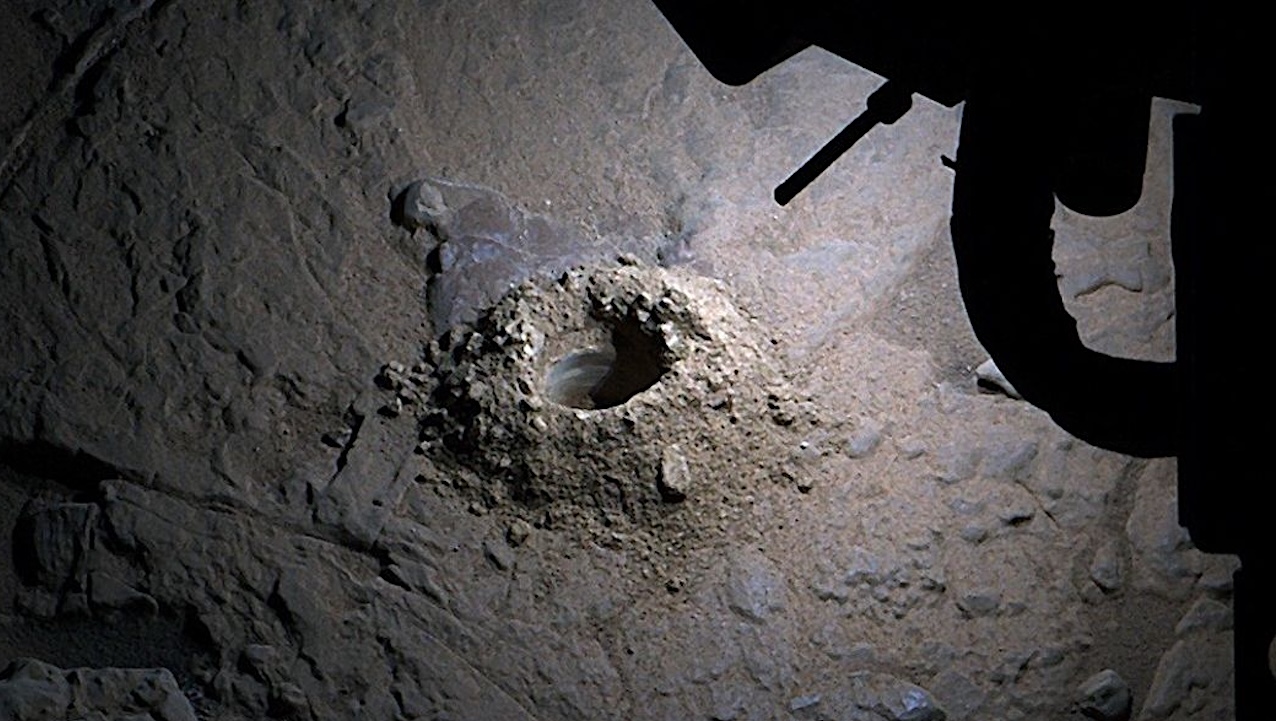
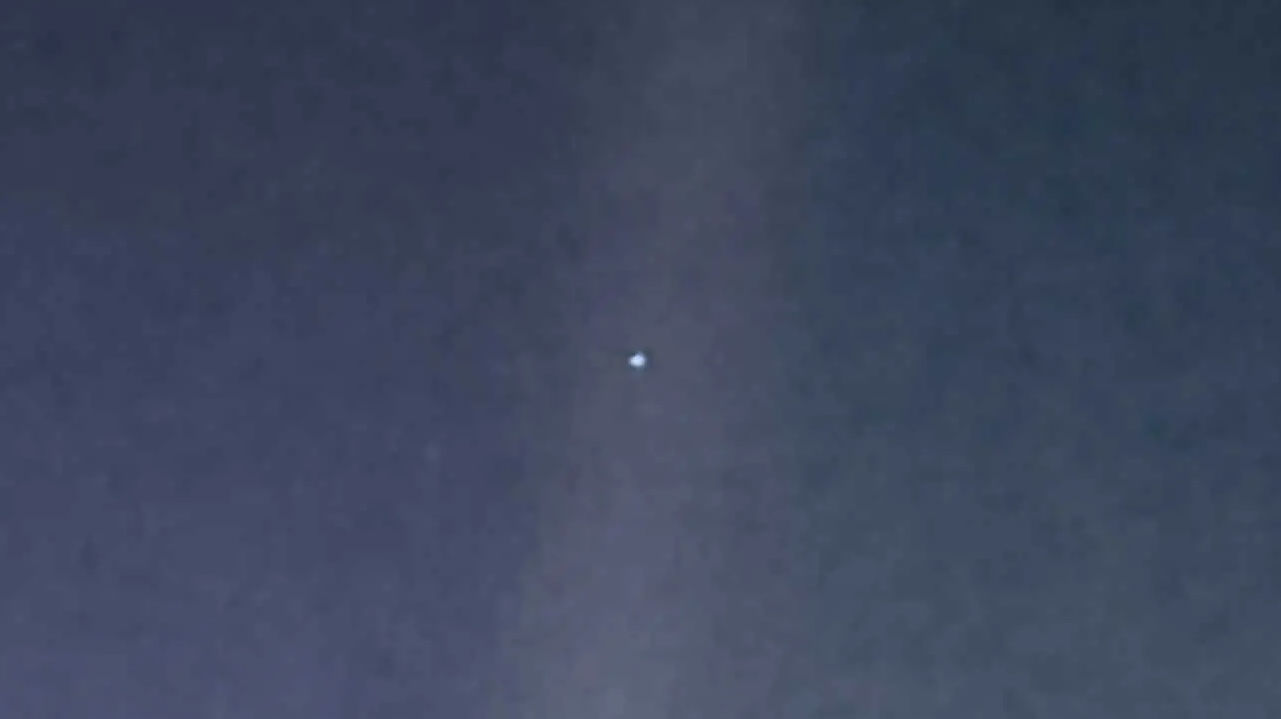
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover used LED lights on the end of its robotic arm to create this rare nighttime view of the Red Planet’s surface on Dec. 6, 2025, the
Astrobiology5- Page
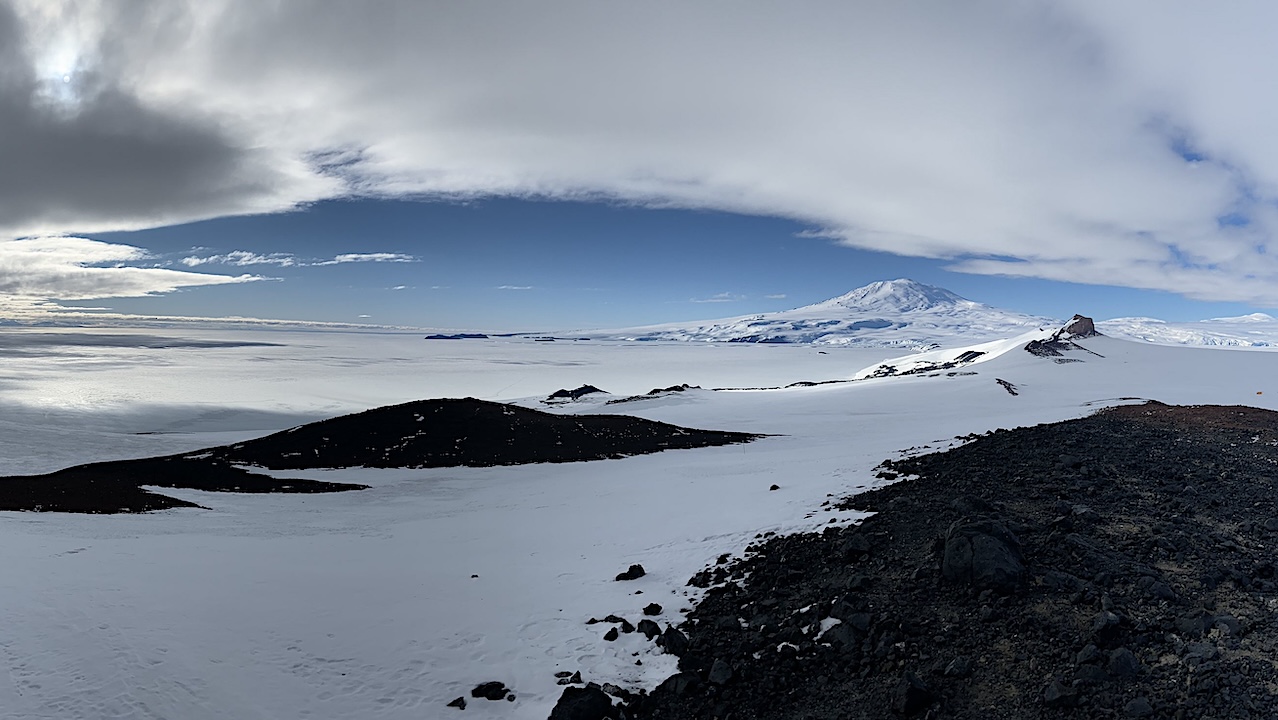
Allan Hills, Antarctica Credit: Photo by Austin Carter, COLDEX Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet in increased danger of following
The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA’s Voyager 1 at a distance of 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) from the Sun.
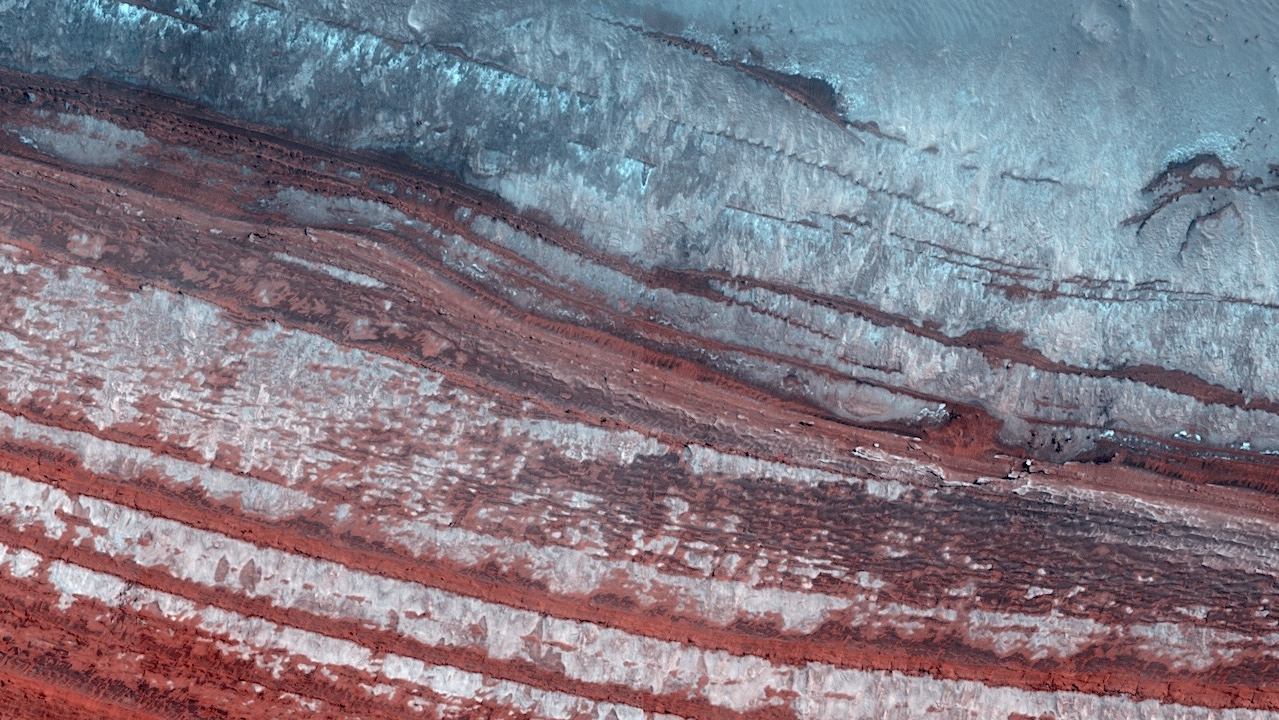
ID: ESP_069857_2650 date: 21 June 2021 altitude: 318 km NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona larger image The North Polar Layered Deposits (NPLD) are large layered deposits of dusty water-ice in the northern
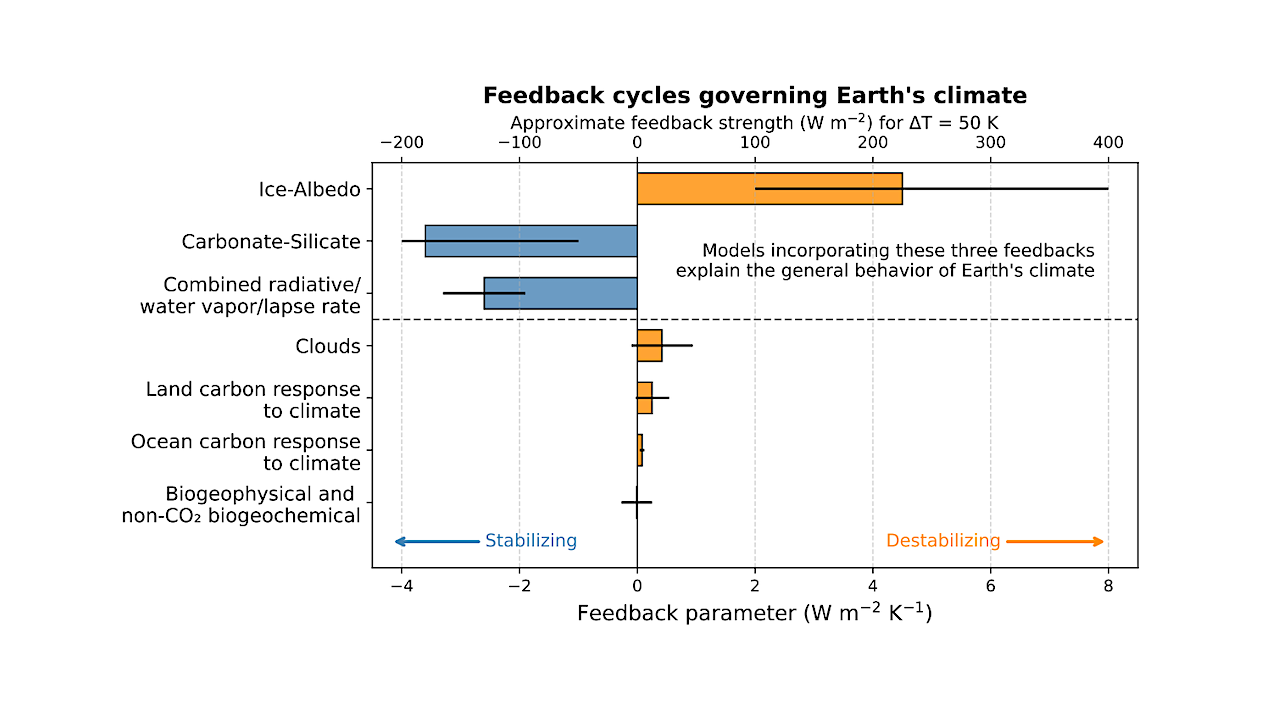
Strength of key long-term feedbacks governing Earth’s climate system (Forster et al. 2021; Arnscheidt & Rothman 2020; Abbot 2016; Koll & Cronin 2018). Each bar represents the feedback parameter in
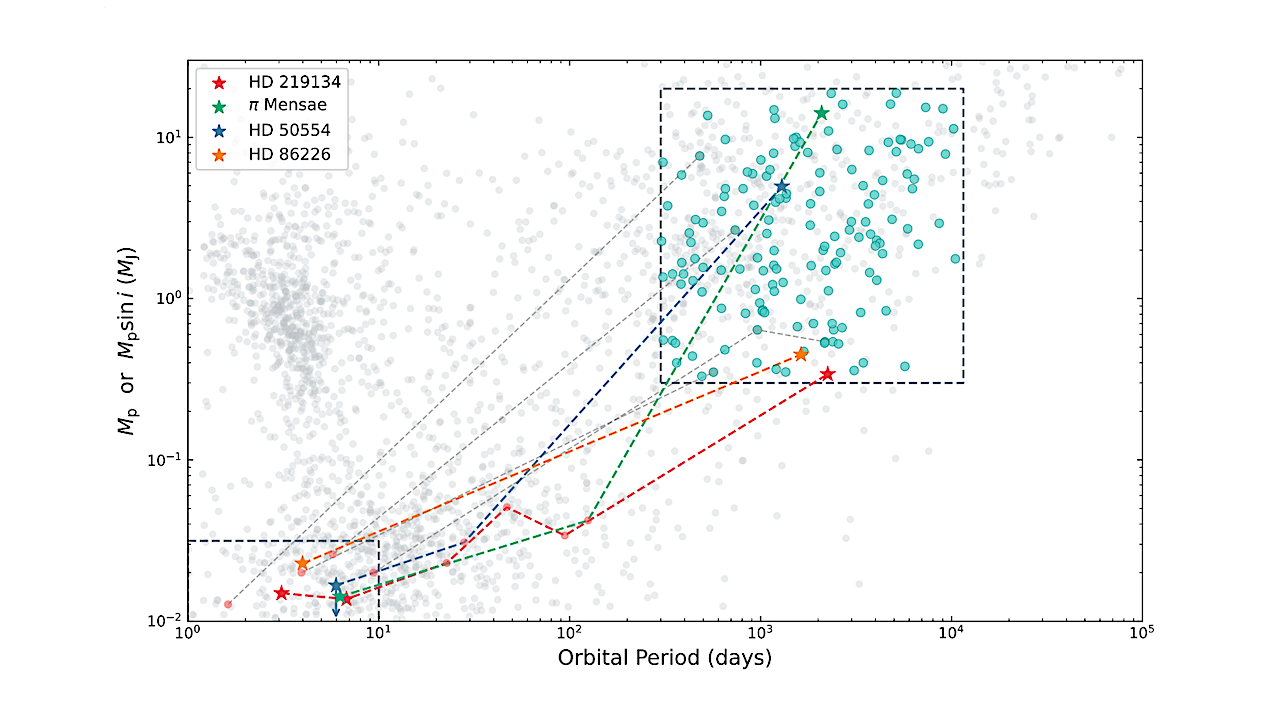
Planet mass (or minimum mass) as a function of orbital period for planetary systems hosting cold Jupiters. Gray points represent the full population of confirmed exoplanets from the NASA Exoplanet
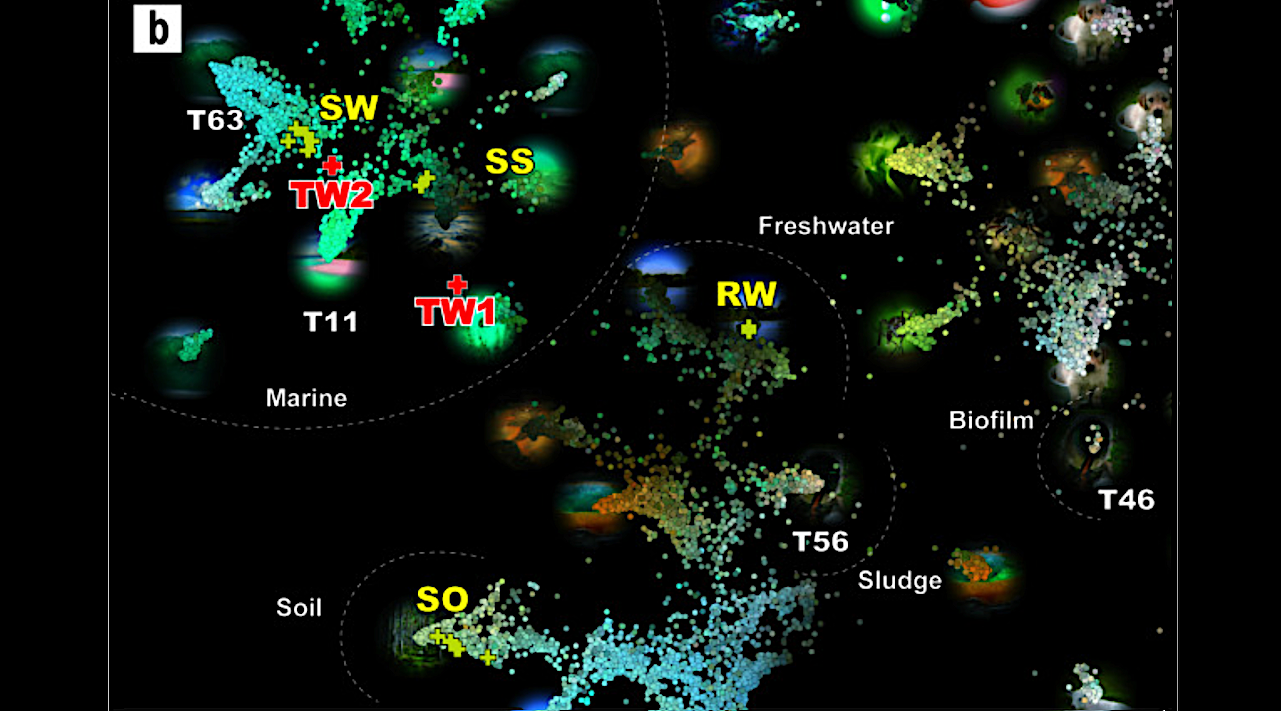
LEA of microbial communities from torus room waters and other environmental samples. Symbol “+” indicates the positions of the samples analyzed in this study, together with the sample names (TW1,
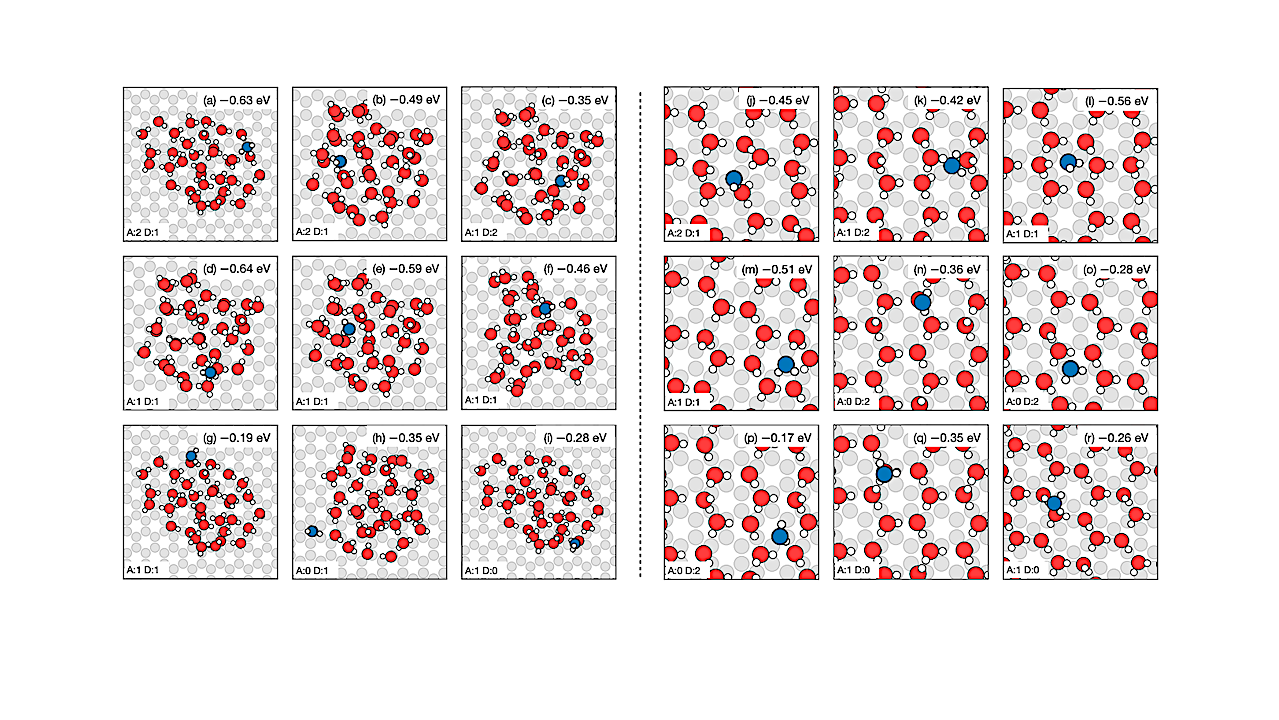
Structures of selected H2O adsorption configurations for cluster (left) and monolayer (right). Ice structures were generated with global optimization. The labels indicate the adsorption energy and the number of hydrogen
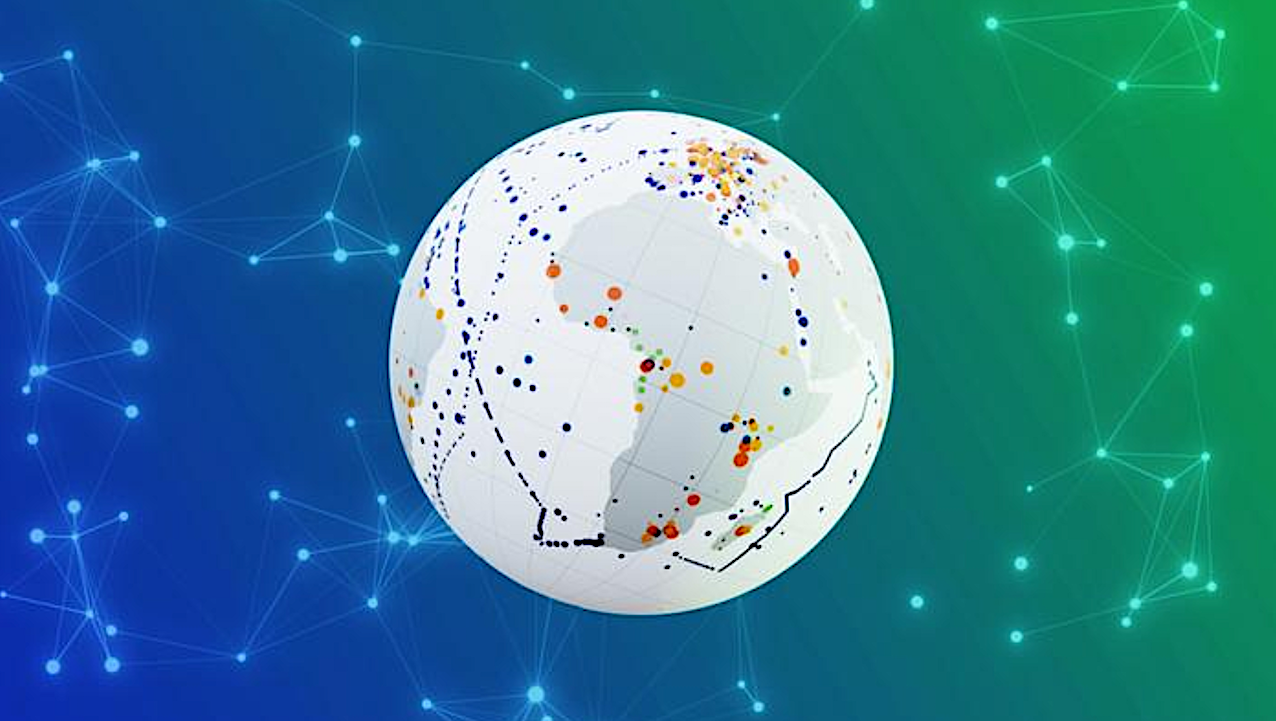
A group of ecologically tolerant microbes known as ‘generalists’ can thrive across very different environments, creating a planet-wide, interconnected network of microbiomes. — Credit Daniela Velasco/EMBL In a new study
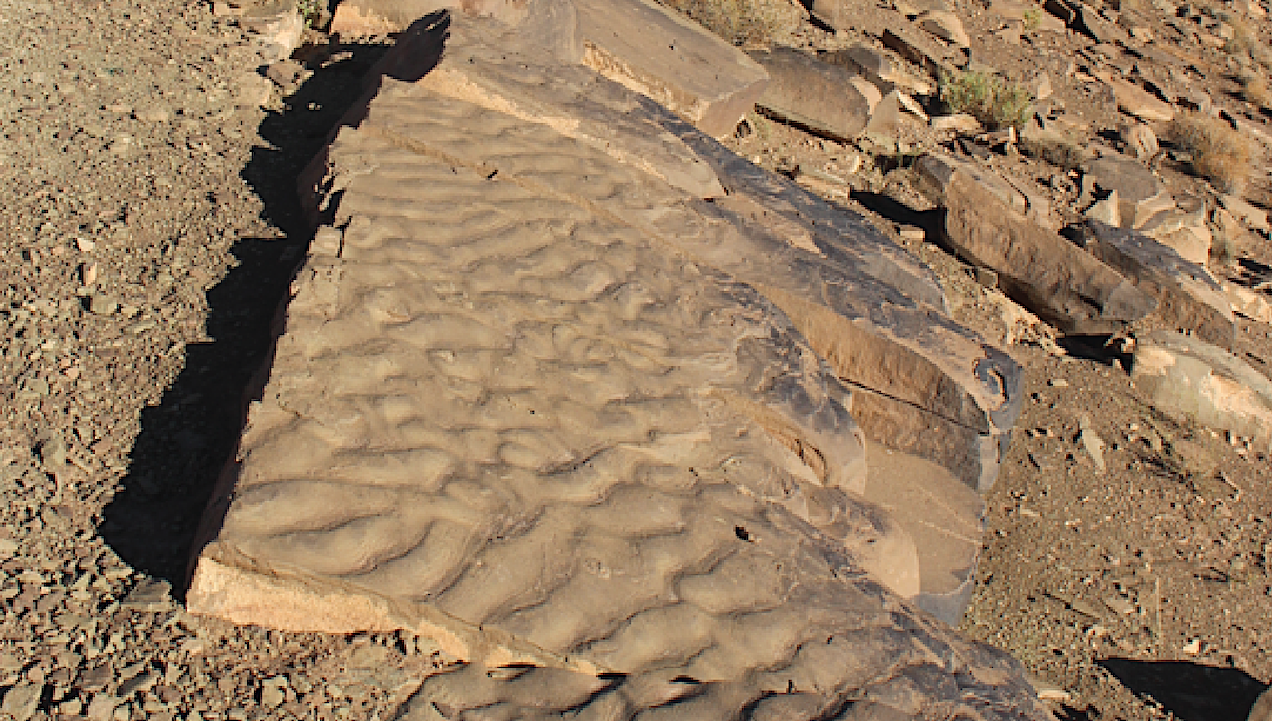
Tagoudite Formation in the Central High Atlas Mountains, Morocco In 2016 while hiking on a hillside in Morocco, geologist Rowan Martindale saw something that made her stop in her tracks:
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly