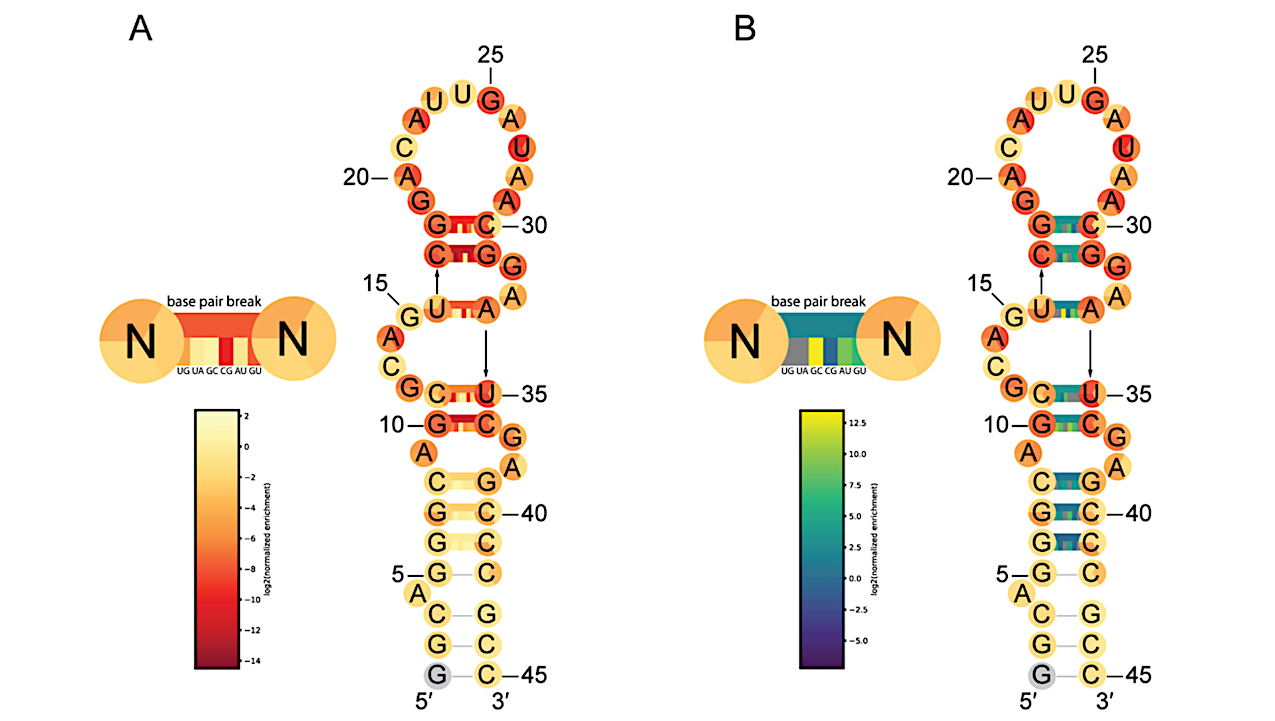
Predicted secondary structure of QT45 ribozyme with nucleotide color corresponding to fitness for each of the three possible single mutations at each position, displayed in the same order as the
Astrobiology4- Page
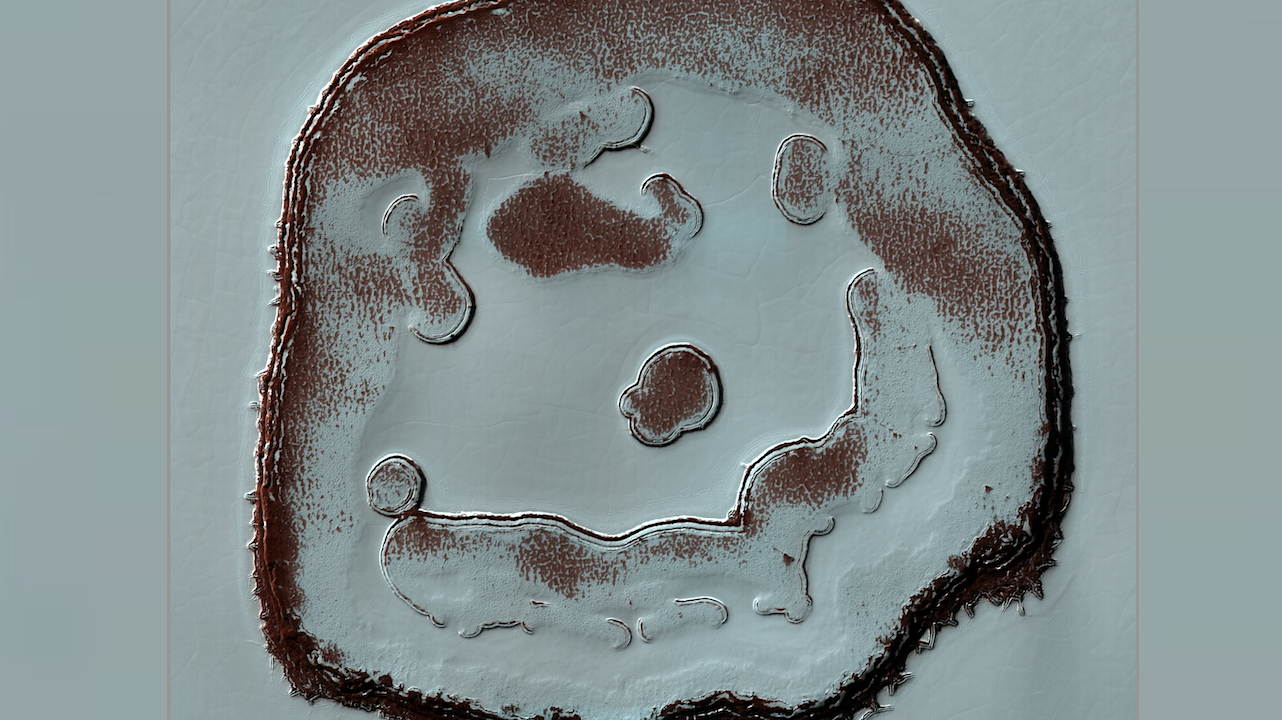
ID: ESP_067414_0945 date: 13 December 2020 altitude: 247 km NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona larger image We’ve monitored the so-called Happy Face Crater in the South Polar region of Mars for over
NASA Astrobiology Expedition 3 to Mars — Astrobiology.com On Monday, February 23, 2026 at 12 pm Eastern Time, the planetary science division will host a webinar overview of program element
EAI Seminar: Deep microbial Colonization During Impact-generated Hydrothermal Circulation Of Impact Structures (Video) Henrik Drake, Professor, Linnaeus University, SwedenTuesday 10th February 2016, 16:00 CET Deeply fractured rocks within
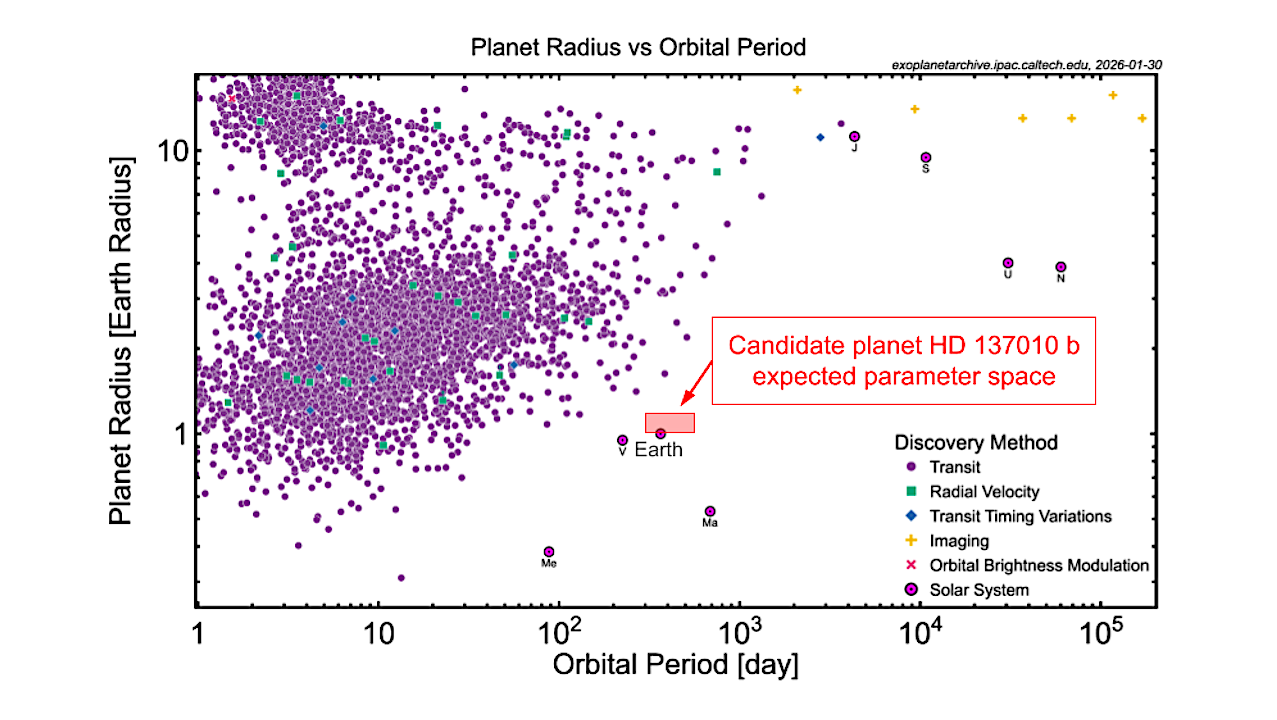
This data plot shows how HD 137010 b may occupy a region of orbital period and radius space similar to Earth’s. — NASA Exoplanet Archive We’ve added a planet candidate
XTREMOLIFE — EU SUMMARY: The EU-funded project XTREMOLIFE aims to accelerate the bioprospecting and biodiscovery of extremophile microorganisms from desert, polar, and volcanic environments, as well as the identification of
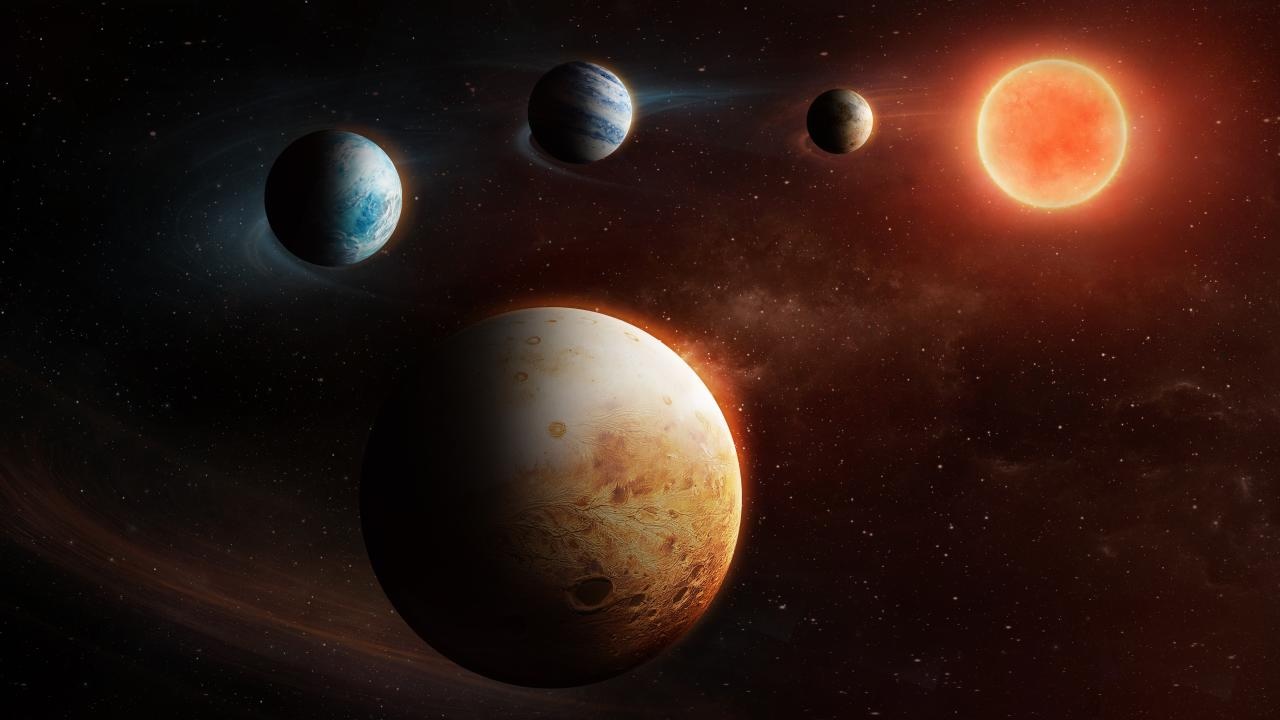
Artist’s impression of the planetary system around the star LHS 1903. Credit: ESA An international scientific team, led by the University of Warwick and involving the Canary Islands Institute of
Birgit Sattler assists Dale Andersen as he begins a diver underneath the ice cover of Lake Untersee, Antarctica — credit: Klemens Weisleitner Keith, Sorry for the quiet—our days have been
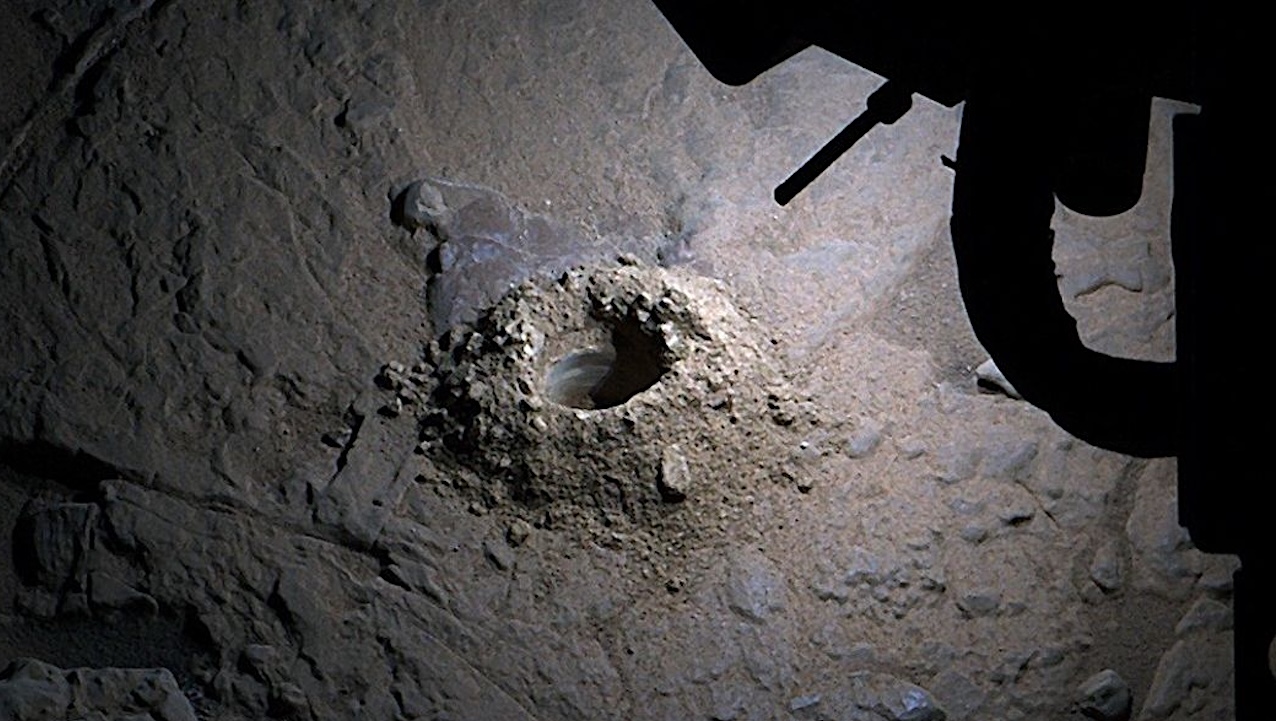
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover used LED lights on the end of its robotic arm to create this rare nighttime view of the Red Planet’s surface on Dec. 6, 2025, the
Allan Hills, Antarctica Credit: Photo by Austin Carter, COLDEX Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet in increased danger of following
-
 01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time
01Two Black Holes Observed Circling Each Other for the First Time -
 02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life
02From Polymerization-Enabled Folding and Assembly to Chemical Evolution: Key Processes for Emergence of Functional Polymers in the Origin of Life -
 03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series)
03Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the Universe (The Adams 101 Series) -
 04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images
04Φsat-2 begins science phase for AI Earth images -
 05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters
05Hurricane forecasters are losing 3 key satellites ahead of peak storm season − a meteorologist explains why it matters -
 06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors
06Thermodynamic Constraints On The Citric Acid Cycle And Related Reactions In Ocean World Interiors -
 07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly
07Binary star systems are complex astronomical objects − a new AI approach could pin down their properties quickly