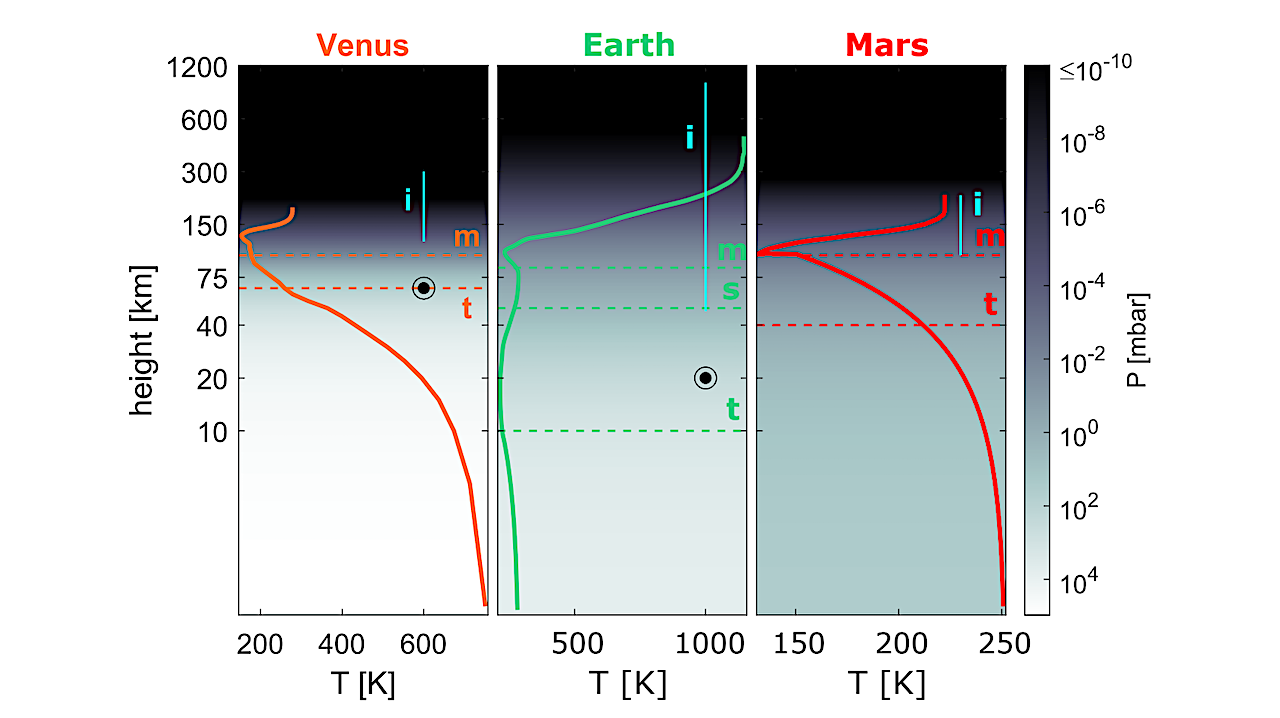
Height scales of atmospheres of Solar System’s terrestrial planets. The solid lines show the temperature profiles against altitude, while the background color reflects the atmospheric pressure. Horizontal dashed lines denote
Astrobiology2- Page
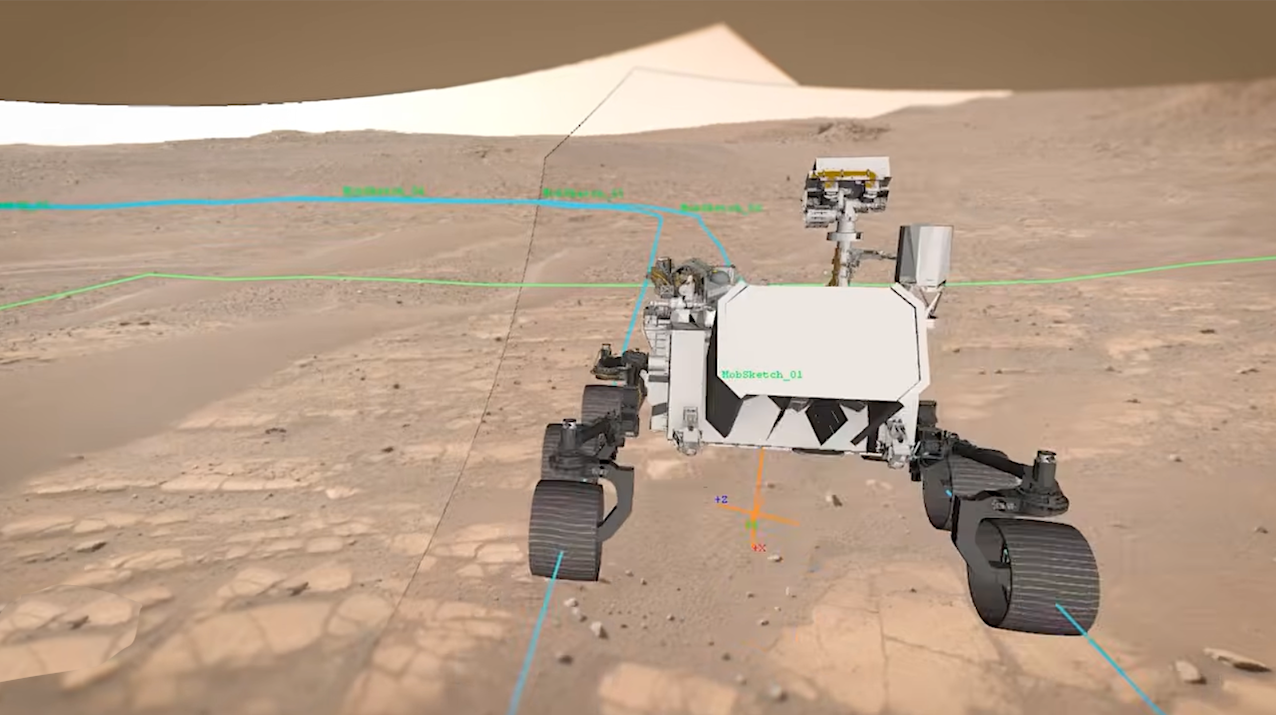
There is no GPS at the Red Planet, but a new technology called Mars Global Localization lets Perseverance determine precisely where it is — without human help. — NASA Imagine
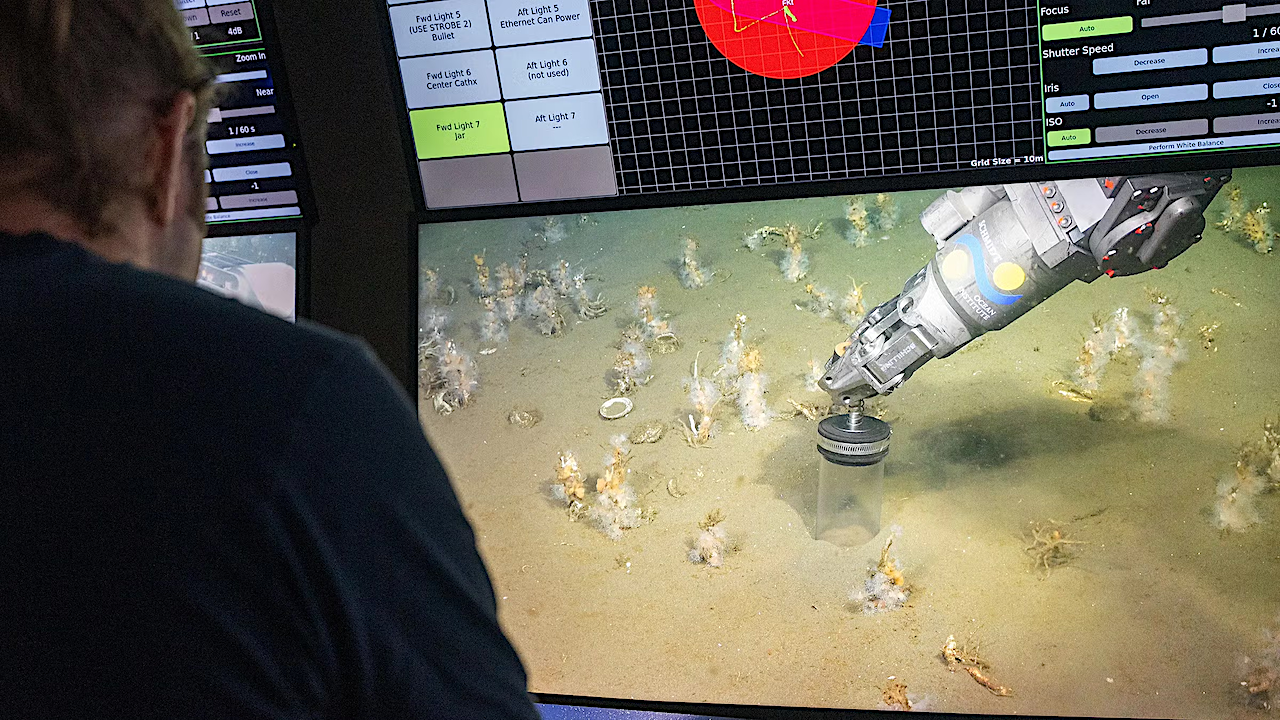
In December 2025, Brett Baker led a research cruise to collect microbial genomes off the coast of Uruguay. In this photo, Tyler Smith pilots a remotely operated vehicle collecting shallow
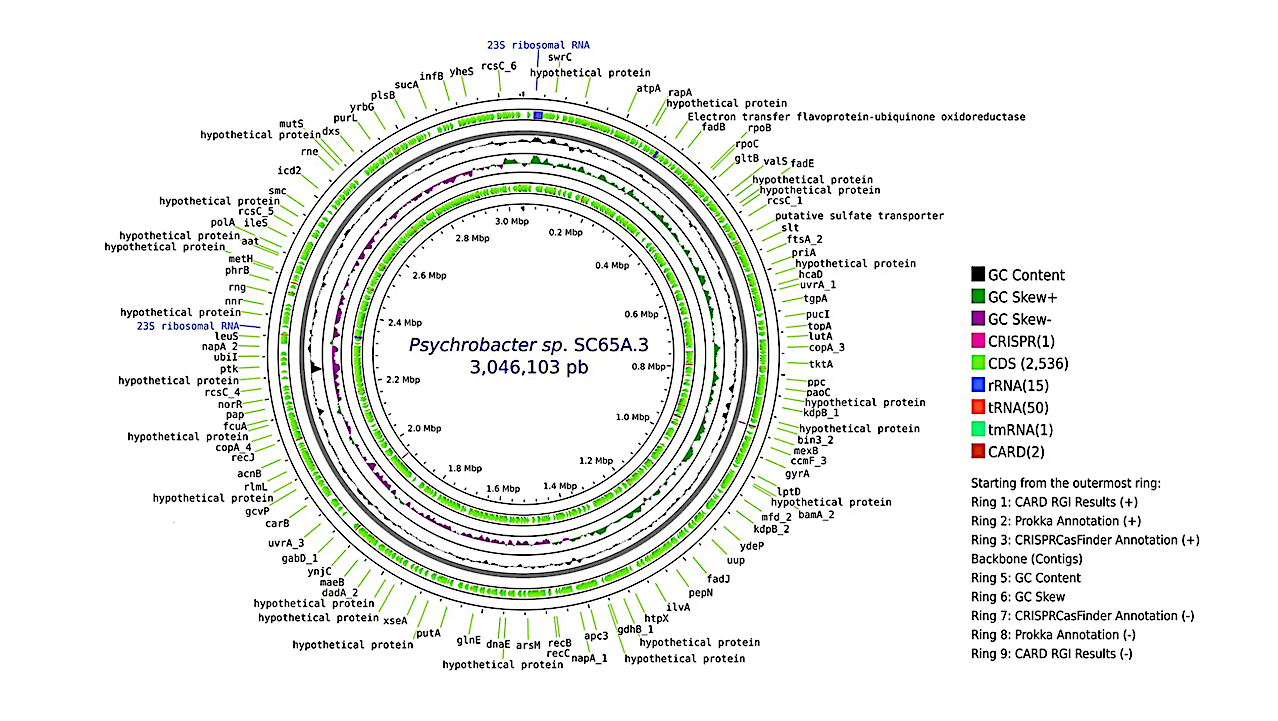
Circular representation of the complete genome of Psychrobacter sp. SC65A.3. From the outermost to the innermost rings: (1) CARD RGI resistance gene hits (positive strand), (2) annotated coding sequences (CDS)
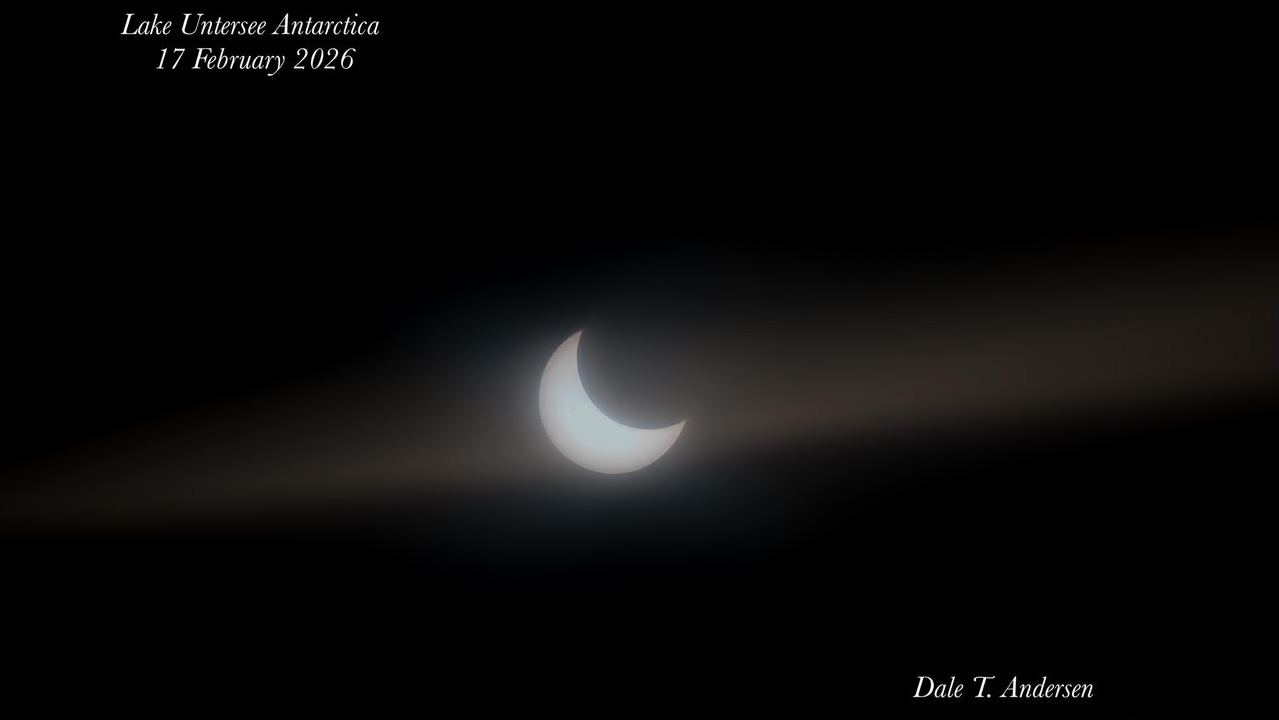
Partial Solar Eclipse at Lake Untersee, Antarctica — Dale T. Andersen Dale: A partial eclipse over Lake Untersee yesterday—an ordinary piece of celestial clockwork that felt anything but ordinary from
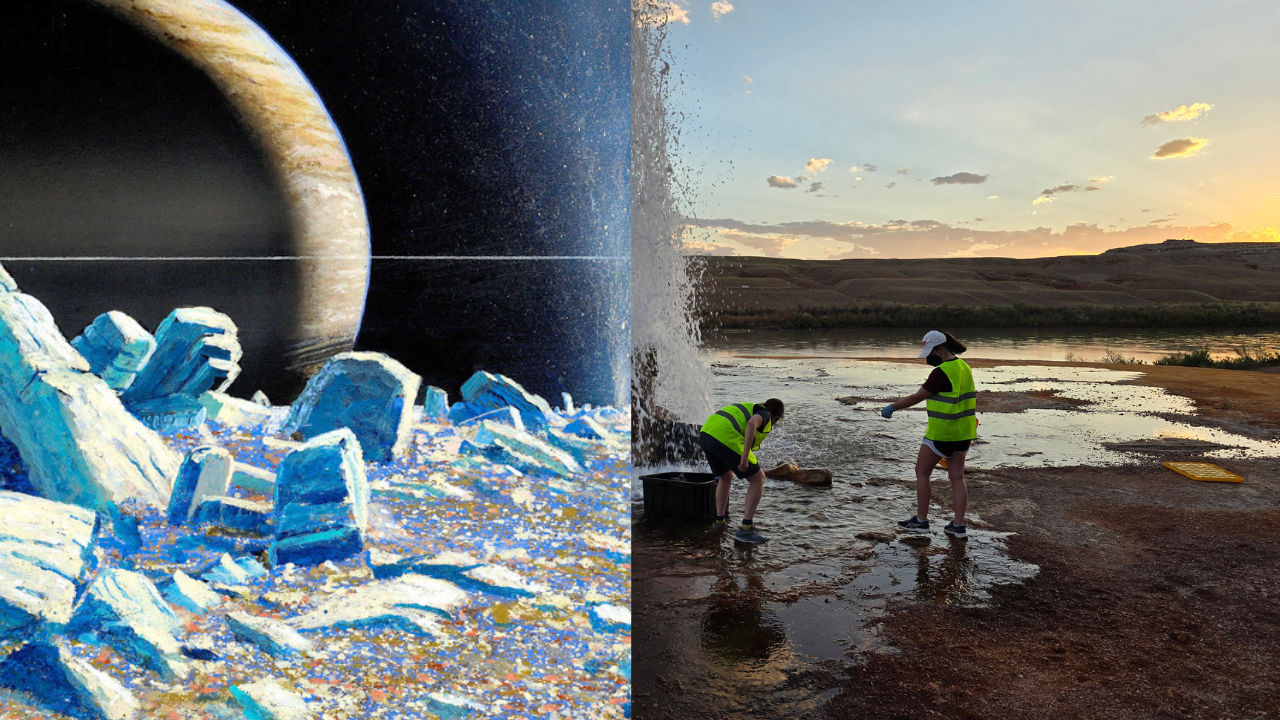
The painting on the left is an artist’s conception of a plume eruption on Saturn’s moon Enceladus. The image on the right is a photo of two researchers in the
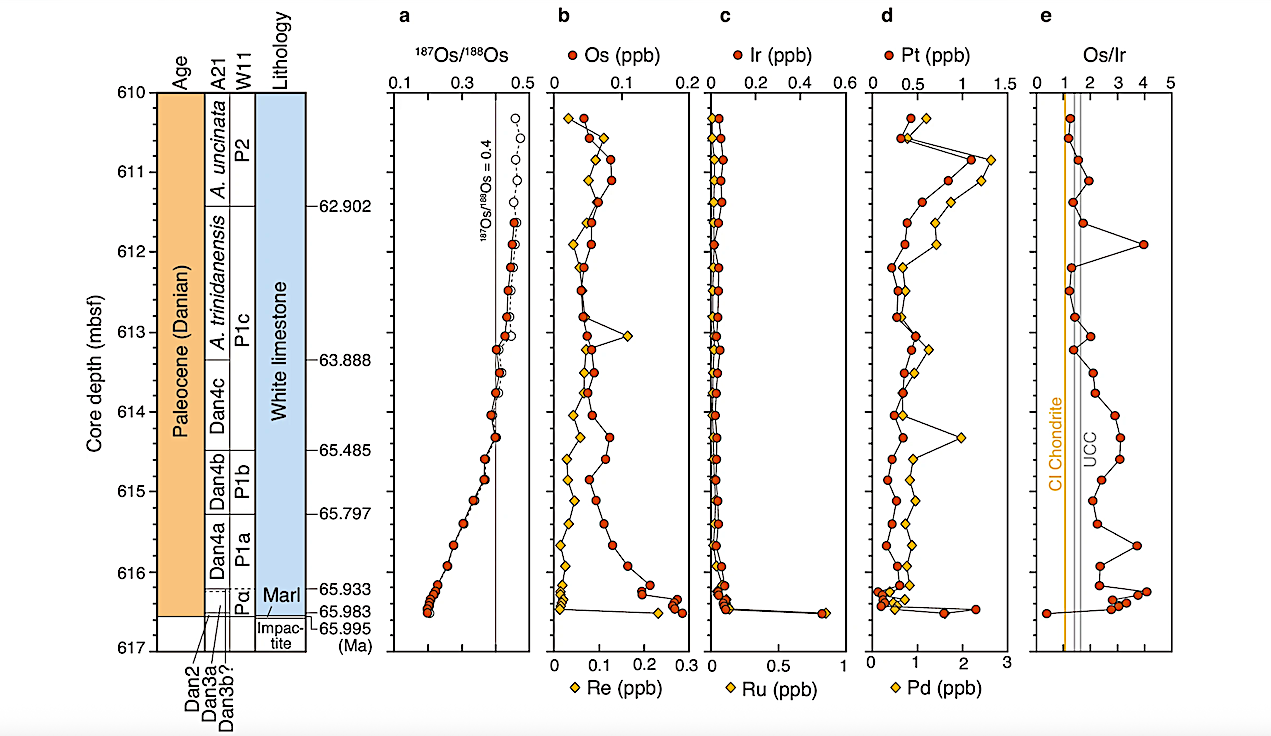
Impact events Press Release University of Texas Austin February 18, 2026 a 187Os/188Os ratios represent age-corrected (red circle) and measured (white circle) isotope ratios. bOs and Re concentrations. cIr and
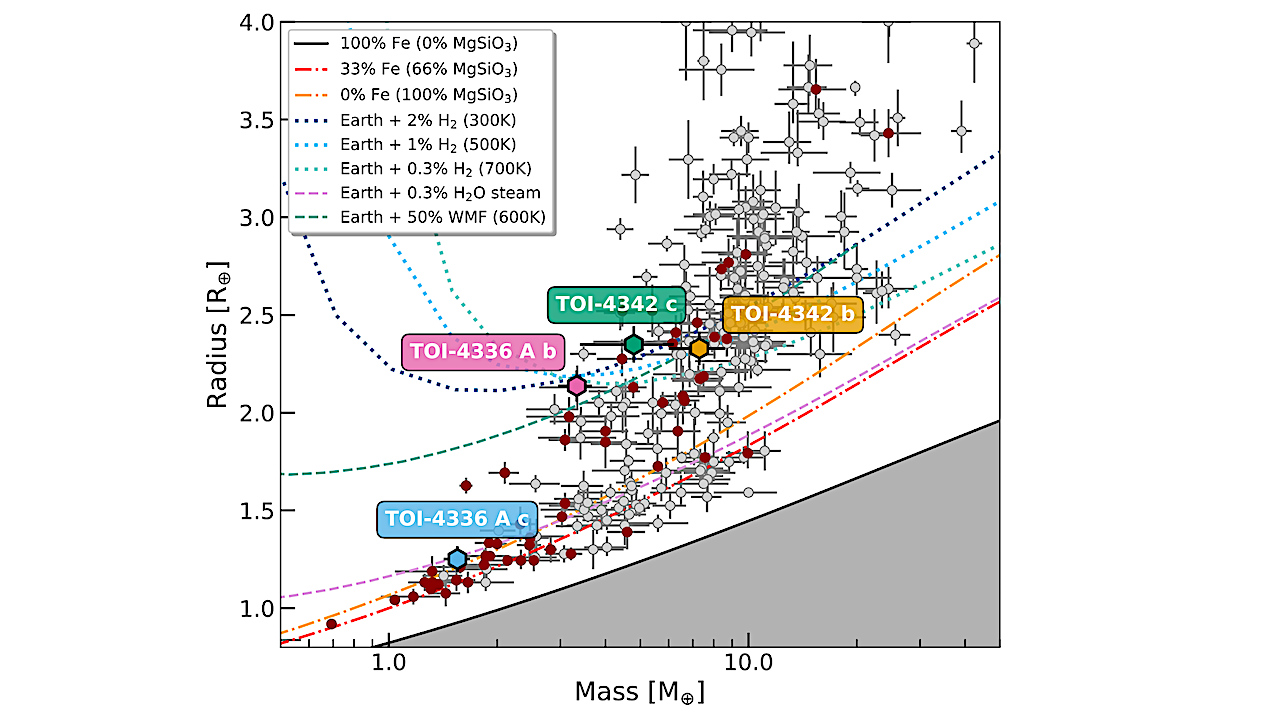
Mass-radius diagram of small exoplanets (with radii ranging from 1–4 R⊕) with precise densities from the PlanetS catalog. The red (gray) dots correspond to exoplanets orbiting M dwarfs (FGK dwarfs).
Keith Cowing Explorers Club Fellow, ex-NASA Space Station Payload manager/space biologist, Away Teams, Journalist, Lapsed climber, Synaesthete, Na’Vi-Jedi-Freman-Buddhist-mix, ASL, Devon Island and Everest Base Camp veteran, (he/him) 🖖🏻 Follow on
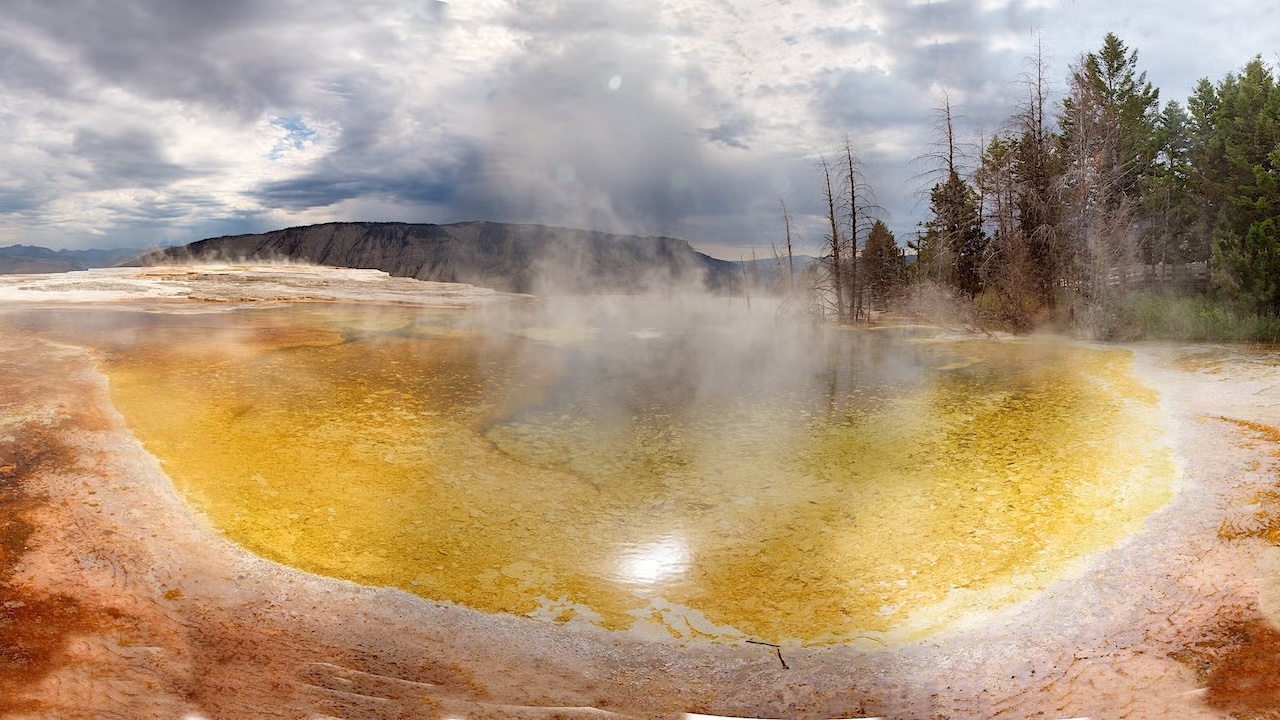
On Earth, life thrives in some of the most seemingly inhospitable environments. Single-celled organisms like bacteria teem in the hot springs of Yellowstone National Park, where temperatures reach nearly 200
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly