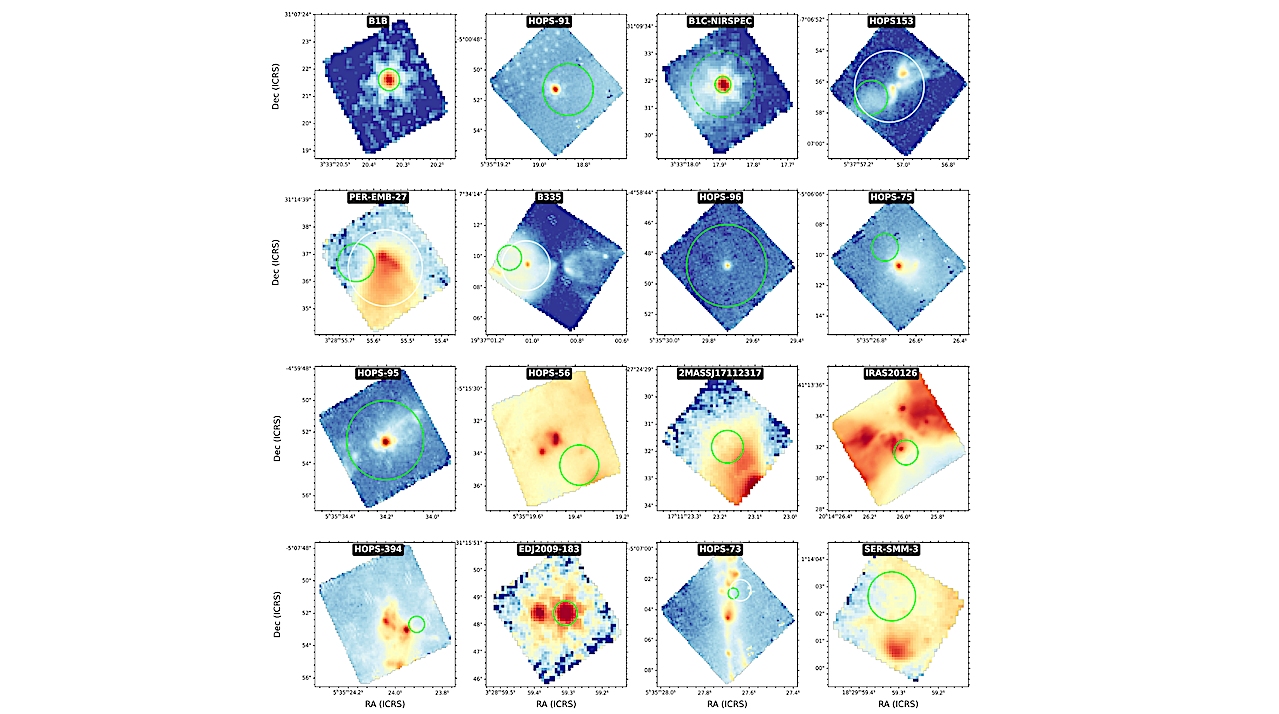
Intensity maps at 4.4 µm with the apertures chosen for the fit. Aperture centers and diameters are listed in Table C.1. — astro-ph.GA Context. There are only six molecules containing
Astrobiology28- Page
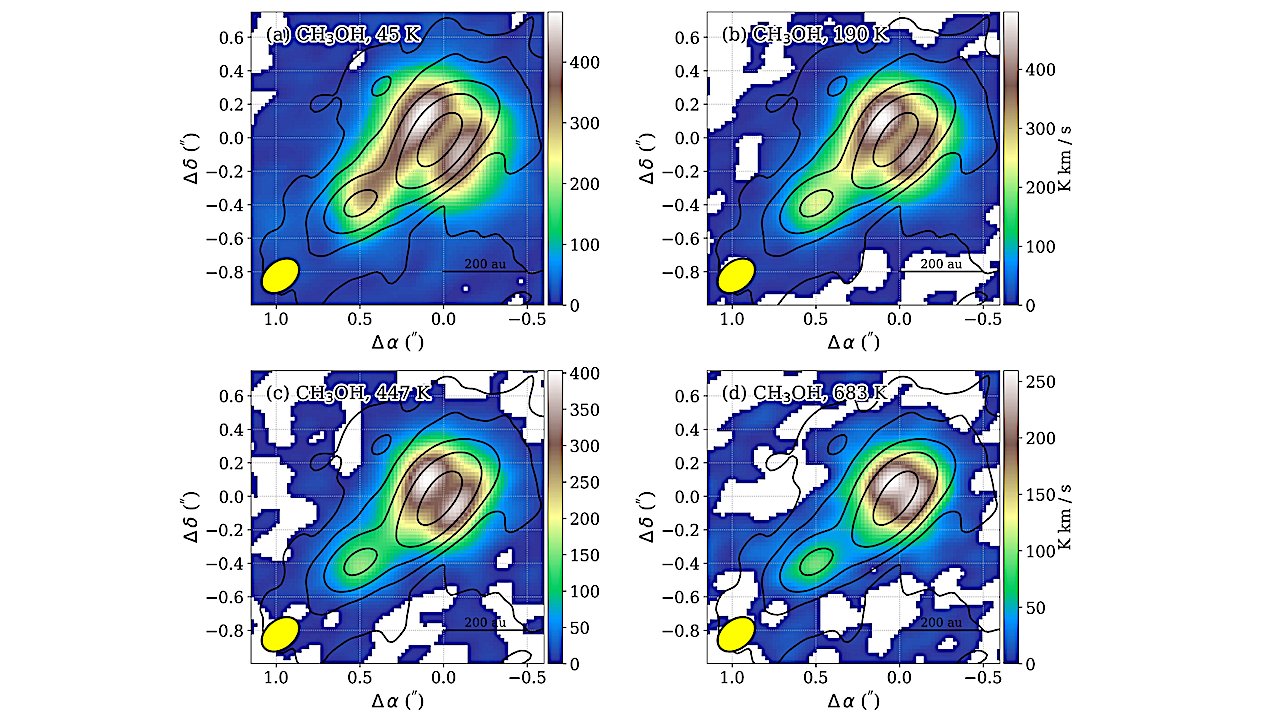
The integrated intensity images of CH3OH transitions overlaid with dust continuum (black contours at σ and σ = 0.10 K). The integration intervals span from −2.5
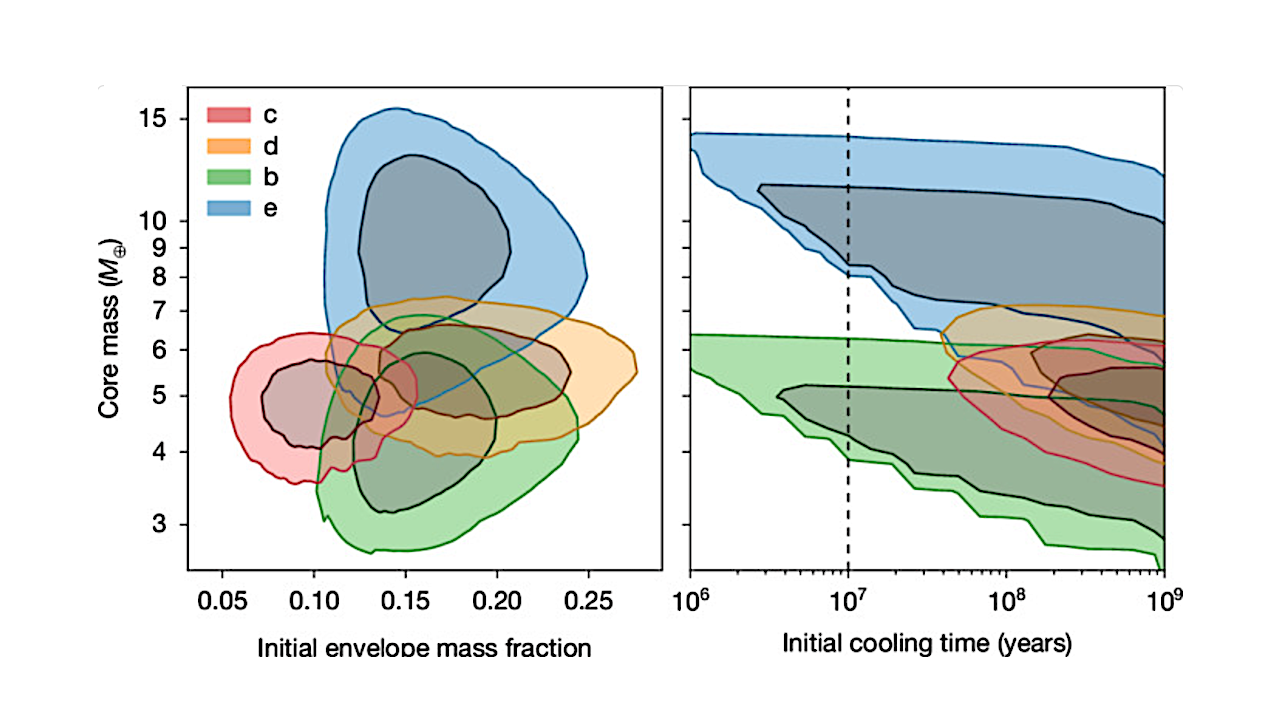
The posteriors were derived by applying the planetary evolution and mass loss framework of ref. 32 to our measured masses and radii for planets c (red), d (orange), b (green)
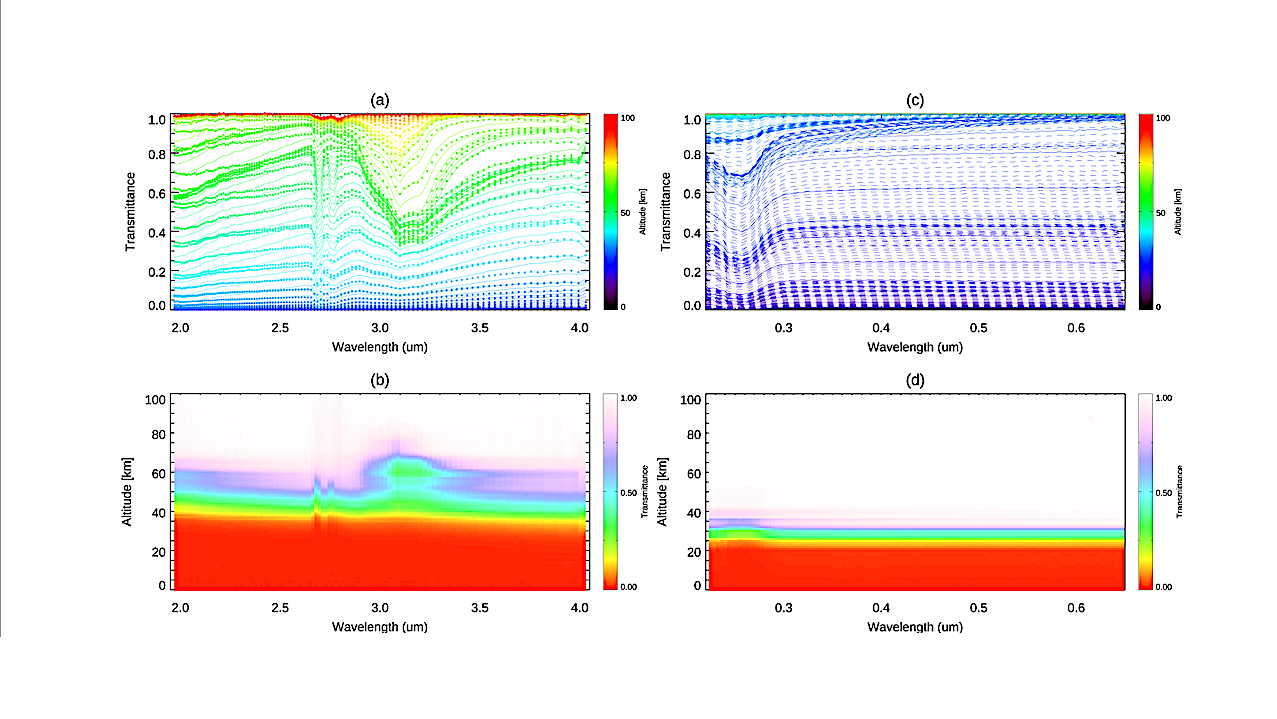
(a,b) An example of the transmittance spectra taken with the full-scan mode of the SO channel of TGO/NOMAD. (c,d) An example of the transmittance spectra taken with the full-scan mode
Deep beneath the surface of distant exoplanets known as super-Earths, oceans of molten rock may be doing something extraordinary: powering magnetic fields strong enough to shield entire planets from dangerous
Tarter Award — SETI Institute The SETI Institute announced that nominations are now open for the 2026 Tarter Award for Innovation in the Search for Life Beyond Earth. The Tarter
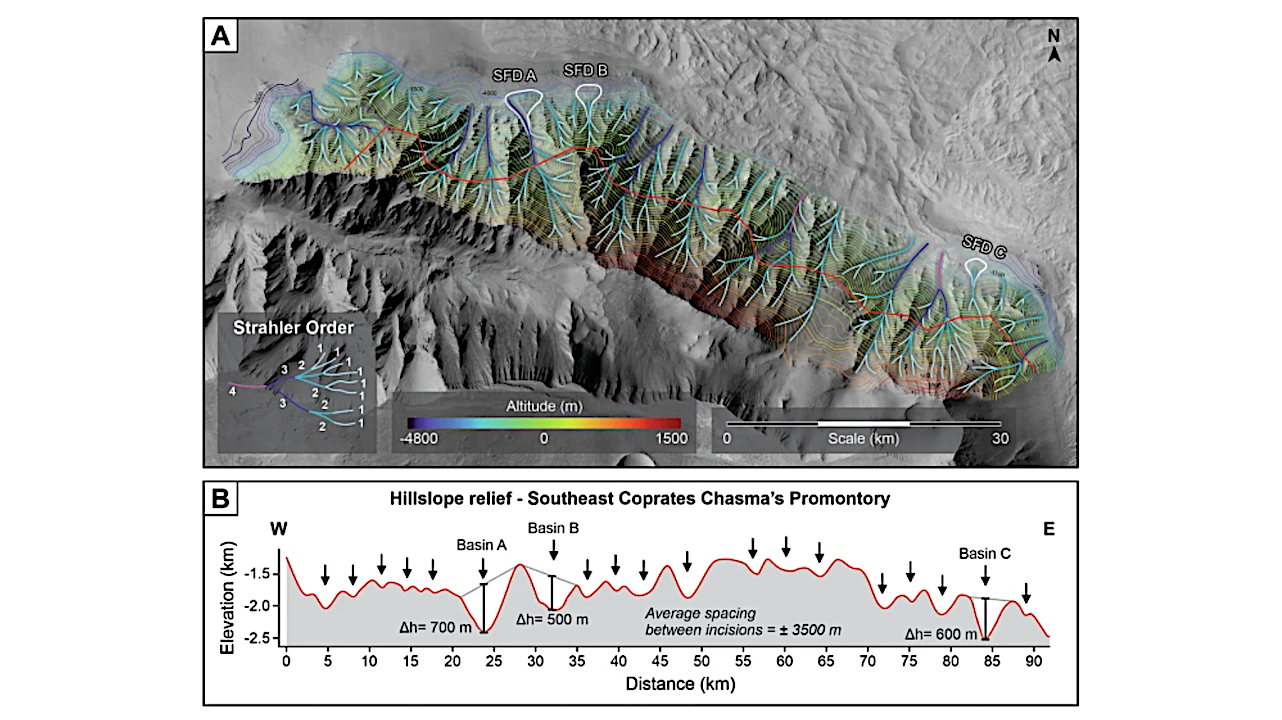
A Tributary channels identified in the northward facing promontory of the Southeast Coprates Chasma and Strahler orders characterizing the geometry of the channel networks in the various drainage basins. B
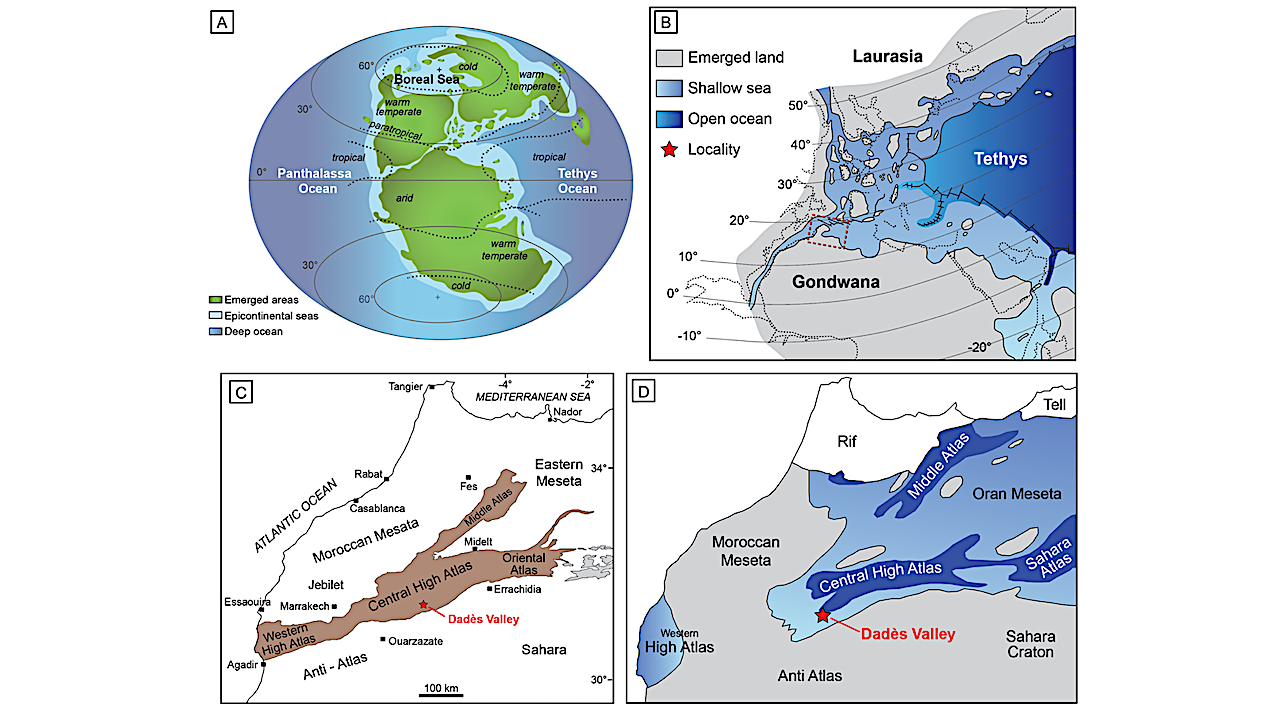
Maps of the study site. A) Toarcian palinspastic and paleoenvironmental reconstruction with paleoclimate belts; modified from Sinha et al. (2021) and references therein. B) Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the western Tethys
New research shows that diverse populations of organisms can persist in the soil despite harsh and extremely dry conditions. Credit Jan Voelkel – University of Cologne A new study shows
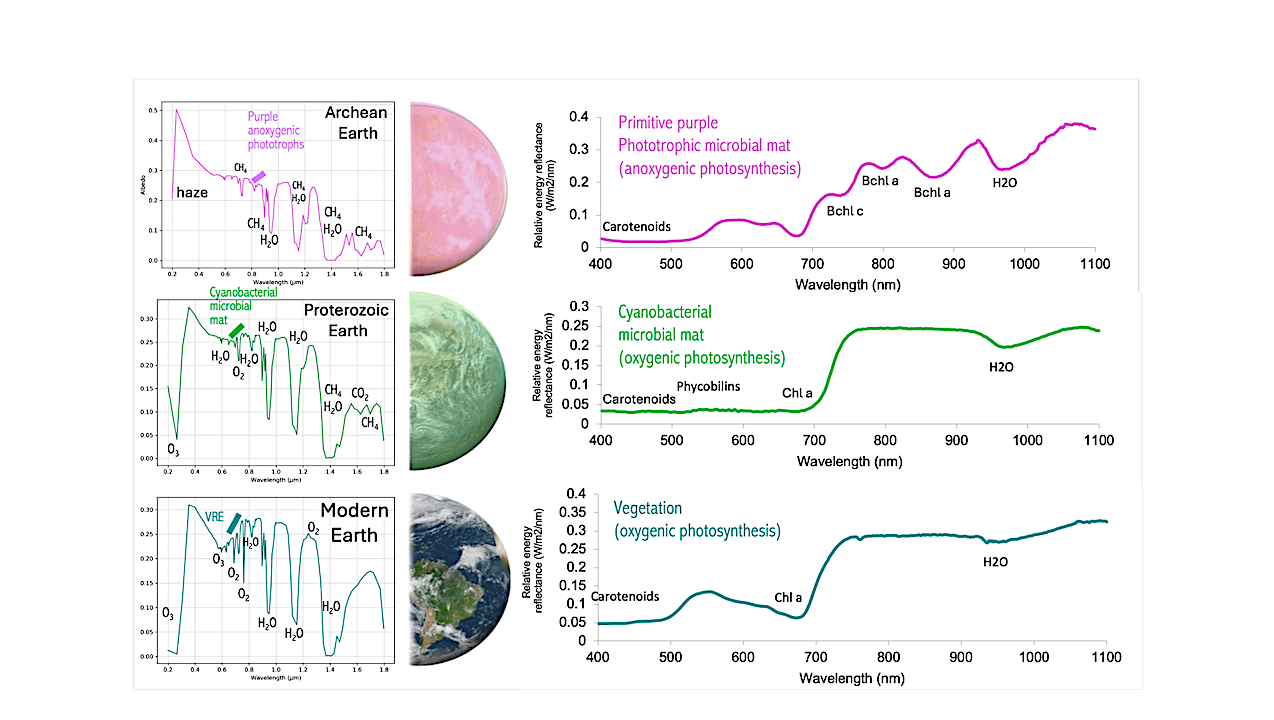
Left: Reflectance spectra of photosynthetic organisms on rock, mineral, and snow/ice abiotic surfaces with Archean, Proterozoic, and Modern atmospheric compositions (planetary spectra provided by Anna Grace Ulses, Univ. of Washington).
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly