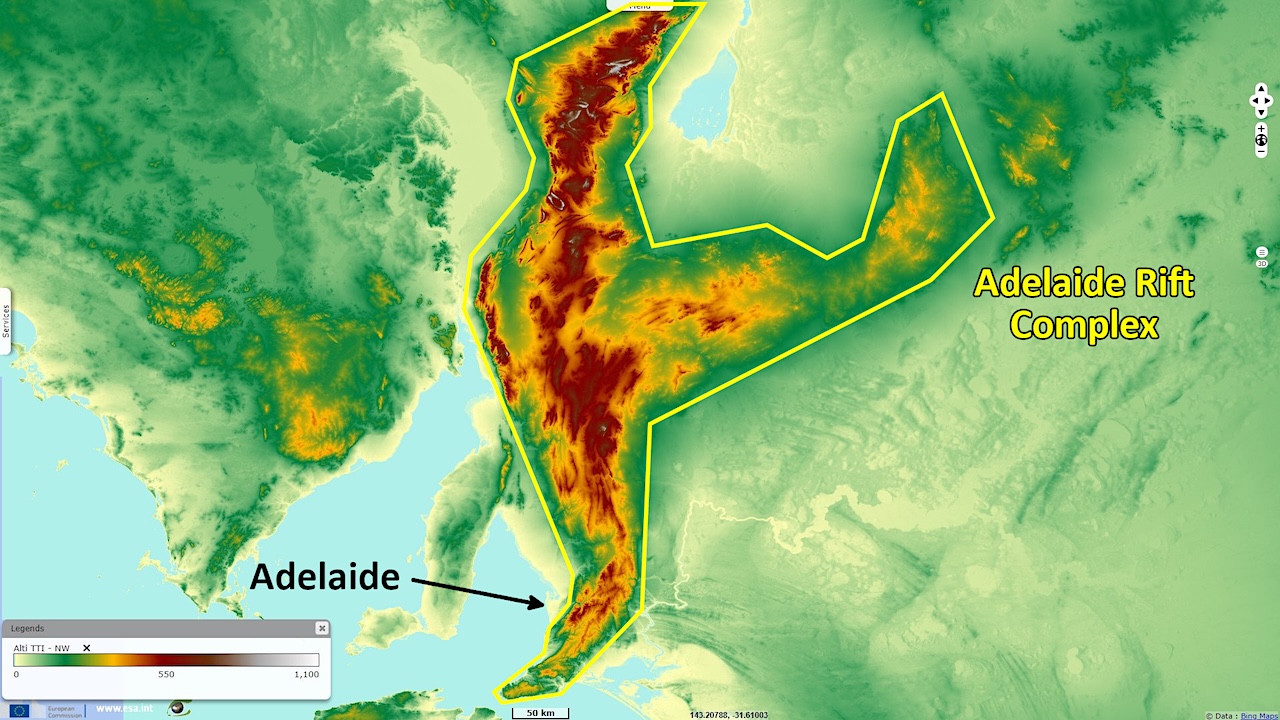
Adelaide Rift Complex — Source, Sentinel EU During the Precambrian, stromatolite reefs played an essential role in the evolution of Earth’s climate and life systems. Many Precambrian basins contain salt-influenced
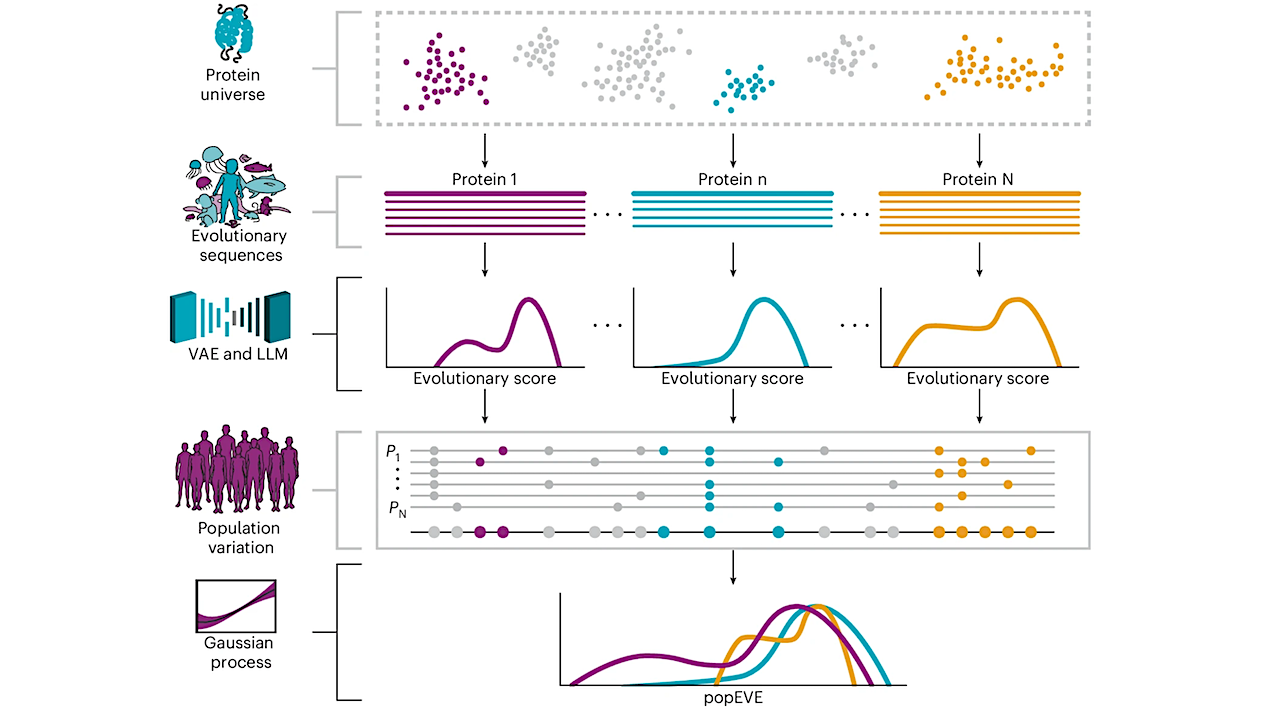
popEVE combines variation from across evolutionary sequences, modeled with EVE and ESM-1v, with variation within the human population (UKBB17 or GnomAD18), using a Gaussian process to learn the relationship between
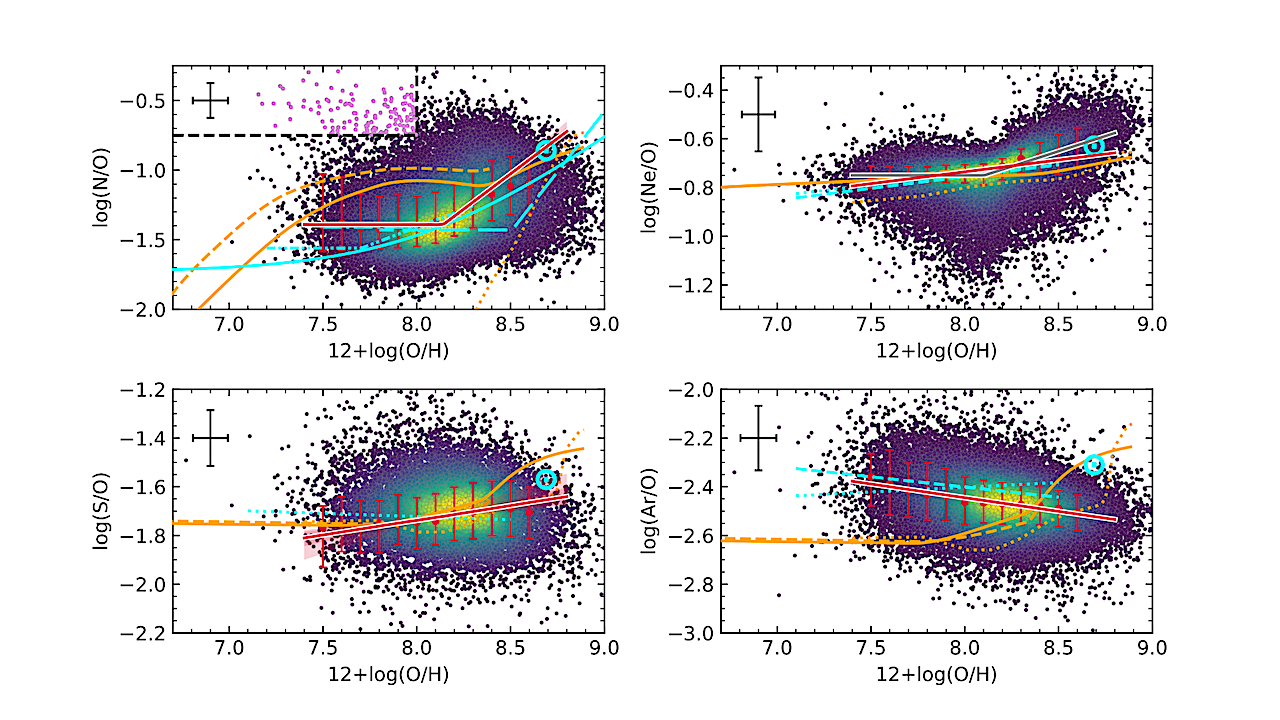
The abundance ratios, log(X/O), versus metallicity for nitrogen (top-left), neon (top-right), sulphur (bottom-left) and argon (bottom-right). The blue lines shows literature relations derived by Izotov et al. (2006), Andrews &
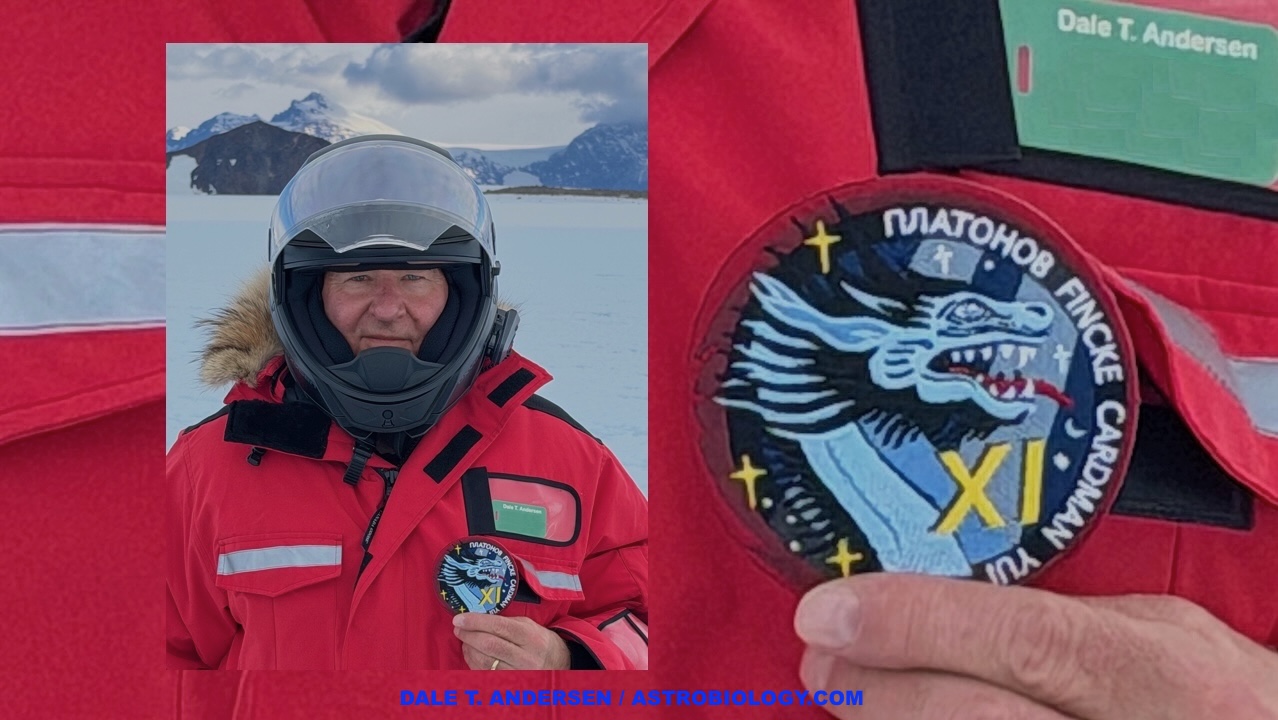
Dale Andersen at Lake Untersee, Antarctica holding up the ISS Crew 11 patch on 11 Jan 2026 – Dale T. Andersen Keith’s note: Dale Andersen and his astrobiology research team
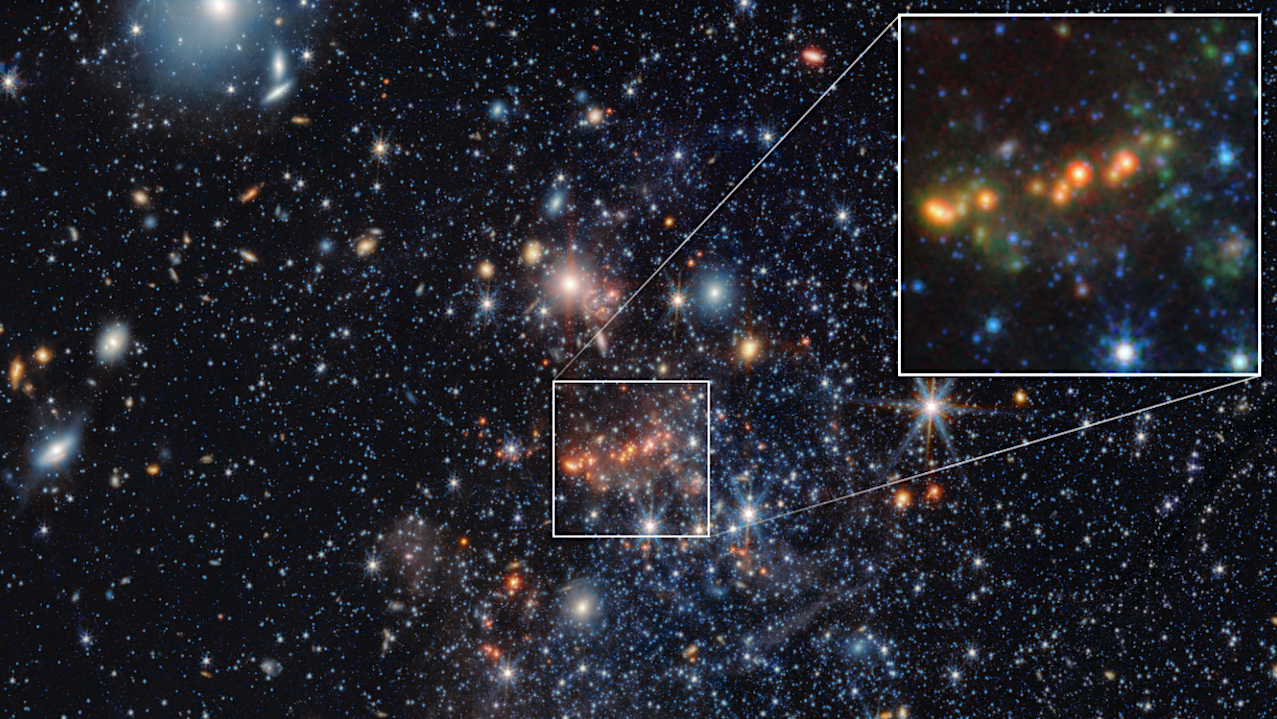
Images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope of the dwarf galaxy Sextans A reveal polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), large carbon-based molecules that can be a signifier of star formation. The
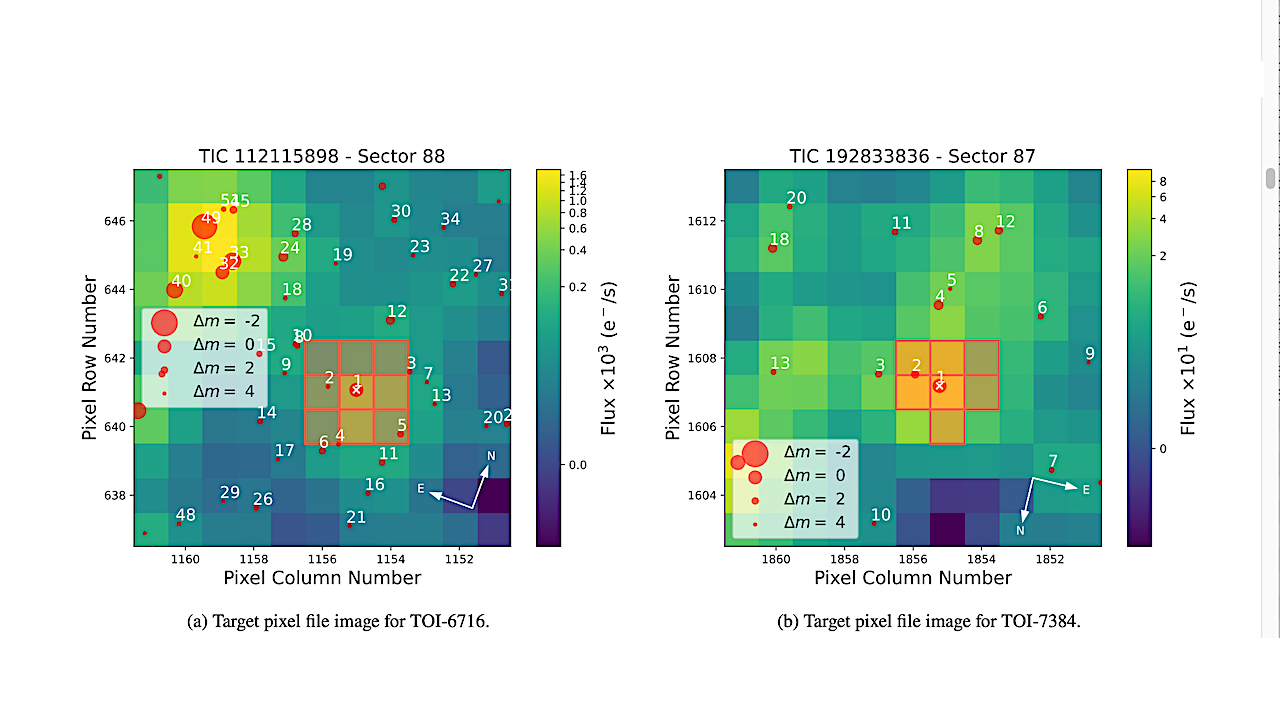
TESS target pixel file image created with tpfplotter for TOI-6716 (left) and TOI-7384 (right) observed in Sector 88 (2025 Jan 14 – 2025 Feb 11) and Sector 87 (2024 Dec
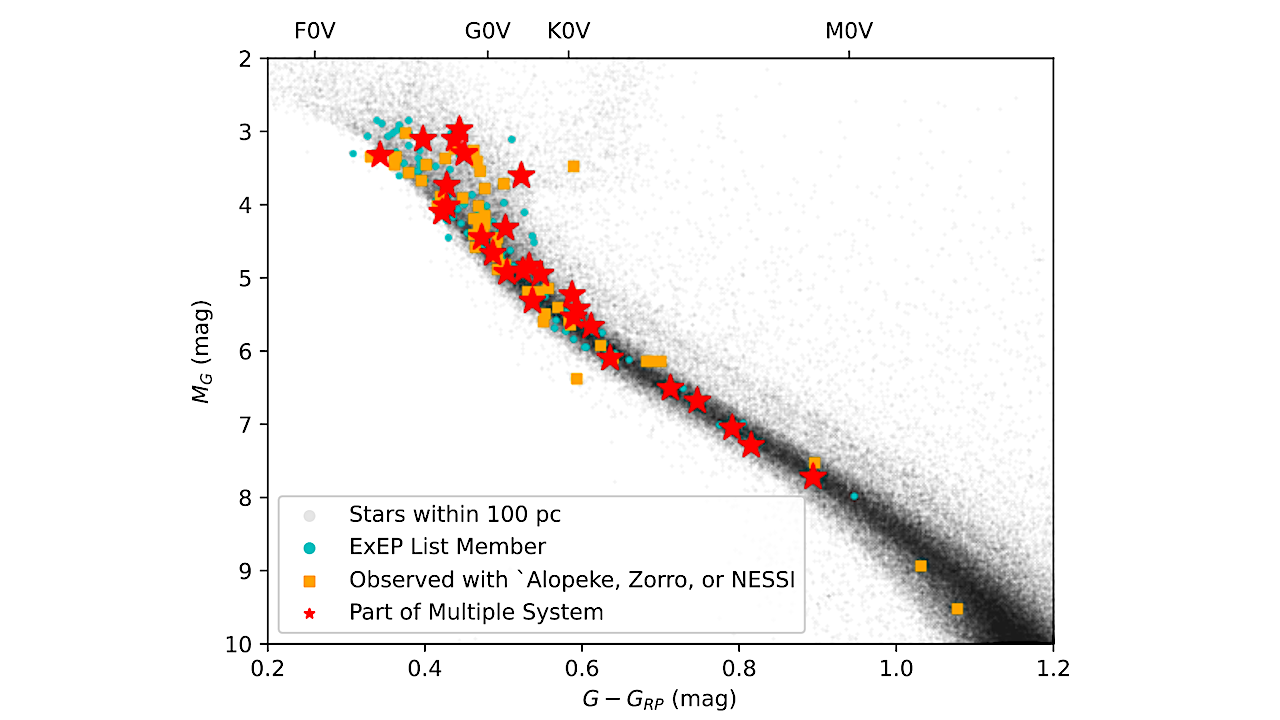
Color-magnitude diagram showing the targets in the ExEP target list for HWO. The grey points represent a sample of stars within 100 pc taken from Gaia DR3. The cyan points
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly